antv/x6_2.0学习使用(二、画布)
画布
一. 创建容器
- 在页面中创建一个 div 标签,用来容纳画布
<div id="container">div>
- 画布常用配置信息
const graph = new Graph({
container: graphRef.value, // 画布容器
width: 800, // 画布宽度,默认使用容器宽度
height: 600, // 画布高度,默认使用容器高度
autoResize: false, // 是否监听容器大小改变,并自动更新画布大小。
background: { color: "#F2F7FA" },
grid: {
// 网格,默认使用 10px 的网格,但不绘制网格背景
size: 10,
visible: true,
// 网格类型,内置四种网格类型
// dot(默认值) -> 点状网格
// fixedDot -> 固定网点大小的点状网格。当画布的缩放比例小于 1 时,网点大小随着画布缩放比例缩放,当画布缩放比例大于 1 时,网点大小为给定的 thickness 的值。
// mesh -> 网状网格
// doubleMesh -> 双线网状网格
type: "doubleMesh",
args: [
{
color: "#eee", // 主网格线颜色
thickness: 1, // 主网格线宽度
},
{
color: "#ddd", // 次网格线颜色
thickness: 1, // 次网格线宽度
factor: 4, // 主次网格线间隔
},
],
},
panning: {
// 画布是否可以拖拽平移,默认禁用。
enabled: true, // 是否开启画布平移交互。
// 触发画布平移的交互方式。支持三种形式或者他们之间的组合:
// leftMouseDown: 按下鼠标左键移动进行拖拽
// rightMouseDown: 按下鼠标右键移动进行拖拽
// mouseWheel: 使用鼠标滚轮滚动拖拽
// mouseWheelDown: 按下鼠标滚轮进行拖拽
eventTypes: ["rightMouseDown"],
},
mousewheel: true, // 鼠标滚轮缩放,默认禁用
connecting: {
allowEdge: false, // 是否允许边链接到另一个边,默认为 true
allowMulti: false, // 是否允许在相同的起始节点和终止之间创建多条边,默认为 true
allowLoop: false, // 是否允许创建循环连线,即边的起始节点和终止节点为同一节点,默认为 true
allowBlank: false, // 是否允许连接到画布空白位置的点
validateConnection({
// 在移动边的时候判断连接是否有效,如果返回 false,当鼠标放开的时候,不会连接到当前元素,否则会连接到当前元素
sourceView,
targetView,
sourceMagnet,
targetMagnet,
}) {
if (!sourceMagnet) return false;
if (!targetMagnet) return false;
return true;
},
},
embedding: {
//可以将一个节点拖动到另一个节点中,使其成为另一节点的子节点
enabled: true,
findParent({ node }) {
const bbox = node.getBBox();
return this.getNodes().filter((node) => {
// 只有 data.parent 为 true 的节点才是父节点
const data = node.getData();
if (data && data.parent) {
const targetBBox = node.getBBox();
return bbox.isIntersectWithRect(targetBBox);
}
return false;
});
},
},
});
二. 渲染节点和边
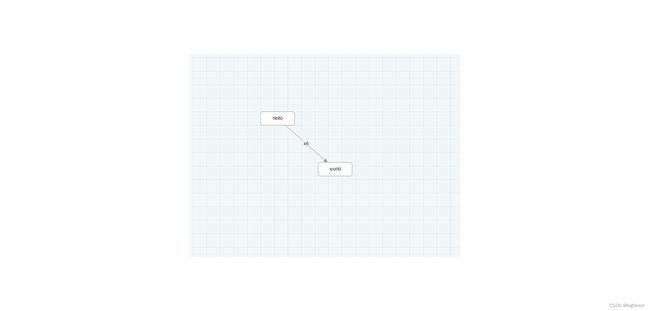
- X6 支持 JSON 格式数据,该对象中 nodes 代表节点数据,edges 代表边数据,可以使用 attrs 属性来定制节点和边的样式(可以类比 CSS)。
// 画布加载的数据
const data = {
nodes: [
{
id: "node1",
shape: "rect",
x: 40,
y: 40,
width: 100,
height: 40,
label: "hello",
attrs: {
body: {
stroke: "#8f8f8f",
strokeWidth: 1,
fill: "#fff",
rx: 6,
ry: 6,
},
},
},
{
id: "node2",
shape: "rect",
x: 160,
y: 180,
width: 100,
height: 40,
label: "world",
attrs: {
body: {
stroke: "#8f8f8f",
strokeWidth: 1,
fill: "#fff",
rx: 6,
ry: 6,
},
},
},
],
edges: [
{
shape: "edge",
source: "node1",
target: "node2",
label: "x6",
attrs: {
line: {
stroke: "#8f8f8f",
strokeWidth: 1,
},
},
},
],
};
graph.fromJSON(data); // 画布渲染数据
graph.centerContent(); // 将画布内容中心与视口中心对齐
三. 画布大小自适应问题
在实例化 Graph 对象的时候,可以通过设置 width 和 height 固定画布大小,如果不设置,就会以画布容器大小初始化画布。
- 在项目实践中,经常会遇到下面两种场景:
- 画布容器还没有渲染完成(此时尺寸为 0),就实例化画布对象,导致画布元素显示异常。
- 页面的 resize 导致画布容器大小改变,导致画布元素显示异常。
可以使用 autoResize 配置来解决上述问题。
<!-- 注意,使用 autoResize 配置时,需要在画布容器外面再套一层宽高都是 100% 的外层容器,在外层容器上监听尺寸改变,当外层容器大小改变时,画布自动重新计算宽高以及元素位置。 -->
<div style="width:100%; height:100%">
<div id="container"></div>
</div>
const graph = new Graph({
container: document.getElementById("container"),
autoResize: true,
});
三. 常用AIP
graph.resize(800, 600) // resize 画布大小
graph.translate(20, 20) // 在 x、y 方向上平移画布
graph.zoom(0.2) // 将画布缩放级别增加 0.2(默认为1)
graph.zoom(-0.2) // 将画布缩放级别减少 0.2
graph.zoomTo(1.2) // 将画布缩放级别设置为 1.2
// 将画布中元素缩小或者放大一定级别,让画布正好容纳所有元素,可以通过 maxScale 配置最大缩放级别
graph.zoomToFit({ maxScale: 1 })
graph.centerContent() // 将画布中元素居中展示