Java原生网络编程 ---- IO多路复用
Java是在jdk1.4引入支持NIO的库。前面博客说过BIO通讯,这种模式下服务端一个线程只处理一个会话。当线程被阻塞在read() 或 write()时,不能够做其他的事情。线程在服务器属于比较昂贵的资源。BIO的方式会造成很大的资源浪费。NIO,被称为IO多路复用,中心思想既是对服务器的线程进行复用,从而提高服务器资源利用的效率。
NIO组件
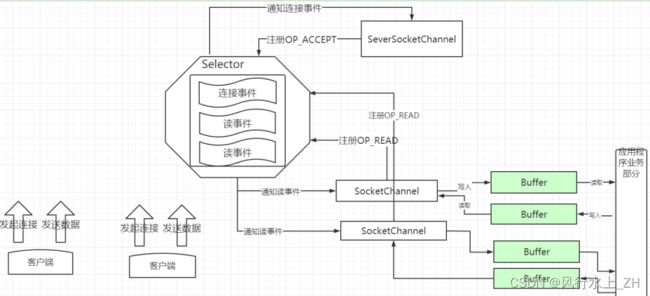
NIO有三大核心组件:Selector选择器、Channel管道、buffer缓冲区。以及一个重要概念SelectionKey。
Selector
Selector,即“选择器”也称为“轮询代理器”、“事件订阅器”、“channel容器管理机”。NIO通讯模型通过选择器,实现用一个线程监控多个通道。如,一个应用向Selector注册自己所关注的事件,到该事件到达时,Selecor将会通知到该应用。
Channel
Channel,用于进行数据交互的通道。当客户端与服务器建立连接时,服务器会建立一个SocketChannel用于与客户端进行通讯。在NIO编程的客户端,也是使用一个SocketChannel与服务器进行通讯。
Buffer
NIO与BIO其中一个不同点是,BIO是面向流的通讯,而NIO是面向缓冲器,既是这里的Buffer。NIO模型中应用通过Buffer与Channel进行交互。缓冲区分为写缓冲区和读缓冲区。Channel将数写入“写缓冲区”,应用从该缓冲区拿到数据,处理后的数据放入“读缓冲区”。Channel从该缓冲区读取数据后再发出去给客户端。
SelectionKey
SelectionKey是用于NIO组件向Selector注册所感兴趣事件。NIO定义了四种Key,分别是:OP_READ(读)、OP_WRITE(写)、OP_CONNECT(请求连接)、OP_ACCEPT(接受连接)。
OP_READ : 当读缓冲区有可读数据就绪时触发,注册该事件的组件会被调起进行数据处理。
OP_WRITE : 当写缓冲区有空闲时就绪。通常不会注册该事件,应用直接向缓冲区进行写入。针对写密集型的任务,缓冲区可能被占满,才会注册该事件,及时直到写缓冲区可用。
OP_CONNECT : 该事件提供给客户端使用,连接请求成功,客户端收到该事件。
OP_ACCEPT : 服务器ServerSocketChannel注册该事件,监听客户端的连接请求。当客户端连接请求到达时,服务器程序收到通知,通常会建一个SocketChannel用于处理与客户端的交互。
NIO工作流程
1、服务器ServerSocketChannel向Selector注册OP_ACCEPT事件;
2、客户端启动SocketChannel向服务器发起连接请求,并注册OP_CONNECT事件;
3、服务器收到客户端连接请求,由于ServerSocketChannel注册了OP_ACCEPT事件,则它响应的方法被执行,会启动一个SocketChannel,用于处理与客户端交互,该SocketChannel可以选择注册OP_READ、OP_WRITE事件,正常都会注册OP_READ,来监听发来的数据。
4、连接建立后,客户端收到OP_CONNECT的通知,则可以选择关注OP_READ、OP_WRITE事件。正常会注册OP_READ来监听发送给自己的数据。
5、客户端与服务器端开始相互发送消息,根据注册的OP_READ、OP_WRITE事件完成数据的传递。
NIO实现
客户端:
private void connectServer() {
selector = Selector.open(); // 获取选择器
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); // 获得SocketChannel
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 设置通道为非阻塞模式
//connect方法时非阻塞的,会立即返回
//返回true,表示连接完成;返回fasle,表示连接没完成,可能还在三次握手建立连接中
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))) {
// 连接成功,注册OP_READ事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else {
// 连接尚未成功,注册OP_CONNECT,关注连接建立的事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
private void startWorking() {
// 开启循环监听selector的事件
while (isWorking) {
selector.select(1000); // 设置每1s唤醒一次
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleKey(key);
}
}
}
// 事件处理
private void handleKey(SelectionKey key) {
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
//连接事件
if (key.isConnectable()) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//读事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 获得关心当前事件的channel
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int readBytes = sc.read(buffer);
if (readBytes >= 0) {
// 进行数据读取
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String result = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
} else {
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}
}
}
服务端:
public doConnect(int port) {
selector = Selector.open();
serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 向selector注册关注连接事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
private void startWorking() {
while (isWorking) {
selector.select(1000);
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleInput(key);
}
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) {
if (!key.isValid()) {
return;
}
// 处理连接请求事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 读数据事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(buffer);
if (readBytes >= 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBytes];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
String result = response(message);
doWrite(sc, result);
} else {
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel sc, String result) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = result.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
}