CUDA编程
第一个程序:用GPU输出Hello World
写一个CUDA C程序步骤
-
用专用扩展名.cu来创建一个源文件
-
使用CUDA nvcc编译器来编译程序
-
从命令行运行可执行文件,这个文件有可在GPU上运行的内核代码
hello.cu
#include "../common/common.h"
#include
/*
* A simple introduction to programming in CUDA. This program prints "Hello
* World from GPU! from 10 CUDA threads running on the GPU.
*/
__global__ void helloFromGPU()
{
printf("Hello World from GPU!\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
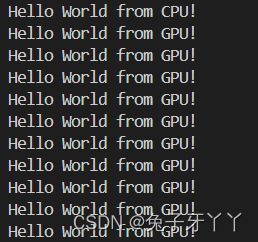
printf("Hello World from CPU!\n");
helloFromGPU<<<1, 10>>>();
CHECK(cudaDeviceReset());
return 0;
}
编译
nvcc hello.cu -o hello运行
./hellocudaDeviceReset()函数是用来显示的释放和清空当前进程中于当前设备有关的所有资源当重置函数移除后 编译运行则只输出hello world from cpu,printf在gpu上被调用,cudaDeviceReset()函数使这些来自gpu的输出发送到主机,然后在控制台输出。没有调用cudaDeviceReset()函数就不能保证这些可以被显示
关于cudaDeviceReset(); 这句话如果没有,则不能正常的运行,因为这句话包含了隐式同步,GPU和CPU执行程序是异步的,核函数调用后成立刻会到主机线程继续,而不管GPU端核函数是否执行完毕,所以上面的程序就是GPU刚开始执行,CPU已经退出程序了,所以我们要等GPU执行完了,再退出主机线程。
common.h
#include
#include
#include
#ifndef _COMMON_H
#define _COMMON_H
cudaError_t ErrorCheck(cudaError_t status,const char* filename,int lineNumber)
{
if(status != cudaSuccess)
{
printf("CUDA API error: \r\ncode=%d, name=%s, description=%s\r\nfile=%s, line=%d\r\n",
status,cudaGetErrorName(status),cudaGetErrorString(status),filename,lineNumber
);
}
return status;
}
#define CHECK(call) \
{ \
const cudaError_t error = call; \
if (error != cudaSuccess) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s:%d, ", __FILE__, __LINE__); \
fprintf(stderr, "code: %d, reason: %s\n", error, \
cudaGetErrorString(error)); \
exit(1); \
} \
}
#define CHECK_CUBLAS(call) \
{ \
cublasStatus_t err; \
if ((err = (call)) != CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, "Got CUBLAS error %d at %s:%d\n", err, __FILE__, \
__LINE__); \
exit(1); \
} \
}
#define CHECK_CURAND(call) \
{ \
curandStatus_t err; \
if ((err = (call)) != CURAND_STATUS_SUCCESS) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, "Got CURAND error %d at %s:%d\n", err, __FILE__, \
__LINE__); \
exit(1); \
} \
}
#define CHECK_CUFFT(call) \
{ \
cufftResult err; \
if ( (err = (call)) != CUFFT_SUCCESS) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, "Got CUFFT error %d at %s:%d\n", err, __FILE__, \
__LINE__); \
exit(1); \
} \
}
#define CHECK_CUSPARSE(call) \
{ \
cusparseStatus_t err; \
if ((err = (call)) != CUSPARSE_STATUS_SUCCESS) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, "Got error %d at %s:%d\n", err, __FILE__, __LINE__); \
cudaError_t cuda_err = cudaGetLastError(); \
if (cuda_err != cudaSuccess) \
{ \
fprintf(stderr, " CUDA error \"%s\" also detected\n", \
cudaGetErrorString(cuda_err)); \
} \
exit(1); \
} \
}
inline double seconds()
{
struct timeval tp;
struct timezone tzp;
int i = gettimeofday(&tp, &tzp);
return ((double)tp.tv_sec + (double)tp.tv_usec * 1.e-6);
}
#define CHECK_EXIT(sts, str) \
if (sts) \
{ \
std::cerr << str << " " << __FILE__ << " " << __LINE__ << std::endl; \
exit(0);\
}
#endif // _COMMON_H
cuda程序执行步骤
-
设置参与运算的GPU cudaSetDevice
-
申请显存 cudaMalloc
-
复制数据 cudaMemcpy(参数cudaMemcpyHostToDevice)
-
调用kernel函数做运算 xxxKernel
-
等待运算结束后同步 cudaDeviceSynchronize(kernel函数的调用是异步的)
-
复制运算结果到到内存 cudaMemcpy (参数cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost)
-
释放显存 cudaFree
两个数组相加
CPU上的两个数据相加
sumArraysOnHost.c
#include
#include
/*
* This example demonstrates a simple vector sum on the host. sumArraysOnHost
* sequentially iterates through vector elements on the host.
*/
void sumArraysOnHost(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N)
{
for (int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++)
{
C[idx] = A[idx] + B[idx];
}
}
void initialData(float *ip, int size)
{
// generate different seed for random number
time_t t;
srand((unsigned) time(&t));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
ip[i] = (float)(rand() & 0xFF) / 10.0f;
}
return;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int nElem = 1024;
size_t nBytes = nElem * sizeof(float);
float *h_A, *h_B, *h_C;
h_A = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
h_B = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
h_C = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
initialData(h_A, nElem);
initialData(h_B, nElem);
sumArraysOnHost(h_A, h_B, h_C, nElem);
free(h_A);
free(h_B);
free(h_C);
return(0);
}
gcc -O2 -std=c99 -o sumArraysOnHost sumArraysOnHost.cCPU上的两个数据相加
sumArraysOnGPU-small-case.cu
#include "../common/common.h"
#include
#include
/*
* This example demonstrates a simple vector sum on the GPU and on the host.
* sumArraysOnGPU splits the work of the vector sum across CUDA threads on the
* GPU. Only a single thread block is used in this small case, for simplicity.
* sumArraysOnHost sequentially iterates through vector elements on the host.
*/
void checkResult(float *hostRef, float *gpuRef, const int N)
{
double epsilon = 1.0E-8;
bool match = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (abs(hostRef[i] - gpuRef[i]) > epsilon)
{
match = 0;
printf("Arrays do not match!\n");
printf("host %5.2f gpu %5.2f at current %d\n", hostRef[i],
gpuRef[i], i);
break;
}
}
if (match) printf("Arrays match.\n\n");
return;
}
void initialData(float *ip, int size)
{
// generate different seed for random number
time_t t;
srand((unsigned) time(&t));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
ip[i] = (float)(rand() & 0xFF) / 10.0f;
}
return;
}
void sumArraysOnHost(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N)
{
for (int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++)
C[idx] = A[idx] + B[idx];
}
__global__ void sumArraysOnGPU(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
if (i < N) C[i] = A[i] + B[i];
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("%s Starting...\n", argv[0]);
// set up device
int dev = 0;
CHECK(cudaSetDevice(dev));
// set up data size of vectors
int nElem = 1 << 5;
printf("Vector size %d\n", nElem);
// malloc host memory
size_t nBytes = nElem * sizeof(float);
float *h_A, *h_B, *hostRef, *gpuRef;
h_A = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
h_B = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
hostRef = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
gpuRef = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
// initialize data at host side
initialData(h_A, nElem);
initialData(h_B, nElem);
memset(hostRef, 0, nBytes);
memset(gpuRef, 0, nBytes);
// malloc device global memory
float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_A, nBytes));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_B, nBytes));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_C, nBytes));
// transfer data from host to device
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_A, h_A, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_B, h_B, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_C, gpuRef, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
// invoke kernel at host side
dim3 block (nElem);
dim3 grid (1);
sumArraysOnGPU<<>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, nElem);
printf("Execution configure <<<%d, %d>>>\n", grid.x, block.x);
// copy kernel result back to host side
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(gpuRef, d_C, nBytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
// add vector at host side for result checks
sumArraysOnHost(h_A, h_B, hostRef, nElem);
// check device results
checkResult(hostRef, gpuRef, nElem);
// free device global memory
CHECK(cudaFree(d_A));
CHECK(cudaFree(d_B));
CHECK(cudaFree(d_C));
// free host memory
free(h_A);
free(h_B);
free(hostRef);
free(gpuRef);
CHECK(cudaDeviceReset());
return(0);
}
计时
#include "../common/common.h"
#include
#include
/*
* This example demonstrates a simple vector sum on the GPU and on the host.
* sumArraysOnGPU splits the work of the vector sum across CUDA threads on the
* GPU. Only a single thread block is used in this small case, for simplicity.
* sumArraysOnHost sequentially iterates through vector elements on the host.
* This version of sumArrays adds host timers to measure GPU and CPU
* performance.
*/
void checkResult(float *hostRef, float *gpuRef, const int N)
{
double epsilon = 1.0E-8;
bool match = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (abs(hostRef[i] - gpuRef[i]) > epsilon)
{
match = 0;
printf("Arrays do not match!\n");
printf("host %5.2f gpu %5.2f at current %d\n", hostRef[i],
gpuRef[i], i);
break;
}
}
if (match) printf("Arrays match.\n\n");
return;
}
void initialData(float *ip, int size)
{
// generate different seed for random number
time_t t;
srand((unsigned) time(&t));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
ip[i] = (float)( rand() & 0xFF ) / 10.0f;
}
return;
}
void sumArraysOnHost(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N)
{
for (int idx = 0; idx < N; idx++)
{
C[idx] = A[idx] + B[idx];
}
}
__global__ void sumArraysOnGPU(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < N) C[i] = A[i] + B[i];
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("%s Starting...\n", argv[0]);
// set up device
int dev = 0;
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp;
CHECK(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev));
printf("Using Device %d: %s\n", dev, deviceProp.name);
CHECK(cudaSetDevice(dev));
// set up data size of vectors
int nElem = 1 << 24;
printf("Vector size %d\n", nElem);
// malloc host memory
size_t nBytes = nElem * sizeof(float);
float *h_A, *h_B, *hostRef, *gpuRef;
h_A = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
h_B = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
hostRef = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
gpuRef = (float *)malloc(nBytes);
double iStart, iElaps;
// initialize data at host side
iStart = seconds();
initialData(h_A, nElem);
initialData(h_B, nElem);
iElaps = seconds() - iStart;
printf("initialData Time elapsed %f sec\n", iElaps);
memset(hostRef, 0, nBytes);
memset(gpuRef, 0, nBytes);
// add vector at host side for result checks
iStart = seconds();
sumArraysOnHost(h_A, h_B, hostRef, nElem);
iElaps = seconds() - iStart;
printf("sumArraysOnHost Time elapsed %f sec\n", iElaps);
// malloc device global memory
float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_A, nBytes));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_B, nBytes));
CHECK(cudaMalloc((float**)&d_C, nBytes));
// transfer data from host to device
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_A, h_A, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_B, h_B, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(d_C, gpuRef, nBytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
// invoke kernel at host side
int iLen = 512;
dim3 block (iLen);
dim3 grid ((nElem + block.x - 1) / block.x);
iStart = seconds();
sumArraysOnGPU<<>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, nElem);
CHECK(cudaDeviceSynchronize());
iElaps = seconds() - iStart;
printf("sumArraysOnGPU <<< %d, %d >>> Time elapsed %f sec\n", grid.x,
block.x, iElaps);
// check kernel error
CHECK(cudaGetLastError()) ;
// copy kernel result back to host side
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(gpuRef, d_C, nBytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
// check device results
checkResult(hostRef, gpuRef, nElem);
// free device global memory
CHECK(cudaFree(d_A));
CHECK(cudaFree(d_B));
CHECK(cudaFree(d_C));
// free host memory
free(h_A);
free(h_B);
free(hostRef);
free(gpuRef);
return(0);
}
nvprof
nvprof ./sumArraysOnGPU-timer