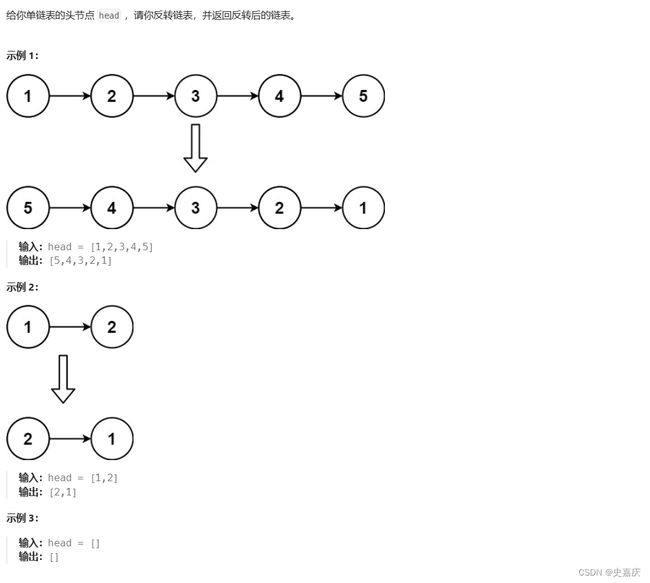
详解单链表OJ题
链表OJ经典题目
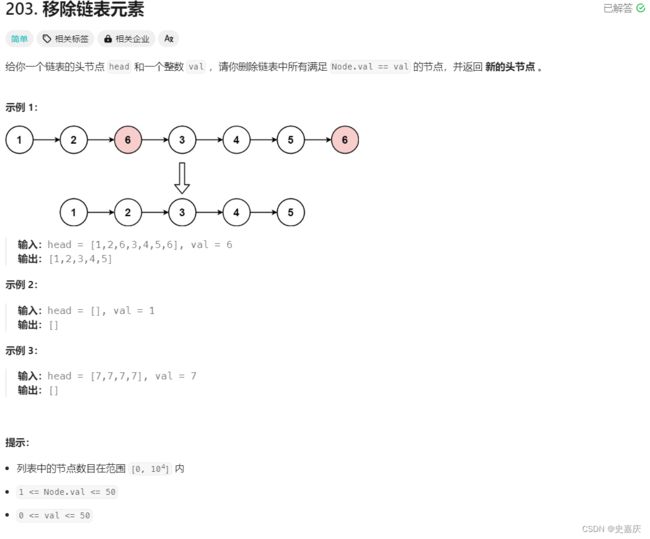
- 一.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点
-
- leetcode链接
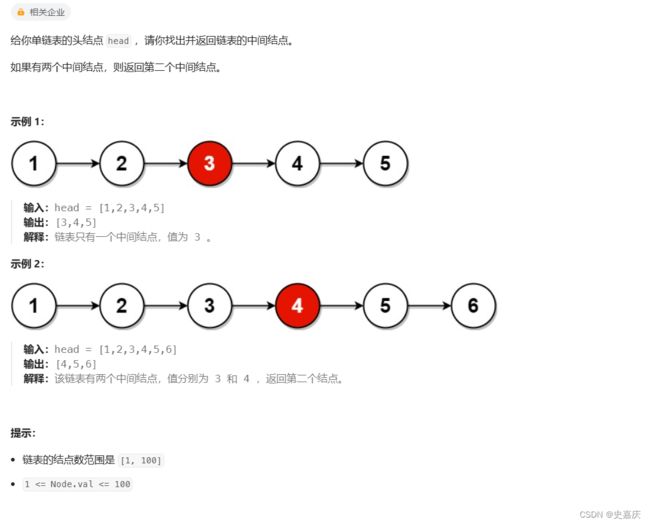
- 二.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
-
- leetcode链接
- 三.反转一个单链表
-
- leetcode链接
- 四.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
-
- nowcoder链接
- 五.链表分割
-
- nowcoder链接
- 六.合并两个有序链表
-
- leetcode链接
- 七.判断单链表是否是回文结构
-
- nowcoder链接
- 八 .输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
-
- leetcode链接
- 九.给定一个链表,判断链表当中是否有环
-
- leetcode链接
- 十.给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
-
- leetcode链接
- 小结
一.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点
leetcode链接
- 创建指向当前节点的前一个节点的指针prev=NULL(头节点的前一个节点为空),指针cur指向链表头节点。
- 以当前节点cur不为空为循环执行条件,判断当前节点的值是否等于val,等于则进行删除,不等于则prev更新为当前节点cur,当前节点cur指向下一个节点。
- 当前节点的值等于val时:
- 如果值为 val 的节点不在头节点(prev 不为 NULL),将 prev 的 next 指针指向当前节点的下一个节点,然后释放当前节点并更新。
- 如果值为 val 的节点在链表头节点(prev 为 NULL),则释放原来的头节点,将 head 更新为当前节点的下一个节点。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* prev =NULL,*cur=head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val==val)
{
if(prev)
{
prev->next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=prev->next;
}
else
{
cur=cur->next;
free(head);
head=cur;
}
}
else
{
prev=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
方法二:遍历原链表,不是val的节点尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct LisatNode* newhead=NULL;//创建新链表的头结点
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* tail=NULL;//创建新链表的尾节点
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val==val)
{
struct ListNode* del=cur;//保存要删除的节点
cur=cur->next;//移动cur
free(del);//将要删除的节点释放,del是局部变量,出了代码块会自动销毁
}
else //不是val的值的节点取下来尾插
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
tail=cur;
newhead=tail;
}
else
{
tail->next=cur;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
tail->next=NULL;
}
}
return newhead;
}
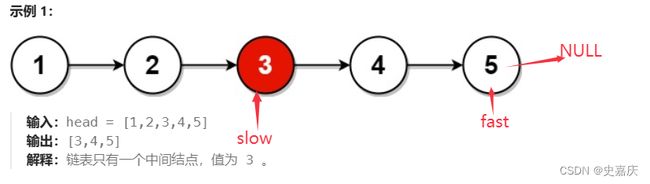
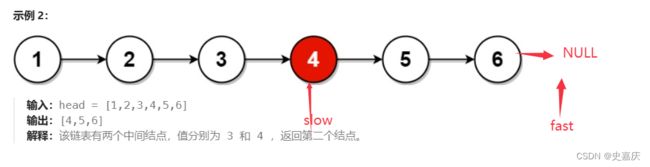
二.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
leetcode链接
思路:快慢指针
定义一个慢指针slow一次移动一个节点,一个快指针fast一次移动两个节点,当快指针走完时,返回慢指针,指向的就是中间节点。
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* slow=head;
ListNode* fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
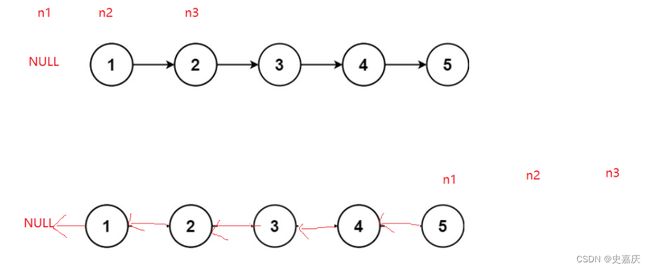
三.反转一个单链表
leetcode链接
思路:
定义n1指向空,从第一个节点开始,将其next改为前一个节点的地址
- 注意,如果只定义n1,n2两个指针,当第一个节点的next指向空时,第二个节点的地址就会丢失,所以在这里还需要引入一个指针n3,用于保存下一个节点的地址
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* n1=NULL;
ListNode* n2=head;
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* n3=head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
if(n3)
n3=n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
};
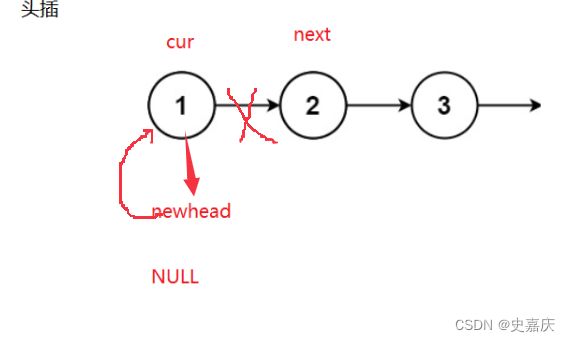
思路二:将原链表按照顺序头插到新链表,这样操作完,原链表的顺序就正好反转了
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* cur =head;
ListNode* newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
ListNode* next=cur->next;//保存下一个节点
cur->next=newhead;//将cur指向newhead(头插)
newhead=cur;//更新新链表地头节点
cur=next;//返回原链表保存的节点,重新循环
}
return newhead;
}
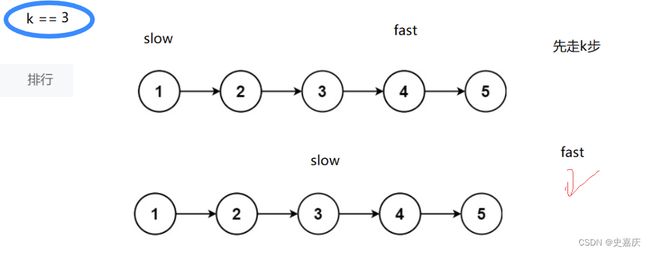
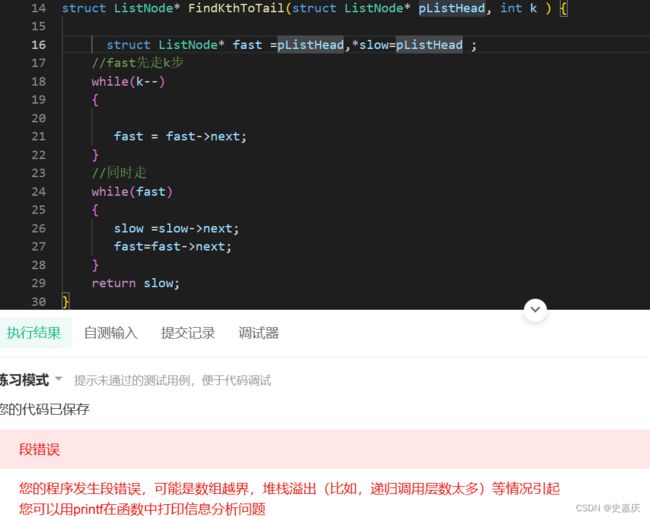
四.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
nowcoder链接
分析思路
定义两个指针指向头节点,先让快指针fast走k步,再让两个指针同时走,这样的话,两个指针之间的距离就是k,当快指针指向空的位置时,慢指针就指向了倒数第k的位置
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode* fast =pListHead,*slow=pListHead ;
//fast先走k步
while(k--)
{
if(fast==NULL)//如果k大于链表节点数,在这个循环中fast就会移动到空,这种情况直接返回NULL
return NULL;
fast = fast->next;
}
//同时走
while(fast)
{
slow =slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
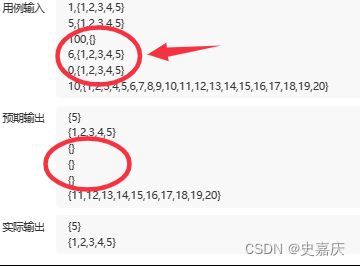
五.链表分割
nowcoder链接
创建两个链表,把小于x的值放到链表1,大于x的放到链表2,再把两个链表连接起来
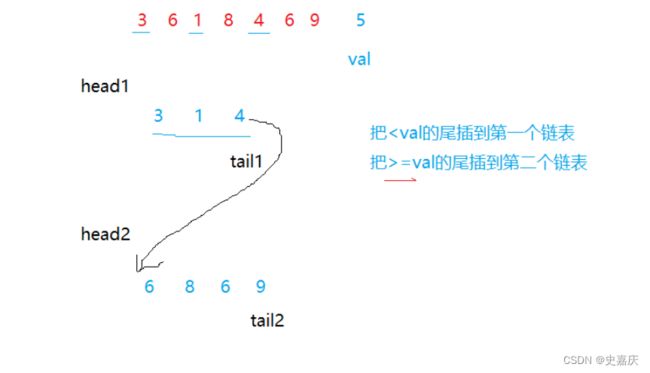
如果给定的值为1的话,第一个链表为空,需要单独判断单独处理,如果给定的值过大,第二个链表也可能为空。因此带上哨兵位会更简单。
带哨兵位的好处:不管哪个链表为空,这四个指针都不为空
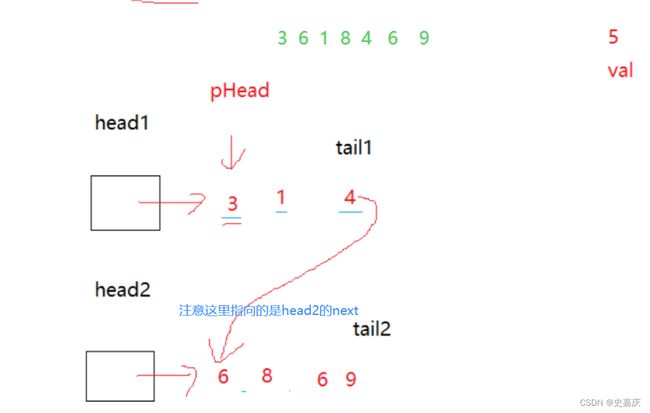
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode*head1,*tail1,*head2,*tail2;
head1=tail1=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head2=tail2=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
//这里直接开辟出头节点的空间,后续访问next就不用考虑为空的情况,更简单一些
struct ListNode* cur =pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
tail1->next=cur;
tail1=tail1->next;
}
else
{
tail2->next=cur;
tail2=tail2->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
tail1->next=head2->next;
pHead=head1->next;
free(head1);
free(head2);
return pHead;
}
上述代码看似没毛病,但是却报错了
考虑一下这种极端情况,如果刚才的数据后再来个1,这里的tail1和tail2就会形成环,造成死循环
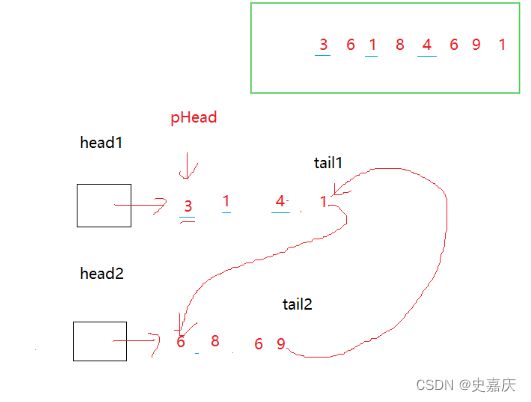
所以要把tail2->next置空才对,以下是正确代码
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode*head1,*tail1,*head2,*tail2;
head1=tail1=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head2=tail2=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* cur =pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
tail1->next=cur;
tail1=tail1->next;
}
else
{
tail2->next=cur;
tail2=tail2->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
tail1->next=head2->next;
tail2->next=NULL;//只改变了这一处
pHead=head1->next;
free(head1);
free(head2);
return pHead;
}
不得不说,这题是真的坑
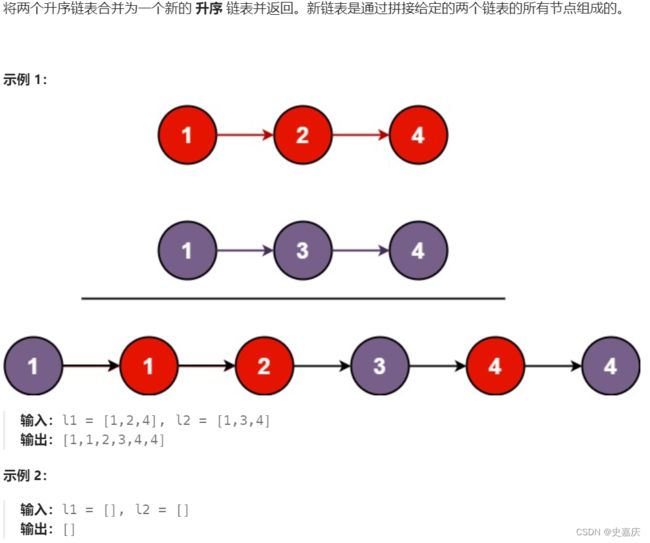
六.合并两个有序链表
leetcode链接
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1==NULL)
return list2;
if(list2==NULL)
return list1;
//创建合并链表之后的尾节点
struct ListNode* tail=NULL;
//创建不带哨兵位的头节点
struct ListNode* head=NULL;
while(list1 && list2)
{
//取小的尾插
if(list1->val<list2->val)
{
//由于不带哨兵位,要判断尾节点是不是空
if(tail==NULL)
{
tail=head=list1;
}
else
{
tail->next=list1;
tail=tail->next;
}
list1=list1->next;
}
else
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
tail=head=list2;
}
else
{
tail->next=list2;
tail=tail->next;
}
list2=list2->next;
}
}
//其中一个链表走到空跳出循环,把不是空的链表剩余部分链接起来
if(list1)
tail->next=list1;
if(list2)
tail->next=list2;
return head;
}
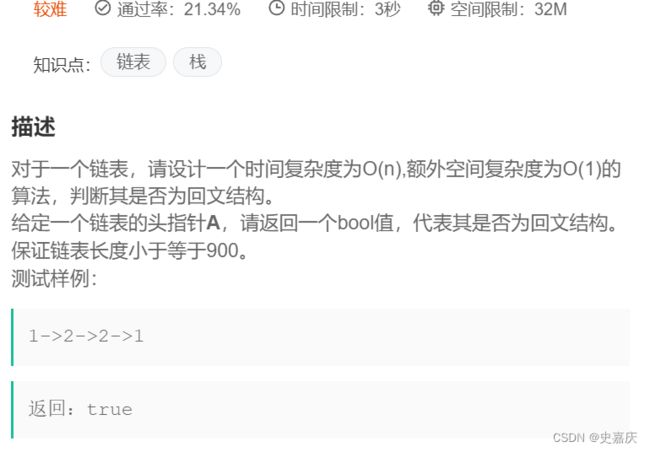
七.判断单链表是否是回文结构
nowcoder链接
思路:
找到中间节点
逆置
比较前半段和后半段,如果相同就是回文序列
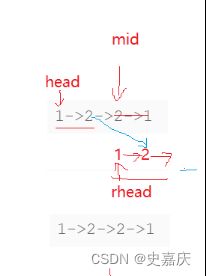
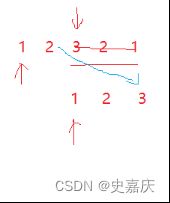
注意奇数个节点和偶数个节点的区别
偶数个节点
奇数个节点
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* slow=head;
ListNode* fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL &&fast->next!= NULL)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* cur =head;
ListNode* newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
ListNode* next=cur->next;//保存下一个节点
cur->next=newhead;//将cur指向newhead(头插)
newhead=cur;//更新新链表地头节点
cur=next;//返回原链表保存的节点,重新循环
}
return newhead;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
//调用返回中间节点的函数
struct ListNode* mid=middleNode(head);
//调用反转链表的函数
struct ListNode* rhead=reverseList(head);
while(head&&rhead)
{
if(head->val!=rhead->val)
return false;
head=head->next;
rhead=rhead->next;
}
return true;
}
八 .输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
leetcode链接
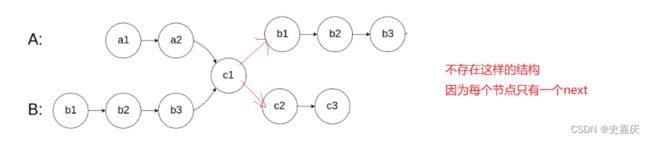
- 先明确下啥叫链表相交
- 这样的才符合
还有一个要注意,节点相交是说节点地址一样,而不是里面的值是相等的
- 怎样判断是否相交????
- 怎么找交点???
思路一:
暴力求解
A链表中所有的节点依次取B链表找一遍
最坏情况是没有交点,时间复杂度O(n^2)
思路二:
分别找到A,B链表的尾节点
尾节点的地址如果相同,则相交
尾节点的地址如果不相同,就不相交
分别求出A,B的长度
长的先走差距步,再同时走,第一个相同的就是交点
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode * cura=headA;
struct ListNode *curb=headB;
int lena=1;
int lenb=1;
//找到链表A的尾节点,并且记录链表A节点个数
while(cura->next)
{
lena++;
cura=cura->next;
}
//找到链表B的尾节点,并且记录链表B节点个数
while(curb->next)
{
lenb++;
curb=curb->next;
}
//如果尾节点都不相同,说明没交点,返回NULL
if(cura!=curb)
{
return NULL;
}
//程序走到这里,说明有交点,存好两个链表的节点差值
int n=abs(lena-lenb);
struct ListNode *longlist=headA,*shortlist=headB;
if(lena<lenb)
{
longlist=headB;
shortlist=headA;
}
//让长的先走差距步
while(n--)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
}
//同时走
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
//程序走到这里,longlist和shortlist都指向了相交的节点
//二者随便返回一个都可以
return shortlist;
}
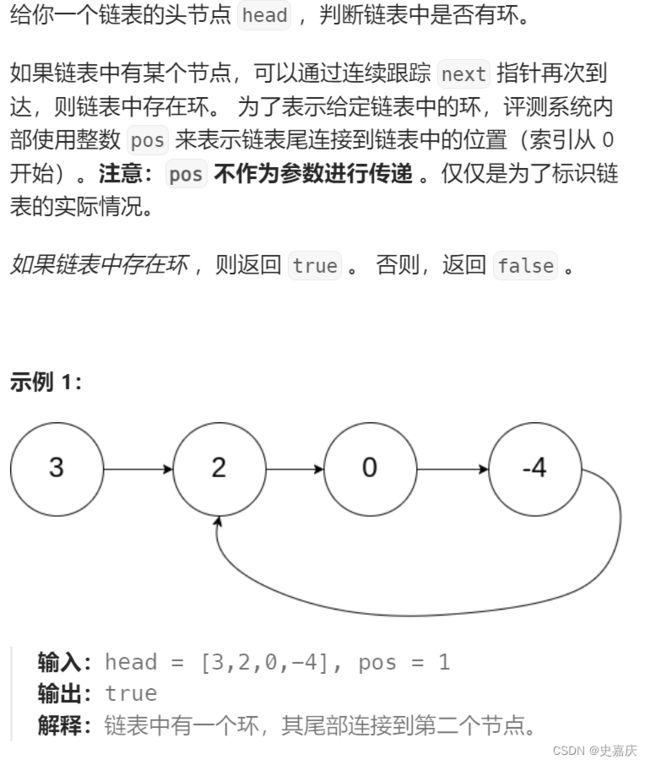
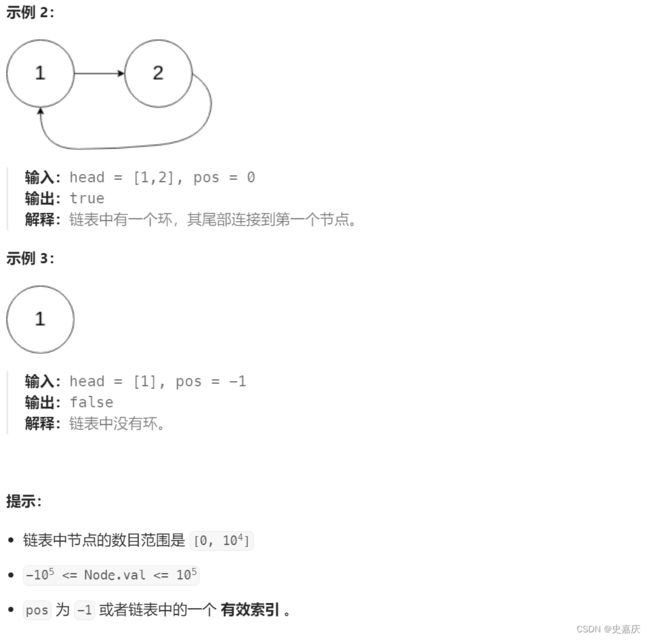
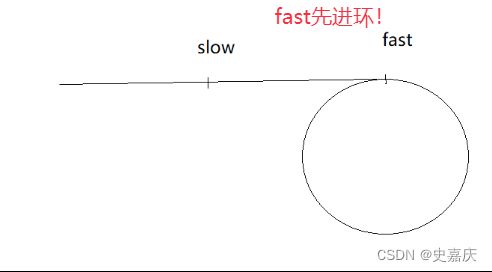
九.给定一个链表,判断链表当中是否有环
leetcode链接
思路
- 给定快慢指针slow,fast
- 快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步
- 如果没有环,fast->next->next最终会指向空指针
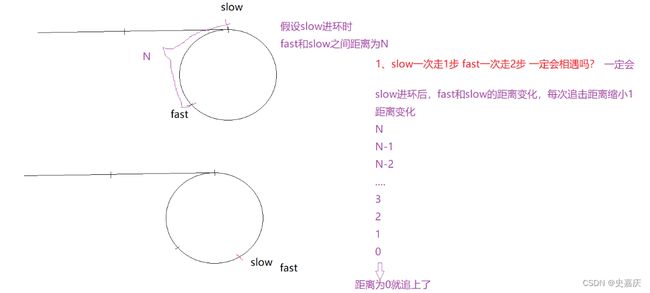
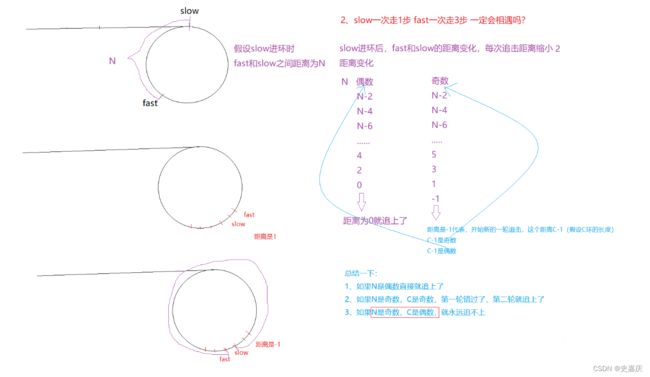
- 如果有环,快指针先进环,当慢指针进入环中时,快指针开始追慢指针
- 每次移动后,快慢指针的距离差值都会缩小1,直到快慢指针相遇
- 代码实现
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
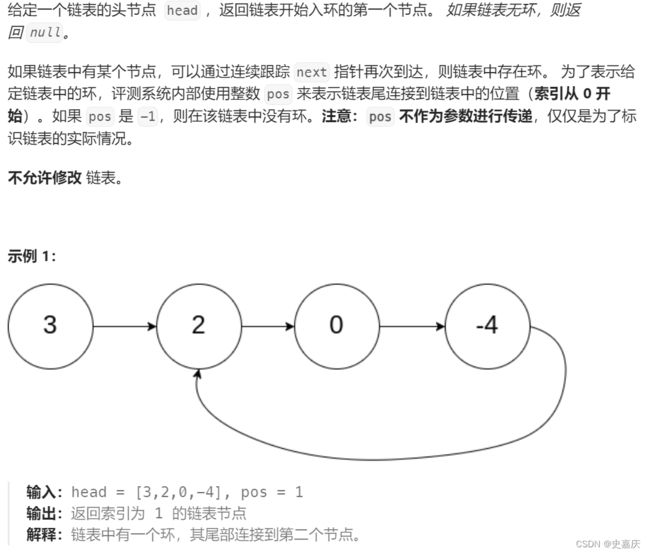
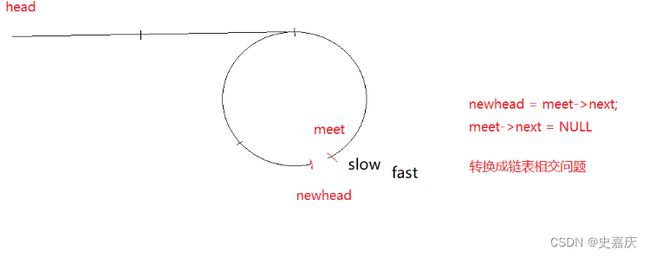
十.给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
leetcode链接
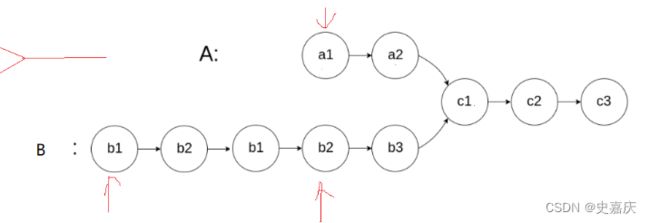
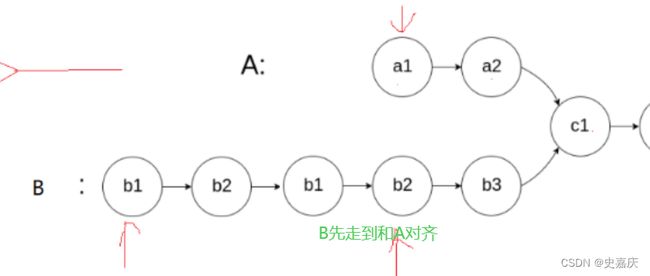
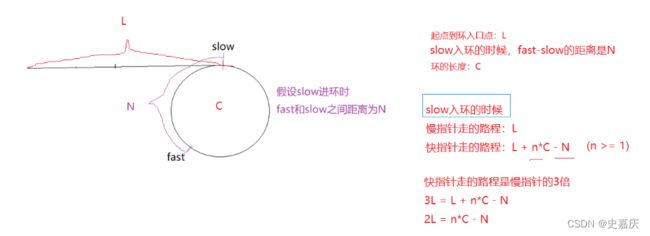
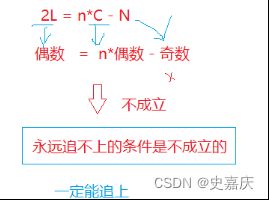
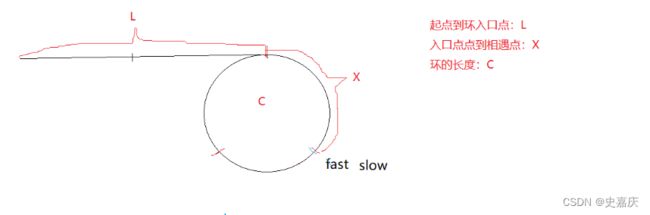
图解:设出未知量
从开始到相遇时slow走的距离:L+x
从开始到相遇fast走的距离L+n*C+x
fast路程=slow路程*2
L+n*C+x=2*(L+x)
n*C==L+x
移项得到L=n*C-x
结论:
一个指针从相遇点开始走,一个指针从头开始走,他们会在入口点处相遇
struct ListNode *detectCycle( struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)//相遇了
{
struct ListNode* meet=slow;
while(head!=meet)//基于上述数学推导
{
meet=meet->next;
head=head->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
//没环
return NULL;
}
小结
- 链表的题目要考虑周全,访问next之前要想一想程序走到此处有没有可能为空
- 注意带哨兵位与不带哨兵位的区别
- 链表一定要多画图