技术阅读周刊第十期
技术阅读周刊,每周更新。
历史更新
20231117:第六期
20231124:第七期
20231201:第八期
20231215:第九期
Golang: 14 Shorthand Tricks You Might Not Know! | by Nidhi D | Dec, 2023 | Canopas
URL: https://blog.canopas.com/golang-14-shorthand-tricks-you-might-not-know-8d8d21954c49
同时声明和初始化变量
// Long form
var message string
message = "Hello, Golang!"
// Shorthand
message := "Hello, Golang!"声明和初始化多个变量
// Long form
var a, b, c int
a = 1
b = 2
c = 3
// Shorthand
a, b, c := 1, 2, 3交换变量
a, b := 1, 2
// Long form
temp := a
a = b
b = temp
// Shorthand
a, b = b, aDefer 函数调用
// Long form
func cleanup() {
// Cleanup logic
}
defer cleanup()
// Shorthand
defer func() {
// Cleanup logic
}()检测 Map 中的数据是否存在
// Long form
value, exists := myMap[key]
if !exists {
// Key doesn't exist in the map
}
// Shorthand
if value, exists := myMap[key]; !exists {
// Key doesn't exist in the map
}使用下标和值迭代切片
// Long form
for i := 0; i < len(numbers); i++ {
fmt.Println(i, numbers[i])
}
// Shorthand
for i, value := range numbers {
fmt.Println(i, value)
}错误检测
// Long form
result, err := someFunction()
if err != nil {
// Handle the error
}
// Shorthand
if result, err := someFunction(); err != nil {
// Handle the error
}创建一个变量的指针
// Long form
var x int
ptr := &x
// Shorthand
ptr := new(int)匿名函数
// Long form
func add(x, y int) int {
return x + y
}
// Shorthand
add := func(x, y int) int {
return x + y
}创建和初始化 Map
// Long form
colors := make(map[string]string)
colors["red"] = "#ff0000"
colors["green"] = "#00ff00"
// Shorthand
colors := map[string]string{
"red": "#ff0000",
"green": "#00ff00",
}声明多个常量
// Long form
const pi float64 = 3.14159
const maxAttempts int = 3
// Shorthand
const (
pi = 3.14159
maxAttempts = 3
)Java Mastery Unleashed: 12 Essential Tips Every Developer Must Embrace
URL: https://blog.stackademic.com/boost-your-java-skills-12-must-know-programming-tips-for-java-developers-34f8381ec431
一些常用的 Java 技巧
善用 Lambda 表达式
// Before
List names = new ArrayList<>();
for (Person person : people) {
names.add(person.getName());
}
// After
List names = people.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList()); 使用 Optionals 替代 null
Optional maybeName = Optional.ofNullable(person.getName());
String name = maybeName.orElse("Unknown"); 使用 stream 简化集合操作
List evenNumbers = numbers.stream()
.filter(num -> num % 2 == 0)
.collect(Collectors.toList()); String.format 拼接字符串
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = " World";
String s = String.format("%s%s", s1, s2);使用 default method 扩展接口
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public interface TimeClient {
void setTime(int hour, int minute, int second);
void setDate(int day, int month, int year);
void setDateAndTime(int day, int month, int year, int hour, int minute, int second);
LocalDateTime getLocalDateTime();
}使用枚举替换常量
public class Main {
enum Level { LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Level myVar = Level.MEDIUM;
System.out.println(myVar);
}
}使用 try-with-Resource 管理资源
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("example.txt");
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader)) {
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
// Process the file
} catch (IOException e) {
// Handle the exception
}SpringBoot Webflux vs Vert.x: Performance comparison for hello world case | Tech Tonic
URL: https://medium.com/deno-the-complete-reference/springboot-webflux-vs-vert-x-performance-comparison-for-hello-world-case-41a6bd8e9f8c
本文对比了 SpringBoot Webflux 和 Vert.x 的性能对比
以下是两个框架写的压测接口:
package hello;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.config.EnableWebFlux;
import org.reactivestreams.Publisher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableWebFlux
@Controller
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
@GetMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public Publisher handler() {
return Mono.just("Hello world!");
}
}
// Vert.x
package com.example.starter;
import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle;
import io.vertx.core.Promise;
import io.vertx.core.http.HttpServer;
import io.vertx.ext.web.Router;
public class MainVerticle extends AbstractVerticle {
@Override
public void start(Promise startPromise) throws Exception {
HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer();
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
router.get("/").respond(ctx -> ctx
.response()
.putHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain")
.end("hello world!"));
server.requestHandler(router).listen(3000);
}
} 最后直接看对比结果吧:
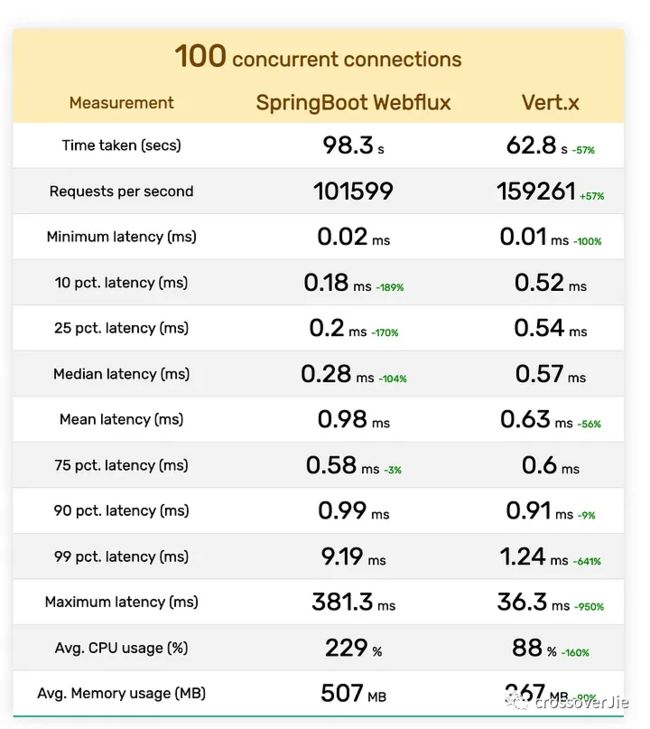
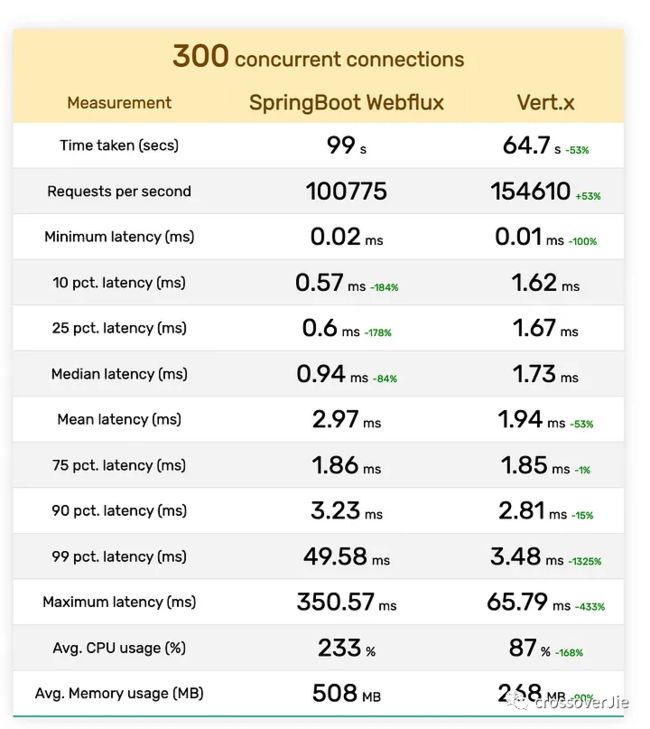 最终作者根据一个计算公式得出两个框架的得分,规则如下:
最终作者根据一个计算公式得出两个框架的得分,规则如下:
不过个人觉得压测结果再好,套上业务后,比如一个接口查询了多个后端服务,后端服务有依赖于多个数据库,最终出来的 RT 大家都差不多。
除非是某些对性能极致要求的场景,比如实时数据分析、物联网中间件等和直接业务不太相关领域。
它的底层依然是 Netty,但比 Netty 提供了跟易用的 API。
Git Cherry Pick Examples to Apply Hot Fixes and Security Patches — Nick Janetakis
URL: https://nickjanetakis.com/blog/git-cherry-pick-examples-to-apply-hot-fixes-and-security-patches?ref=dailydev
讲解了 git cherry-pick 的作用,什么时候该用,什么时候不用。
举个例子:一些大型的开源项目往往都会有一个主分支,同时维护了不同版本的子分支,有些用户可能就会一直使用一些长期维护的子分支,比如 v2.1.0 \ v2.3.0
但对于大部分的开发者来说主要会维护主分支,也会在主分支上推进一些新功能,这些新功能不一定会同步到上述提到的两个老版本中。
但对于一些安全漏洞,重大 bug 等是需要同步到这些子分支的,但又不能把一些不兼容的新特性同步到子分支中。
此时就可以使用 cherry-pick 这个功能,只将某一个提交给 pick 到目标分支中。
# Cherry pick more than 1 SHA.
#
# This could be useful if you have a handful of commits that you want to bring over,
# you'll likely want to order them with the oldest commit being first in the list.
git cherry-pick
# Edit the git commit message for the newly applied commit.
#
# This could be useful if want to customize the git commit message with extra context.
git cherry-pick --edit
# Avoid automatically creating the commit which lets you edit the files first.
#
# This could be useful if you need to make manual code adjustments before committing,
# such as applying a security patch which uses an older library with a different API.
git cherry-pick --no-commit 文章链接:
https://blog.canopas.com/golang-14-shorthand-tricks-you-might-not-know-8d8d21954c49
https://blog.stackademic.com/boost-your-java-skills-12-must-know-programming-tips-for-java-developers-34f8381ec431
https://medium.com/deno-the-complete-reference/springboot-webflux-vs-vert-x-performance-comparison-for-hello-world-case-41a6bd8e9f8c
https://nickjanetakis.com/blog/git-cherry-pick-examples-to-apply-hot-fixes-and-security-patches?ref=dailydev


