Python的入门
文章目录
- 一、Python的特点
- 1.1Python是什么
-
-
- 1.1.2胶水语言
- 1.1.3脚本语言
- 1.1.4面向对象语言
- 1.2Python的特点
-
- 二、python之hello world!
-
- 2.1hello world程序
- 2.2Python运行方式
-
- 2.2.1Shell方式
- 2.2.2文件方式
- 三、Python的环境搭建
-
- 3.1Anaconda
-
- 3.1.1下载
- 3.1.2安装
- 3.1.3使用
- 四、Python输出/输入
-
- 4.1输出
- 4.2输入
- 五、Python风格
-
- 5.1注释
- 5.2续行符
- 5.3一行多语句
- 5.4缩进
- 六、Python语法基础
-
- 6.1变量
-
- 6.1.1变量名
- 6.1.2命名方式
- 6.2关键字
- 6.3运算符
-
- 6.3.1算数运算符
- 6.3.2位运算符
- 6.3.3比较运算符
- 6.3.4逻辑运算符
- 6.4表达式
- 6.5赋值
-
- 6.5.1赋值语句
- 6.5.2增量赋值
- 6.5.3链式赋值
- 6.5.4多重赋值
- 6.6语句
- 七、Python数据类型
-
- 7.1标准数据类型
- 7.2整型
- 7.3布尔型
- 7.4浮点型
- 7.5复数型
- 7.6序列类型
-
- 7.6.1字符串
- 7.6.2列表
- 7.6.2元组
- 7.7映射类型
-
- 7.7.1字典
- 八、Python基本运算
-
- 8.1算数运算
- 8.2比较运算
- 8.3逻辑运算
- 8.4字符运算
- 8.5综合运算
- 8.6四则运算迷你编程小练习
- 九、Python的函数、模块和包
-
- 9.1函数
- 9.2模块
-
- 9.2.1import
- 9.2.2多模块导入
- 9.3包
- 9.4库
- 9.5库、包、模块、函数之间的关系
- 9.6编写一个输入输出程序
- 十、参考资料
-
- 9.4库
- 9.5库、包、模块、函数之间的关系
- 9.6编写一个输入输出程序
- 十、参考资料
一、Python的特点
1.1Python是什么
1.1.2胶水语言
很容易和其他程序语言连接(C/C++),集成封装
1.1.3脚本语言
高级脚本语言,比普通脚本语言处理能力更强
1.1.4面向对象语言
完全支持继承、重载、派生、多继承
1.2Python的特点
可移植、可升级、可拓展
健壮性、解释性、编译性
易学、易读、易维护
内存管理器
高级、面向对象
快速原型开发工具
二、python之hello world!
2.1hello world程序
#eg:
myString ='Hello,World!'
print(myString)
2.2Python运行方式
2.2.1Shell方式
shell是交互式解释器
输入一行命令,解释器就解释运行出相应结果
对代码段较短时使用
#eg:
>>>myString='Hello,World!'
>>>print(myString)
Hello,World!
>>>myString
'Hello,World!'
2.2.2文件方式
在Python的IDE环境中,创建一个以py为拓展名的文件
用Python解释器在Shell中运行出结果
对代码段较长时使用
#eg:
#Filename:helloworld.py
myString='Hello,World!'
print(myString)
三、Python的环境搭建
3.1Anaconda
3.1.1下载
去[Anaconda官网](Anaconda | Anaconda Distribution)下载
3.1.2安装
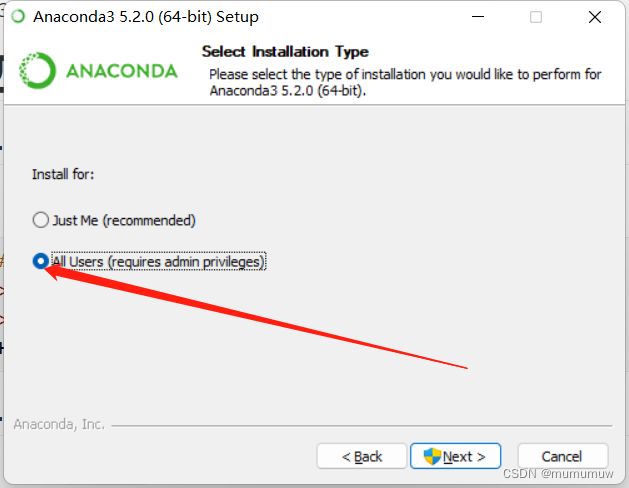
勾选下面的使得所有用户可用
修改安装路径
上面一个勾选上,使得Anaconda加到系统的环境变量
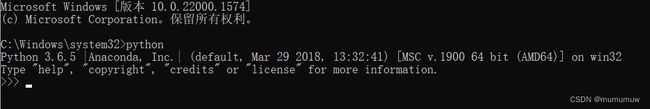
可通过cmd输入python以及pip来检查环境是否安装
3.1.3使用
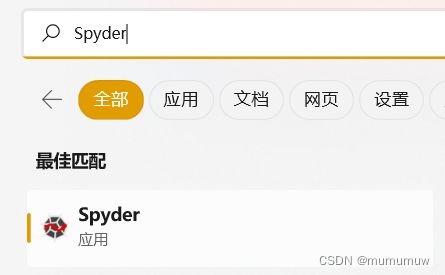
Win在搜索窗口中输入Spyder或Jupyter
点击后打开相应环境
四、Python输出/输入
4.1输出
使用print()函数实现输出即print(变量)或print(字符串)
#eg:
>>>myString='Helllo,World!'
>>>print(myString)
Hello,World!
4.2输入
使用input(),可在括号内用单引号括起要提示的内容
input()返回值类型是字符型
#eg:
>>>price=input('input the stock price of Apple:')
input the stock price of Apple:109
>>>price
'109'
>>>type(price)
<class 'str'>
>>>price=int(input('input the stock price of Apple:'))
>>>price=eval(input('input the stock price of Apple:'))
五、Python风格
5.1注释
单行注释用#,可位于各种位置,作用到本行结束
#eg:
>>>#comment No.1
>>>print('Hello,World!') #comment No.2
Hello,World!
5.2续行符
续行用\
作用:一条语句较长,可分为多行写
#eg:
>>># long sentence
>>>if signal=='red' and\
car=='moving':
car='stop'
elif signal=='green' and\
car=='stop':
car='moving'
#等价于
>>># long statement
>>>if signal=='red' and car=='moving':
car=='stop'
elif signal=='green' and car=='stop':
car='moving'
无需续行符可直接换行的情况:
1.小括号、中括号、花括号的内部可以多行书写
2.三引号包括下的字符串也可以跨行书写
#eg:
>>>#triple quotes
>>>print("hi everybody,
welcom to python's course.
Here we can learn something about
python.Good lucky!")
5.3一行多语句
即将多行语句同时写在一行,大部分在这几行语句之间的关联性比较强的时候才用,语句之间用;隔开
#eg:
>>>x='Today';y='is';z='Thursday';print(x,y,z)
Today is Thursday
#等价于
>>>x='Today'
>>>y='is'
>>>z='Thursday'
>>>print(x,y,z)
Today is Thurday
5.4缩进
增加缩进表示语句块的开始
相同的缩进表示同级别语句块
减少缩进表示语句块的退出
#eg:
>>>Indentation
>>>if signal=='red'and car='moving':
car='stop'
signal='yellow'
elif signal=='green' and car=='stop':
car='moving'
signal='yellow'
六、Python语法基础
6.1变量
6.1.1变量名
作用:引用对象、标识对象
命名规则:标识符是指Python语言中允许作为变量名/其他对象名称的有效符号
-
首字母为字母/下划线
-
其余可以是字母/下划线/数字
-
大小写敏感
有些特殊的变量名:
- 全大写的变量名常认为是符号常量
- 尽量避免下划线开头的变量名,特别是双下划线(下划线对于解释器而言表内建标识符使用的符号,当作私有的)
- 尽量少用拼音
#eg:
>>>#variable
>>>p=3.14159
>>>myString='is a mathematic circular constant'
>>>print(p,myString)
out:3.14159 is a mathematic circular constant
6.1.2命名方式
-
驼峰式
首个单词的首字母小写后每个单词的首字母大写,例如
stuName -
下划线式
单词之间用下划线连接,例如
stu_name两个方式尽量不要混用
6.2关键字
基本固定的组合,在IDE中常以不同颜色的字体出现
#eg:
>>>import keyword
>>>print(keyword.kwlist)
常见关键字:
| False | None | True | and | as | break | class | continue | def | del | elif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| except | finally | for | from | global | if | import | in | is | lambda | not |
| or | pass | raise | return | try | wile | with | yield | assert | else | nonlocal |
6.3运算符
6.3.1算数运算符
| 乘方 | 正负号 | 乘除 | 整数 | 取余 | 加减 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ** | ± | */ | // | % | ± |
6.3.2位运算符
| 取反 | 与 | 或 | 异或 | 左移 | 右移 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~ | & | | | ^ | << | >> |
6.3.3比较运算符
| 小于 | 大于 | 小于等于 | 大于等于 | 等于 | 不等于 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < | > | <= | >= | == | != |
6.3.4逻辑运算符
| 非 | 与 | 或 |
|---|---|---|
| not | and | or |
6.4表达式
运算符有优先级顺序
表达式必须有运算结果
#eg:
>>>#expression
>>>PI=3.14159
>>>r=2
>>>c_circ=2*PI*r #2*PI*r是表达式,运算结果赋给c_circ
>>>print("The circle's circum is",c_circ)
6.5赋值
6.5.1赋值语句
变量第一次赋值,同时获得类型和“值”
- Python是动态的强类型语言
- 不需要显式声明,根据“值”确定类型
- 以“引用”的方式实现赋值(
a和b值相同时但引用内存空间不同在a is b时答案为False,具体可用id()函数查看,在[-5,256]可行)
#eg:
>>>#Identifier
>>>PI=3.14159
>>>pi='one word'
>>>print(PI)
3.14159
>>>print(pi)
one word
#eg:
>>>#Identifier
>>>PI=3.14159
>>>pi=PI
>>>print(PI)
3.14159
>>>print(pi)
3.14159
>>>p=3
>>>q=3
>>>p is q
True
6.5.2增量赋值
+= -= *= /= %= **= <<= >>= &= ^= |=
#eg:
>>>#assignment
>>>m=18;
>>>m%=5; #等价于m=m%5
>>>m
3
>>>m**=2; #等价于m=m**2
>>>m
9
6.5.3链式赋值
#eg:
>>>#assignment
>>>PI=pi=3.14159
>>>PI
3.14159
>>>pi
3.14159
#eg:
>>>#assignment
>>>PI=3.14159
>>>pi=PI=PI*2
>>>pi
6.28318
6.5.4多重赋值
等号左右边都以元组的方式出现
#eg:
>>>#assignment
>>>x=1
>>>y=2
>>>x,y
(1,2)
>>>x,y=y,x
>>>x,y
(2,1)
#eg:
>>>#assignment
>>>PI,r=3.14159,3
>>>PI
3.14159
>>>r
3
>>>(PI,r)=(3.14159,3) #same as no round brackets
6.6语句
完整执行一个任务的一行逻辑代码
而表达式是任务中的一个具体组成部分
七、Python数据类型
7.1标准数据类型
(长)整型、复数型、字符串、元组、浮点数、布尔型、字典、列表
7.2整型
整型和长整型并不严格区分
Python2支持整型值后加L表长整型
#integer
type(3)
<class 'int'>
7.3布尔型
整型的子类
仅有两个值:True、False
本质上是用整型的1、0分别存储的
#boolean
x=True
int(x)
#out:1
y=False
int(y)
#out:0
7.4浮点型
即数学中的实数
可以类似科学计数法表示
#float
3.22
#out:3.22
9.8e3 #e后数字表示10^
#out:9800.0
-4.78e-2
#out:-0.0478
type(-4.78e-2)
<class 'float'>
7.5复数型
j=√ ̄-1,则j为虚数
实数+虚数就是复数
虚数部分必须有j
#complex
2.4+5.6j
#out:(2.4+5.6j)
type(2.4+5.6j)
#out: 复数可以分离实数部分和虚数部分
-
复数.real
-
复数.imag
复数的共轭
-
复数.conjugate()
#complex
x=2.4+5.6j
x.imag
#out:5.6
x.real
#out:2.4
x.conjugate()
#out:(2.4-5.6j)
7.6序列类型
7.6.1字符串
单引号''、双引号""、三引号''''''(可表示多行的字符串)内的都是字符串,不可变类型
myString='Hello World!'
print(myString) #若要取字符串中的e可以用myString[1]
#out:Hello World!
myString="Hello World!"
print(myString)
#out:Hello World!
myString='''Hello World!'''
print(myString)
#out:Hello World!
7.6.2列表
强大的类型,用方括号[]界别,可变类型
7.6.2元组
与列表相似,用小括号()界别,不可变类型
7.7映射类型
7.7.1字典
用大括号{}界别
类似于哈希表的键值对
#dictionary
d={'sine':'sin','cosine':'cos','pi':3.14159}
d['sine']
#out:'sin'
八、Python基本运算
8.1算数运算
算数运算符优先级**(乘方) +-(正负号) */(乘除) //(整除) %(取余) +-(加减)
#arithmetic
pi=3.14159
r=3
circum=2*pi*r
x=1
y=2
z=3
result1=x+3/y-z%2
result2=(x+y**z*4)//5
print(circum,result1,result2)
#out:18.84954 1.5 6
8.2比较运算
数值的比较:按值比较大小
字符串的比较:按ASCII码值大小
#compare1
3<4<7 #same as 3<4 and 4<7
#out:True
4>3==3 #same as 4>3 and 3==3
True
4<3<5 != 2<7
False
#compare2
2==2
#out:True
2.46<=8.33
#out:True
'abc'=='xyz'
#out:False
'abc'>'xyz'
#out:False
'abc'<'xyz'
#out:True
8.3逻辑运算
逻辑运算符优先级:not and or
#logical
x,y=3.1415926536,-1024
x<5.0
#out:True
not x<5.0
#out:False
x<5.0 or y>2.718281828
#out:True
not x is y
#out:True
3<4<7 #same as "3<4 and 4<7"
#out:True
8.4字符运算
原始字符串操作数(r/R)
-
用于一些不希望转义字符起作用的地方
所有的字符串都是Unicode字符串
-
Python 2.x中需转换成Unicode字符串
#u in Python 2.x
print u'Hello \nWorld'
'''out:hello
World'''
#r
f=open('c:\python\test.py','w')
'''out:Traceback(most recent call last):
File"",line1,in
f=open('c:\python\test.py','w')
IOError:[Errno 22]invalid mode('w')or filename:'c:\\python\test.py' '''
f=open(r'c:\python\test.py','w')
f=open('c:\\python\\test.py','w')
8.5综合运算
运算综合后的运算的优先级:
算数运算符、位运算符、比较运算符、逻辑运算符
#mix
3<2 and 2<1 or 5>4
#out:True
x+3/y-z%2>2
#out:False
3-2<<1
#out:2
3-2<<1<3
#out:True
8.6四则运算迷你编程小练习
题:从键盘输入两个整数,求这两个整数的和、差、积、商(尝试用一般除法和整除两种方式)并输出
提示:注意input()函数的返回类型
#mycode
x=int(input())
y=int(input())
print("x+y=",x+y)
print("x-y=",x-y)
print("x*y=",x*y)
print("x/y=",x/y)
print("x//y=",x//y)
九、Python的函数、模块和包
9.1函数
函数可以堪称类似于数学中的函数
完成一个特定功能的一段代码
- 绝对值函数abs(x)
- 类型函数type(x)
- 四舍五入函数round(x)
内建函数
str()和type等适用于所有标准类型
| 数值型内建函数 | ||
|---|---|---|
| abs() | bool() | oct() |
| round() | int() | hex() |
| divmod() | ord() | pow() |
| float() | chr() | complex() |
| 实用函数 | |
|---|---|
| dir() | input() |
| help() | open() |
| len() | range() |
9.2模块
9.2.1import
非内建函数如何使用
#round-off floor
floor(5.4)
'''out:
Traceback(most recent call last):
File"",line1,in
floor(5.4)
NameError:name 'floor' is not defined'''
要使用先将模块import
#round-off floor
import math
math.floor(-35.4)
#out:-36
math.floor(-35.5)
#out:-36
math.floor(-35.8)
#out:-36
一个完整的Python文件就是一个模块
- 文件:物理上的组织方式math.py
- 模块:逻辑上的组织方式math
Python通常用“import模块”的方式将现成的模块中的函数、类等重用到其他代码块中
math.pi的值可以直接使用,不需要自行定义
#module
import math
math.pi
#out:3.141592653589793
9.2.2多模块导入
导入多个模块
模块里导入指定的模块属性,也就是把指定名称导入到当前作用域
import ModuleName
import ModuleName1,ModuleName2
form Module1 import ModuleElement #导入模块内的具体属性
9.3包
一个有层次的文件目录结构
定义了一个由模块和子包组成的Python应用程序执行环境

import AAA.CCC.C1
AAA.CCC.c1.func1(123)
from AAA.CCC.c1 import func1
func1(123)
9.4库
库是一组具有相关功能的模块的集合
Pyhon的一大特色就是具有强大的标准库、以及第三方库、以及自定义模块
例如:数值型相关标准库:decimal、math、cmath、random、operator、array
9.5库、包、模块、函数之间的关系
包是包含了模块或者库
在模块或者库里面会有很多的函数或者类
对这些库和模块里面的函数和方法都是编程利器
9.6编写一个输入输出程序
题:简答的输入输出:编程实现输入姓、名的提示语并接受用户输入,并单独显示姓、名和全名,执行效果如下所示:
Input your surname:ZHANG
Input your firstname:Dazhuang
Your surname is:ZHANG
Your firstname is:Dazhuang
Your full name is:ZHANG Dazhuang
#my
sur=input("Input your surname:")
first=input("Input your firstname:")
print("Your surname is:",sur)
print("Your firstname is:",first)
print("Your full name is:",sur,first)
十、参考资料
序执行环境[外链图片转存中…(img-RcxY8C9K-1677843250211)]
import AAA.CCC.C1
AAA.CCC.c1.func1(123)
from AAA.CCC.c1 import func1
func1(123)
9.4库
库是一组具有相关功能的模块的集合
Pyhon的一大特色就是具有强大的标准库、以及第三方库、以及自定义模块
例如:数值型相关标准库:decimal、math、cmath、random、operator、array
9.5库、包、模块、函数之间的关系
包是包含了模块或者库
在模块或者库里面会有很多的函数或者类
对这些库和模块里面的函数和方法都是编程利器
9.6编写一个输入输出程序
题:简答的输入输出:编程实现输入姓、名的提示语并接受用户输入,并单独显示姓、名和全名,执行效果如下所示:
Input your surname:ZHANG
Input your firstname:Dazhuang
Your surname is:ZHANG
Your firstname is:Dazhuang
Your full name is:ZHANG Dazhuang
#my
sur=input("Input your surname:")
first=input("Input your firstname:")
print("Your surname is:",sur)
print("Your firstname is:",first)
print("Your full name is:",sur,first)
十、参考资料
[1]用Python玩转数据