MySQL笔记
登录、创建账号和退出
安装好mysql,进入命令提示符后,键入
mysql -uroot -p输入根密码,即可登录。
在windows系统中,每次计算机启动时自动启动Mysql数据库服务器,输入命令net stop mysql可以终止它,输入net start mysql可以重启它。
创建账户
创建用户名为scott,密码为tiger的账户:
create user 'scott'@'localhost' identified by 'tiger';
grant select,insert,update,create,drop,execute,references on *.* to 'scott'@'localhost';退出mysql控制台
exit;用账号登录
mysql -uscott -ptiger数据库创建、使用
创建数据库
create database databaseName;使用某数据库
use databaseName;表创建、删除
创建表
create table users(
id int(5) not null auto_increment comment 'ID',
name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名',
account char(8) not null comment '账号',
password varchar(20) not null comment '密码',
role tinyint(1) default 0 comment '身份(管理员1或普通用户0)',
primary key (id)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8表只能有一个自增列,且该自增列必须被定义为主键 。
删除表
drop table tablename;字段查看、添加、修改
查看表字段
desc tablename;添加表字段
#不指定字段位置
alter table tablename add column columnname varchar(20) default null comment '字段描述';
#指定字段位置
alter table tablename add column columnname varchar(20) default null comment '字段描述' after columnname1;更改字段
#将表tablename中的列columnname数据类型改为varchar(20)
alter table tablename modify column columnname varchar(20);
#为字段添加其他内容,已指定int,要添加auto_increment,修改时也要加上int
alter table tablename modify column columnname int auto_increment;记录插入、删除、更改
插入记录
#按照所有字段顺序插入记录
insert into tablename(id,name,account,password,role) values(2,'张三','00000003','zhangsan',0);
#仅指定部分字段插入
insert into tablename(name,account,password,role) values('张三','00000003','zhangsan',0);
#省略字段名插入,值需要一一对应
insert into tablename values(2,'张三','00000003','zhangsan',0);
#插入多条记录,values后面用逗号隔开
insert into tablename values(2,'张三','00000003','zhangsan',0),(3,'李四','00000004','lisi',0)同时设置了自增(auto_increment)和非空(not null)的字段在插入记录时不需要指定;
删除记录
#删除字段名为'value'的记录,不加筛选会删除所有记录
delete from tablename where filedname='value';更改记录
#将字段columnName3值为'value3'的columnName1,columnName2列分别设为'value1','value2'
update tableName set columnName1='value1',columnName2='value2' where columnName3='value3';
#不指定条件会修改所有记录
update tableName set columnName1='value1';查询
基础查询
#查询所有字段
select * from tablename;
#条件查询
select * from tablename where fieldname='fieldvalue';返回字段名fieldname值为'fieldvalue'的记录
#多条件查询多列
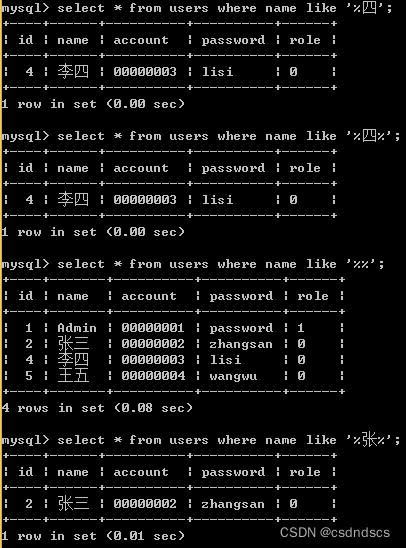
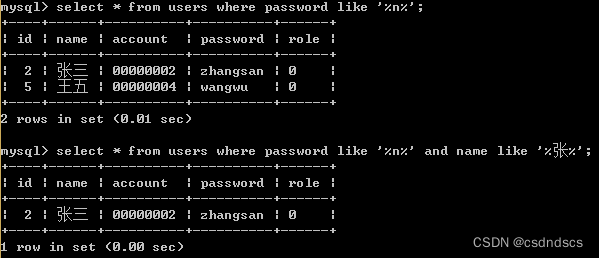
select fieldname1,filedname2 from tablename where fieldname1='fieldvalue1' and fieldname2='fieldvalue2';模糊查询:like
MySQL LIKE 子句 | 菜鸟教程
SQL LIKE 子句中使用百分号 %字符来表示任意字符,类似于UNIX或正则表达式中的星号 *。
如果没有使用百分号 %, LIKE 子句与等号 = 的效果是一样的。
在 where like 的条件查询中,SQL 提供了四种匹配方式。
- %:表示任意 0 个或多个字符。可匹配任意类型和长度的字符,有些情况下若是中文,请使用两个百分号(%%)表示。
- _:表示任意单个字符。匹配单个任意字符,它常用来限制表达式的字符长度语句。
- []:表示括号内所列字符中的一个(类似正则表达式)。指定一个字符、字符串或范围,要求所匹配对象为它们中的任一个。
- [^] :表示不在括号所列之内的单个字符。其取值和 [] 相同,但它要求所匹配对象为指定字符以外的任一个字符。
- 查询内容包含通配符时,由于通配符的缘故,导致我们查询特殊字符 “%”、“_”、“[” 的语句无法正常实现,而把特殊字符用 “[ ]” 括起便可正常查询。
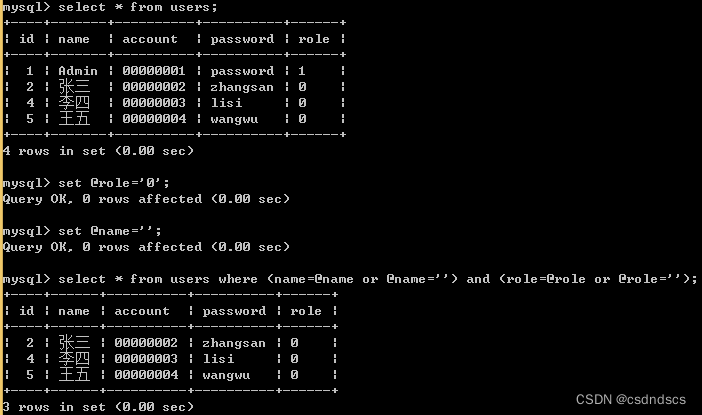
含变量的条件查询
含变量的条件查询可以将用户输入的多个条件值赋给mysql变量,值为空则不查(返回所有),非空则查。(SQL语句当查询条件为空时默认查询全部数据,不为空是则按照条件进行查询_sql不为空就查作为条件查询-CSDN博客)
以下以name(varchar(20))和role(char(1))为查询条件,set语句用于设置变量值(以@开头):
Java的mySQL
Java使用MySQL数据库需要 1.加载驱动程序 2.建立连接 3.创建语句 4.执行语句 几个步骤:
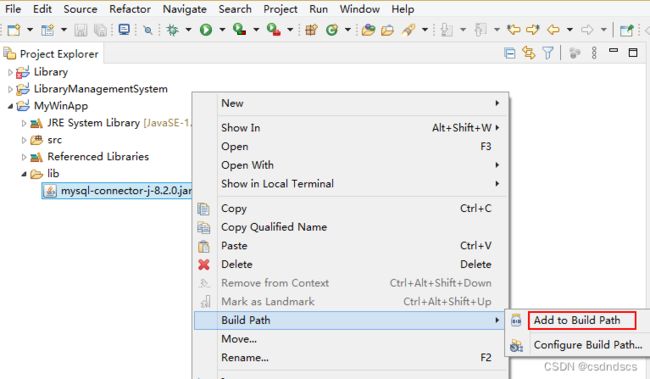
驱动器需要下载 后添加到路径中才能使用(可以放在src同级的lib文件夹内,然后Add to Build Path):
//加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//或Class.forName("om.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//建立连接,需要传入你的数据库名,访问账号及密码
Connection connection=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/Library","scott","tiger");
//创建语句
Statement statement=connection.createStatement();
//执行语句
//执行查询语句,返回ResultSet对象
ResultSet resultSet=statement.executeQuery("select userpassword,userrole from users where userAccount='"+account+"'");
//当resultSet非空时,可以用.get.String(index)方法读取器内容字符串,index从1开始,用next方法访问下一行
while(resultSet.next()) {
TableItem tableItem=new TableItem(this, SWT.MULTI);
for(int i=1;i<=headerStrArray.length;i++)
tableItem.setText(i-1, resultSet.getString(i));
}
//执行插入、更改语句、删除语句,不需要返回对象
statement.execute("insert into records(operationDateTime,userAccount,userName,isbn,bookName,operationType,operationCount) values('"+returnDateTime+"','"+account+"','"+userName+"','"+isbn+"','"+bookName+"','归还',"+returnCount+")");
statement.execute("update states set returnedCount="+(thisUserReturnedCount+returnCount)+",unReturnedCount="+(thisUserUnReturnedCount-returnCount)+" where userAccount='"+account+"' and isbn='"+isbn+"'");
statement.execute("delete from books where isbn='"+textArrayList.get(1-1).getText()+"'");注意,用statement.executteQuery()方法返回的resultSet结果不能交替使用,如下列语句会报错,因为第二次查询后第一次的结果已经关闭:
ResultSet resultSet1=statement.executeQuery("select userpassword from users where userAccount='"+account+"'");
ResultSet resultSet2=statement.executeQuery("select userrole from users where userAccount='"+account+"'");
while(resultSet1.next())
//to do解决方法是先使用第一次的结果,再进行第二次查询。或者创建多个statement对象分别查询。
获取ResultSet的长度
Java获取ResultSet的长度-CSDN博客
ResultSet没有size()方法,当非空时,可用如下代码获取其长度:
rs.last()可以不用设置可滚动结果集,直接到rs的最后一行,最后一行的行号就是结果集的长度。
若遇到此错误Operation not allowed for a result set of type ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,是因为默认参数只能调用next()方法,此时需要将
Statement statement=connection.createStatement();改为
Statement statement=connection.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);即可(解决Operation not allowed for a result set of type ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY.问题_gzg521的博客-CSDN博客)。括号里也可以是其他参数,只要不是ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY(默认)就好。
其他类型查询结果如下:
ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY:这是默认类型,游标只能在结果集中向前移动。 ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE:游标可以前后移动,结果集对创建结果集后其他人对数据库所做的更改不敏感。
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE:游标可以向前和向后移动,结果集对创建结果集后其他人对数据库所做的更改敏感。
基于并发性,有两种类型的ResultSet对象。
ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY:结果集是只读的,这是默认的并发类型。 ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE:可以使用ResultSet更新方法来更新行数据