卷积神经网络经典backbone
特征提取是数据分析和机器学习中的基本概念,是将原始数据转换为更适合分析或建模的格式过程中的关键步骤。特征,也称为变量或属性,是我们用来进行预测、对对象进行分类或从数据中获取见解的数据点的特定特征或属性。
1.AlexNet
paper:https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3065386
作者: Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton
显然该网络是按照作者名字命名的,但是现在这个bacbone比较老了,性能欠佳
框架:
整体结构主要由五个卷积层、三个全连接层构成,中间穿插着最大池化、ReLU、Dropout
使用ReLu非线性激活函数
code_Pytorch
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
"""
Neural network model consisting of layers propsed by AlexNet paper.
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
"""
Define and allocate layers for this neural net.
Args:
num_classes (int): number of classes to predict with this model
"""
super().__init__()
# input size should be : (b x 3 x 227 x 227)
# The image in the original paper states that width and height are 224 pixels, but
# the dimensions after first convolution layer do not lead to 55 x 55.
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=96, kernel_size=11, stride=4), # (b x 96 x 55 x 55)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2), # section 3.3
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 96 x 27 x 27)
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, padding=2), # (b x 256 x 27 x 27)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 256 x 13 x 13)
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, padding=1), # (b x 384 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, padding=1), # (b x 384 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, padding=1), # (b x 256 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 256 x 6 x 6)
)
# classifier is just a name for linear layers
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=(256 * 6 * 6), out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=num_classes),
)
self.init_bias() # initialize bias
def init_bias(self):
for layer in self.net:
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0)
# original paper = 1 for Conv2d layers 2nd, 4th, and 5th conv layers
nn.init.constant_(self.net[4].bias, 1)
nn.init.constant_(self.net[10].bias, 1)
nn.init.constant_(self.net[12].bias, 1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Pass the input through the net.
Args:
x (Tensor): input tensor
Returns:
output (Tensor): output tensor
"""
x = self.net(x)
x = x.view(-1, 256 * 6 * 6) # reduce the dimensions for linear layer input
return self.classifier(x)2.VGG
paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
作者:Karen Simonyan, Andrew Zisserman
超级超级经典的网络,从14年到现在还是广泛使用
框架:
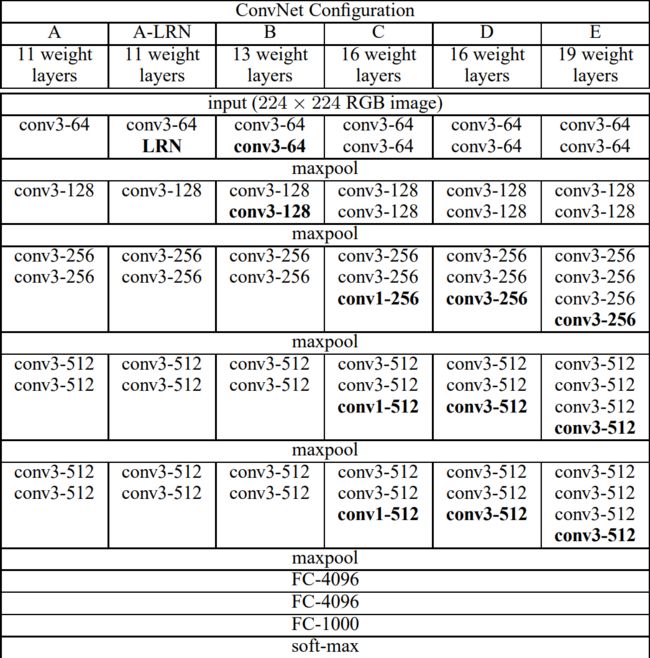
相比AlexNet而言加深了网络的深度,VGG16(13层conv+3层FC)和VGG19(16层conv+3层FC)是指表中的D、E两个模型。
code_vgg_Pytorch
'''
Modified from https://github.com/pytorch/vision.git
'''
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.init as init
__all__ = [
'VGG', 'vgg11', 'vgg11_bn', 'vgg13', 'vgg13_bn', 'vgg16', 'vgg16_bn',
'vgg19_bn', 'vgg19',
]
class VGG(nn.Module):
'''
VGG model
'''
def __init__(self, features):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(512, 10),
)
# Initialize weights
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == 'M':
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if batch_norm:
layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2d(v), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
else:
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
cfg = {
'A': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'B': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'D': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'E': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M',
512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
def vgg11():
"""VGG 11-layer model (configuration "A")"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['A']))
def vgg11_bn():
"""VGG 11-layer model (configuration "A") with batch normalization"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['A'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg13():
"""VGG 13-layer model (configuration "B")"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['B']))
def vgg13_bn():
"""VGG 13-layer model (configuration "B") with batch normalization"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['B'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg16():
"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D")"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['D']))
def vgg16_bn():
"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D") with batch normalization"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['D'], batch_norm=True))
def vgg19():
"""VGG 19-layer model (configuration "E")"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['E']))
def vgg19_bn():
"""VGG 19-layer model (configuration 'E') with batch normalization"""
return VGG(make_layers(cfg['E'], batch_norm=True))3.ResNet
paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
作者:Kaiming He、Xiangyu Zhang、Shaoqing Ren;Microsoft Research;
使用残差网络避免模型变深带来的梯度爆炸和梯度消失的问题,使得网络层数可以达到很深。
框架:
残差连接:
(1)完成恒等映射:浅层特征可以直接的传递到深层特征中。
(2)梯度回传:深层的梯度可以通过残差的结构直接传递到浅层的网络中。
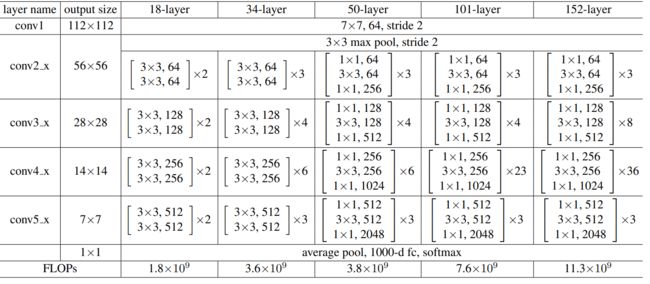
基于上面的分析提出残差连接结构,构建了不同的网络,有18、34、50、101、152等。
code_ResNet_Pytorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.models.resnet
from torchvision.models.resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck
class ResNet(torchvision.models.resnet.ResNet):
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, group_norm=False):
if group_norm:
norm_layer = lambda x: nn.GroupNorm(32, x)
else:
norm_layer = None
super(ResNet, self).__init__(block, layers, num_classes, norm_layer=norm_layer)
if not group_norm:
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, ceil_mode=True) # change
for i in range(2, 5):
getattr(self, 'layer%d'%i)[0].conv1.stride = (2,2)
getattr(self, 'layer%d'%i)[0].conv2.stride = (1,1)
def resnet18(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18']))
return model
def resnet34(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3])
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34']))
return model
def resnet50(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3])
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50']))
return model
def resnet50_gn(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], group_norm=True)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50']))
return model
def resnet101(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3])
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101']))
return model
def resnet101_gn(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], group_norm=True)
return model
def resnet152(pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3])
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152']))
return model