半监督节点分类上的HyperGCN
1.Title
HyperGCN: Hypergraph Convolutional Networks for Semi-Supervised Classification(Naganand Yadati、Prateek Yadav、Madhav Nimishakavi、Anand Louis、Partha Talukdar)【ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data 2022】
2.Conclusion
This paper explore the use of GCNs for hypergraph-based SSL and propose HyperGCN, an SSL method which uses a layer-wise propagation rule for convolutional neural networks operating directly on hypergraphs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first principled adaptation of GCNs to hypergraphs. HyperGCN is able to encode both the hypergraph structure and hypernode features in an effective manner. Through detailed experimentation, it demonstrate HyperGCN’s effectiveness at hypergraph-based SSL.
3.Good Sentences
1、This assumption might restrict modeling capacity, as graph edges need not encode node similarity, but could instead contain other information such as pointwise mutual semantic information (Zhuang and Ma 2018), or knowledge graph relationship information (Wang, Ye, and Gupta 2018)(The restriction of graph Laplacian regulariser)
2、The crucial working principle here is that the hypernodes in the same hyperedge are similar and hence are likely to share the same label (The basic principal of Hypergraph).
3、HyperGCN may be augmented with such approaches for even more improved performance. On the hypergraph side, our HyperGCN model currently is designed for undirected hypergraphs. Extending the model for directed hypergraphs (where the direction captures a casual relationship) (Zhang et al. 2017), and partial-order hypergraphs (Feng et al. 2018) can be an interesting avenue for further research. Investigating the recently proposed p-Laplacians for submodular hypergraphs (Li and Milenkovic 2018) is also an interesting direction.(Some possbile future works based on HyperGCN)
Introduction
在传统的基于图的SSL问题中,损失函数被定义为标记数据上的监督损失和图结构的正则化器的加权和。 典型的正则化器是拉普拉斯算子,它依赖图中连接的节点可能共享相同的标签这一假设。这种假设可能会限制建模能力,因为图的边不一定编码节点相似性,而可能包含其他信息。
典型的正则化器是拉普拉斯算子,它依赖图中连接的节点可能共享相同的标签这一假设。这种假设可能会限制建模能力,因为图的边不一定编码节点相似性,而可能包含其他信息。
为了避免这种限制,后来的人引入了卷积神经网络,而本文填补了超图上的卷积网络的空白,主要贡献如下:
- 提出了HyperGCN,第一个基于GCN的超图方法。
-
与以前的非神经方法相比,HyperGCN能够有效地合并和修改超图节点上的特征。
-
通过在多个真实世界数据集上进行的广泛实验,我们证明了HyperGCN与其他最先进的基线相比的有效性
HyperGCN的代码是开源的
Background: Graph Convolutional Network
 令
令![]() 是对应图G的数据矩阵,A是其邻接矩阵,数据矩阵具有图中每个节点的p维实值向量表示。图卷积可作为图拉普拉斯算子的线性函数。GCN的基本公式来源于卷积定理,真实信号S∈
是对应图G的数据矩阵,A是其邻接矩阵,数据矩阵具有图中每个节点的p维实值向量表示。图卷积可作为图拉普拉斯算子的线性函数。GCN的基本公式来源于卷积定理,真实信号S∈![]() 和滤波器F∈
和滤波器F∈![]() 的卷积C可以表示为
的卷积C可以表示为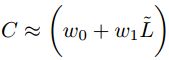 。
。![]() 都是可学习的权重参数,
都是可学习的权重参数,![]() 是标准图拉普拉斯卷积,其中L是对称归一化图拉普拉斯算子,
是标准图拉普拉斯卷积,其中L是对称归一化图拉普拉斯算子,![]() 是其最大特征值,
是其最大特征值,![]() ,D是
,D是![]() 的对角矩阵
的对角矩阵![]() 滤波器F取决于图(图拉普拉斯算子L)的结构,这里的关键点是,两个图信号的卷积是图拉普拉斯L的线性函数。
滤波器F取决于图(图拉普拉斯算子L)的结构,这里的关键点是,两个图信号的卷积是图拉普拉斯L的线性函数。
GCN (Kipf and Welling 2017)
GCN以邻接矩阵A(底层图结构)和数据矩阵X(输入特征)为条件。简单的两层GCN的正向模型采用以下简单形式: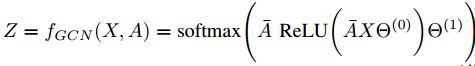
而对于具有q类的半监督多类分类,可以最小化标记示例集上的交叉熵误差![]()
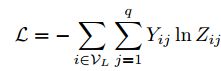 图卷积网络的权重,即θ(0)和θ(1),使用梯度下降进行训练。
图卷积网络的权重,即θ(0)和θ(1),使用梯度下降进行训练。
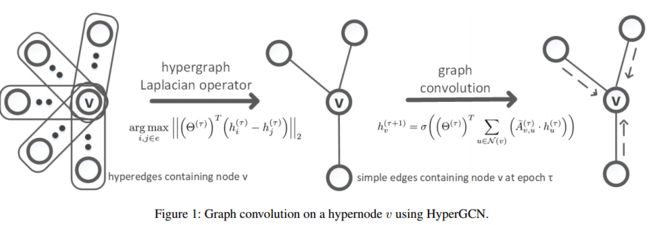
超图卷积网络
最关键的原理在于: 同一超边中的超节点是相似的,因此可能共享相同的标签。
假设用![]() 来表示V中的一些超节点,然后对于任意超边
来表示V中的一些超节点,然后对于任意超边![]() ,函数
,函数![]() 在超边e中的超节点的向量彼此接近时会很小,因此,把这个函数作为正则化器时可能实现“相同超边中的超节点具有相似表示”这一目标。而拉普拉斯算子也具有相似的功能
在超边e中的超节点的向量彼此接近时会很小,因此,把这个函数作为正则化器时可能实现“相同超边中的超节点具有相似表示”这一目标。而拉普拉斯算子也具有相似的功能
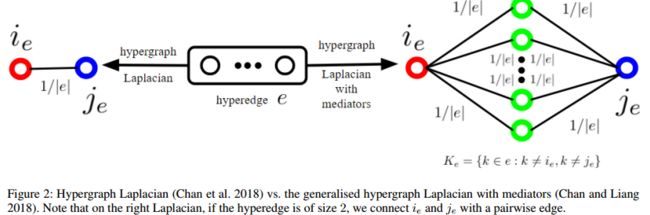
超图拉普拉斯
给定一个实值信号S,![]() 定义在超节点上,L(S)的计算步骤如下:
定义在超节点上,L(S)的计算步骤如下:
- 对于每个超边
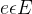 ,让
,让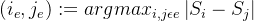 随机断开连接
随机断开连接 - 通过添加带权重w的边
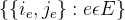 来构造顶点集V上的加权图
来构造顶点集V上的加权图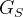 ,然后对于每个顶点v,添加足够权重的自循环,使得顶点在
,然后对于每个顶点v,添加足够权重的自循环,使得顶点在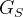 中的度数等于
中的度数等于 。把
。把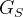 的加权邻接矩阵记作
的加权邻接矩阵记作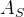
- 对称归一化的拉普拉斯算子计算公式如下:

HyperGCN
 图卷积运算可以使用如下所示的迭代方程在神经消息传递框架中重写:
图卷积运算可以使用如下所示的迭代方程在神经消息传递框架中重写:
τ是epoch次数,![]() 是节点v的新隐藏层表示, σ是非线性激活函数,Θ是可训练学习的权重参数,N(v)是节点v的邻居集,
是节点v的新隐藏层表示, σ是非线性激活函数,Θ是可训练学习的权重参数,N(v)是节点v的邻居集,![]() 是超边(v,u)上经过标准化的权重,随着节点被嵌入,关联矩阵也被重新构建。HyperGCN模型可以被视为基于超图总变化进行隐式正则化。
是超边(v,u)上经过标准化的权重,随着节点被嵌入,关联矩阵也被重新构建。HyperGCN模型可以被视为基于超图总变化进行隐式正则化。
带中介的拉普拉斯算子是一种HyperGCN的改进,不带介质的超图拉普拉斯算子忽略了给定epoch时,![]() 中的超节点。(Chan和Liang 2018已经证明
中的超节点。(Chan和Liang 2018已经证明![]() 中的超节点充当“中介”的广义超图拉普拉斯算子满足由(Chan等人)给出的拉普拉斯算子的所有性质
中的超节点充当“中介”的广义超图拉普拉斯算子满足由(Chan等人)给出的拉普拉斯算子的所有性质