- 一篇文章了解IntentService的工作原理
ljingya
IntentService简介:继承自Service,可以做耗时任务的Service。使用创建Service继承IntentService创建MyIntentService继承IntentService,实现onHandleIntent方法。publicclassMyIntentServiceextendsIntentService{privateStringTAG=getClass().getS
- Android中的异步处理技术之IntentService
itfitness
目录定义IntentService为Service的子类,它能够进行耗时任务。原理IntentService具有和Service一样的生命周期,同时提供了在后台线程中处理异步任务的机制,与HandlerThread类似,IntentService也是在一个后台线程中顺序执行所有任务,我们通过给Context.startService传递一个Intent类型的参数可以启动IntentService的
- Android基础(24)多线程(二)IntentService
perry_Fan
1)IntentService问题1:IntentService如何单独开启一个新的工作线程?//IntentService源码中的onCreate()方法@OverridepublicvoidonCreate(){super.onCreate();//HandlerThread继承自Thread,内部封装了Looper//通过实例化andlerThread新建线程并启动//所以使用IntentS
- 京东android面试题(2018 顶级互联网公司面试题系列)
40岁资深老架构师尼恩
java
以下来自于北京的一个兄弟的面试题1.静态内部类和非静态内部类有什么区别2.谈谈你对java多态的理解3.如何开启线程,run和runnable有什么区别4.线程池的好处5.说一下你知道的设计模式有哪些,介绍下适配器模式6.android四大组件,Activity启动模式,广播有哪些类型,app内广播原理7.IntentService和Service有什么区别8.AIDL9.内存优化疯狂创客圈:如果
- IntentService的使用
Yangxy_Lazy
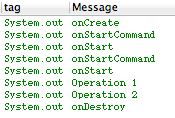
网络请求中的注意事项:1、在网络请求的调试过程中,不要单步运行,因为这是一个异步才做,单步调试不能走到请求里面,需要设置多个断点,进行调试。四、IntentService的使用:1、为什么要用IntentService:Service的回调方法(onCreate,onStartCommand,onBind,onDestroy)都是运行在主线程的,通过startService启动Service之后,
- 72.sleep和wait的区别
SlideException
/***每天一个知识点day72TODOsleep()和wait()的区别、IntentService**sleep()和wait()的区别*1.sleep是线程方法,wait是Object方法*2.sleep不会释放锁,wait会释放锁,并且加入等待队列。*3.sleep方法不需要依赖于synchronized,wait方法需要依赖于synchronized。*4.sleep不需要被唤醒,在休眠
- Android多线程开启如何选择
工程师丶佛爷
原创android
目录前言AsyncTask分析总结HandlerThread推荐分析总结Service和IntentService分析总结RxJava/RxAndroid分析总结Kotlin协程推荐分析总结Executor推荐分析总结前言线程开启方式取决于你的应用程序需求和场景。在Android开发中,有几种常用的线程开启方式AsyncTask分析印象里面很多人说AsyncTask是有内存泄漏的,静态内部类没有回
- Service.onStartCommand()返回值
使劲挤海绵
onStartCommand()方法必须返回一个整数,这个整数是一个描述了在系统的杀死事件中,系统应该如何继续这个服务的值(虽然你能够修改这个值,但是IntentService处理还是为你提供了默认实现)。从onStartCommand()方法中返回的值必须是以下常量:START_NOT_STICKY如果系统在onStartCommand()方法返回之后杀死这个服务,那么直到接受到新的Intent
- Servicec-IntentSercice
Yison_a169
好处:1.不需要开线程,IntentService自带线程,且不在主线程中;2.只需要处理onHandleIntent()方法;3.自己stop(),不需要调用stopservice()使用场景主要适用于单线程完成某项任务,完成后自动关闭service优点可以个性化封装线程和操作用法/源码https://www.jianshu.com/p/332b6daf91f0
- 我要做 Android 之要点总结
Jiwenjie
Q:开启一个线程的方法有哪些?销毁一个线程的方法呢?直接使用Thread类。使用Runnable和Thread。使用Runnable和线程池。使用AsyncTask。使用HandlerThread。使用IntentService。直接使用Thread类开启子线程这是最简单开启子线程的方法,也是最本质的方法,其他开启子线程的方法都是在此方法基础上的扩展。一,使用示例如下:newThread(){@O
- Android 认知与理解Service(二)
LovingMy
AndroidService基础知识点IntentService概念IntentService是Android里面的一个封装类,继承自四大组件之一的Service特性在后台执行耗时的异步任务,当任务完成后会自动销毁拥有较高的优先级,不易被系统杀死(继承自Service的缘故),因此比较适合执行一些高优先级的异步任务内部通过HandlerThread和Handler实现异步操作创建IntentSer
- Android 进阶解密阅读笔记5
jkwen
接上篇Android进阶解密阅读笔记4内容,以下代码是基于API28版本进行的分析,分析思路还是参阅的「Android进阶解密」,不过书上好像有个小错误,所以我就参照着书本做的分析。//ActiveServicesintbindServiceLocked(IApplicationThreadcaller,IBindertoken,Intentservice,StringresolvedType,f
- [Android] bindService的binder通信过程分析
aaajj
Android
关于bindService方法publicclassContextWrapperextendsContext{ContextmBase;publicContextWrapper(Contextbase){mBase=base;}publicbooleanbindService(Intentservice,ServiceConnectionconn,intflags){returnmBase.bin
- Android Studio的代码笔记--IntentService学习
新手上路狂踩坑
Androidandroidstudio笔记学习javaandroid
IntentService学习IntentService常规用法清单注册服务服务内容开启服务IntentService一个HandlerThread工作线程,通过Handler实现把消息加入消息队列中等待执行,通过传递的intent在onHandleIntent中处理任务。(多次调用会按顺序执行事件,服务停止清除消息队列中的消息。)适用:线程任务按顺序在后台执行,例如下载不适用:多个数据同时请求1
- Android启动优化实践
游侠_6fb7
Android启动主要优化点1、Application初始化的一些动作挪到IntentService;2、SP存储优化3、layout优化4、与UI无关的操作可挪到IdleHandler5、减少dex,gradledependencies分析依赖优化工具AS+Debug.startMethodTracing("trace")Debug.stopMethodTracing()从对应的/mnt/sdc
- 多线程和线程池
lanxuan1993
Adroid面试题android
子线程Android的线程主要分为主线程和子线程两类,主线程主要处理和界面相关的工作,子线程主要处理耗时操作。除Thread之外,Android中还有其他扮演线程的角色如AsyncTask、IntentService、HandleThread,其中AsyncTask的底层用到了线程池,IntentService和HandleThread的底层直接使用了线程。AsyncTask内部封装了线程池和Ha
- 【Android】IntentService
nor1take
Androidandroid
Service中的代码都是默认运行在主线程当中的,如果直接在Service里处理一些耗时的逻辑,就很容易出现ANR(ApplicationNotResponding)的情况。所以,我们应该在Service的每个具体的方法里开启一个子线程,然后在这里处理那些耗时的逻辑。但是,这种Service一旦启动,就会一直处于运行状态,必须调用stopService()或stopSelf()方法,或者被系统回收
- Android异步之旅:探索IntentService
Hdnw
AndroidandroidIntentService
1.介绍IntentServiceIntentService是Android中的一个Service类,用于在后台执行耗时操作,而不会阻塞UI线程。它封装了HandlerThread和Handler,使得我们可以方便地在后台执行任务,而不需要自己管理线程和消息处理。以下是IntentService的主要特点和用法:自动停止:当所有的请求都被处理完毕后,IntentService会自动停止,无需手动调
- Android中的特殊线程——IntentService
Samuel_Tom
IntentService是什么IntentService是特殊的Service,继承于Service,内部封装了Handler和HandlerThread,可以执行耗时的后台任务,同时由于IntentService是一个Service服务,所以它的优先级比普通的线程要高,因此可用于执行一些优先级比较高的耗时任务。当耗时任务执行完成之后,IntentService会自动停止,不需要跟Service
- IntentService与普通Service的区别
lostfish123
AndroidAndroidIntentService
1.onCreate在IntentService的onCreate方法里:创建HandlerThread创建ServiceHandler,所以发送消息给ServiceHandler的话,事件将会在HandlerThread上处理。publicabstractclassIntentServiceextendsService{privatevolatileLoopermServiceLooper;pr
- Android多线程的四种方式:Handler、AsyncTask、ThreadPoolExector、IntentService
break妖
Androidandroid前端面试多线程java
1.Handler(适用于多个异步任务的更新UI)采用生产者-消费者模型,Handler就是生产者,通过他可以生产需要执行的任务,Looper就是消费者,不断从MessageQueue中取出message进行消费。异步通信机制,将工作线程中需更新UI的操作信息传递到UI主线程,从而实现工作线程对UI的更新处理,最终实现异步消息的处理。Handler不仅仅能将子线程的数据传递给主线程,它能实现任意两
- IntentServic
昨天剩下的一杯冷茶
这个例子是在我上一篇文章的基础上修改的Service启动和停止https://www.jianshu.com/p/760a7a61bcd0Layout新建一个类集成IntentServicpackagecom.example.hzx.myservice;importandroid.app.IntentService;importandroid.content.Intent;importandroi
- 安卓intentService源码
勤能不能补拙
IntentService是handlerThread与Service的结合,因为实质是串行的执行,所以该service不适合执行频繁的网络请求类型的操作,但是他是一个用完自动停止的service,并且减轻主线程looper的压力,所以非常适合做一些非及时性的耗时操作,如后台数据统计等.用法创建一个intentService,模拟一个耗时操作,发送一个广播到uipublicclassMyInten
- 如何检查服务是否在Android上运行?
asdfgh0077
androidandroid-service
如何检查后台服务是否正在运行?我想要一个可切换服务状态的Android活动-它可以让我在关闭状态下将其打开,在开启状态下将其关闭。#1楼这更适用于IntentService调试,因为它们会生成线程,但也可能适用于常规服务。我发现这个线程归功于Binging就我而言,我与调试器一起玩耍并找到了线程视图。看起来有点像MSWord中的项目符号图标。无论如何,您不必处于调试器模式即可使用它。单击该过程,然
- Android App卡顿慢优化之多线程优化
apple_51426592
大数据
本博客涉及的内容有:多线程并发的性能问题,介绍了AsyncTask,HandlerThread,IntentService与ThreadPool分别适合的使用场景以及各自的使用注意事项,这是一篇了解Android多线程编程不可多得的基础文章,清楚的了解这些Android系统提供的多线程基础组件之间的差异以及优缺点,才能够在项目实战中做出最恰当的选择。1)ThreadingPerformance(线
- Service、IntentService
justin_crashed
Service是android中四大组件之一,用于处理后台任务,不能处理耗时任务,否则会造成ANR而IntentService继承自Service,但是可以处理耗时任务,因为在内部开启了一个子线程。Service生命周期Service的生命周期分为两种情形,一种是通过startService启动,另一种是通过bindService启动。在这两种情况下时,Service的生命周期是有差异的。star
- 我的android多线程编程之路(1)之经验详解,源码分析
say_from_wen
android多线程android多线程源码经验编程
写在伊始android开发这么久了,对于多线程这块一直处于似懂非懂的神奇状态,今天总结出来,分享一下,希望大家多多指正。共同交流,恳望得到您的建议。本文简介本文会基于自己在开发中对于线程这块的实际使用,大概从线程进程的概念,线程的创建(Thread和Runnable)和使用,线程的各个方法的介绍,线程池的介绍等,及Handler,AsyncTask,IntentService及现在使用的RxJav
- 第一行代码笔记⑨
Dominiczz
android笔记androidandroidstudio
第一行代码笔记⑨9.1服务是什么9.2Android多线程编程1在子线程中更新UI2解析异步消息处理机制3使用AsyncTask9.3服务的基本用法定义一个服务启动和停止服务活动和服务进行通信9.4服务的生命周期9.5服务的更多技巧前台服务使用IntentService后台默默的劳动者——探究服务9.1服务是什么服务(Service)是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,它非常适合去执行那
- Android ANR、内存泄漏、内存溢出、内存抖动
Stride.Xue
Androidjava
ANRANR(Applicatinonotresponding)是指程序无响应,主要原因为:1主线程被io操作阻塞(4.0后网络io不允许主线程中)。2主线程做了耗时任务超过5秒。3Service做了耗时操作超过20秒,这是由于service默认执行在主线程,可以使用IntentService。4BroadcastReceiver的onReciver做了耗时操作超过10秒。解决方式:1开一个子线程
- service理解
我想做个程序猿
关于service的理解经过start启动的service由独立的生命周期,不依赖该组件。多次调用start会多次调用onStartCommand,start启动的service必须通过调用stopService或者stopSelf来停止service(intentservice会自动调用stopself)多次调用onbind只会调用一次onBindbind绑定的service依赖于组件,组建销毁
- 如何用ruby来写hadoop的mapreduce并生成jar包
wudixiaotie
mapreduce
ruby来写hadoop的mapreduce,我用的方法是rubydoop。怎么配置环境呢:
1.安装rvm:
不说了 网上有
2.安装ruby:
由于我以前是做ruby的,所以习惯性的先安装了ruby,起码调试起来比jruby快多了。
3.安装jruby:
rvm install jruby然后等待安
- java编程思想 -- 访问控制权限
百合不是茶
java访问控制权限单例模式
访问权限是java中一个比较中要的知识点,它规定者什么方法可以访问,什么不可以访问
一:包访问权限;
自定义包:
package com.wj.control;
//包
public class Demo {
//定义一个无参的方法
public void DemoPackage(){
System.out.println("调用
- [生物与医学]请审慎食用小龙虾
comsci
生物
现在的餐馆里面出售的小龙虾,有一些是在野外捕捉的,这些小龙虾身体里面可能带有某些病毒和细菌,人食用以后可能会导致一些疾病,严重的甚至会死亡.....
所以,参加聚餐的时候,最好不要点小龙虾...就吃养殖的猪肉,牛肉,羊肉和鱼,等动物蛋白质
- org.apache.jasper.JasperException: Unable to compile class for JSP:
商人shang
maven2.2jdk1.8
环境: jdk1.8 maven tomcat7-maven-plugin 2.0
原因: tomcat7-maven-plugin 2.0 不知吃 jdk 1.8,换成 tomcat7-maven-plugin 2.2就行,即
<plugin>
- 你的垃圾你处理掉了吗?GC
oloz
GC
前序:本人菜鸟,此文研究学习来自网络,各位牛牛多指教
1.垃圾收集算法的核心思想
Java语言建立了垃圾收集机制,用以跟踪正在使用的对象和发现并回收不再使用(引用)的对象。该机制可以有效防范动态内存分配中可能发生的两个危险:因内存垃圾过多而引发的内存耗尽,以及不恰当的内存释放所造成的内存非法引用。
垃圾收集算法的核心思想是:对虚拟机可用内存空间,即堆空间中的对象进行识别
- shiro 和 SESSSION
杨白白
shiro
shiro 在web项目里默认使用的是web容器提供的session,也就是说shiro使用的session是web容器产生的,并不是自己产生的,在用于非web环境时可用其他来源代替。在web工程启动的时候它就和容器绑定在了一起,这是通过web.xml里面的shiroFilter实现的。通过session.getSession()方法会在浏览器cokkice产生JESSIONID,当关闭浏览器,此
- 移动互联网终端 淘宝客如何实现盈利
小桔子
移動客戶端淘客淘寶App
2012年淘宝联盟平台为站长和淘宝客带来的分成收入突破30亿元,同比增长100%。而来自移动端的分成达1亿元,其中美丽说、蘑菇街、果库、口袋购物等App运营商分成近5000万元。 可以看出,虽然目前阶段PC端对于淘客而言仍旧是盈利的大头,但移动端已经呈现出爆发之势。而且这个势头将随着智能终端(手机,平板)的加速普及而更加迅猛
- wordpress小工具制作
aichenglong
wordpress小工具
wordpress 使用侧边栏的小工具,很方便调整页面结构
小工具的制作过程
1 在自己的主题文件中新建一个文件夹(如widget),在文件夹中创建一个php(AWP_posts-category.php)
小工具是一个类,想侧边栏一样,还得使用代码注册,他才可以再后台使用,基本的代码一层不变
<?php
class AWP_Post_Category extends WP_Wi
- JS微信分享
AILIKES
js
// 所有功能必须包含在 WeixinApi.ready 中进行
WeixinApi.ready(function(Api) {
// 微信分享的数据
var wxData = {
&nb
- 封装探讨
百合不是茶
JAVA面向对象 封装
//封装 属性 方法 将某些东西包装在一起,通过创建对象或使用静态的方法来调用,称为封装;封装其实就是有选择性地公开或隐藏某些信息,它解决了数据的安全性问题,增加代码的可读性和可维护性
在 Aname类中申明三个属性,将其封装在一个类中:通过对象来调用
例如 1:
//属性 将其设为私有
姓名 name 可以公开
- jquery radio/checkbox change事件不能触发的问题
bijian1013
JavaScriptjquery
我想让radio来控制当前我选择的是机动车还是特种车,如下所示:
<html>
<head>
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js" type="text/javascript"><
- AngularJS中安全性措施
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS安全性XSRFJSON漏洞
在使用web应用中,安全性是应该首要考虑的一个问题。AngularJS提供了一些辅助机制,用来防护来自两个常见攻击方向的网络攻击。
一.JSON漏洞
当使用一个GET请求获取JSON数组信息的时候(尤其是当这一信息非常敏感,
- [Maven学习笔记九]Maven发布web项目
bit1129
maven
基于Maven的web项目的标准项目结构
user-project
user-core
user-service
user-web
src
- 【Hive七】Hive用户自定义聚合函数(UDAF)
bit1129
hive
用户自定义聚合函数,用户提供的多个入参通过聚合计算(求和、求最大值、求最小值)得到一个聚合计算结果的函数。
问题:UDF也可以提供输入多个参数然后输出一个结果的运算,比如加法运算add(3,5),add这个UDF需要实现UDF的evaluate方法,那么UDF和UDAF的实质分别究竟是什么?
Double evaluate(Double a, Double b)
- 通过 nginx-lua 给 Nginx 增加 OAuth 支持
ronin47
前言:我们使用Nginx的Lua中间件建立了OAuth2认证和授权层。如果你也有此打算,阅读下面的文档,实现自动化并获得收益。SeatGeek 在过去几年中取得了发展,我们已经积累了不少针对各种任务的不同管理接口。我们通常为新的展示需求创建新模块,比如我们自己的博客、图表等。我们还定期开发内部工具来处理诸如部署、可视化操作及事件处理等事务。在处理这些事务中,我们使用了几个不同的接口来认证:
&n
- 利用tomcat-redis-session-manager做session同步时自定义类对象属性保存不上的解决方法
bsr1983
session
在利用tomcat-redis-session-manager做session同步时,遇到了在session保存一个自定义对象时,修改该对象中的某个属性,session未进行序列化,属性没有被存储到redis中。 在 tomcat-redis-session-manager的github上有如下说明: Session Change Tracking
As noted in the &qu
- 《代码大全》表驱动法-Table Driven Approach-1
bylijinnan
java算法
关于Table Driven Approach的一篇非常好的文章:
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/42732/Table-driven-Approach
package com.ljn.base;
import java.util.Random;
public class TableDriven {
public
- Sybase封锁原理
chicony
Sybase
昨天在操作Sybase IQ12.7时意外操作造成了数据库表锁定,不能删除被锁定表数据也不能往其中写入数据。由于着急往该表抽入数据,因此立马着手解决该表的解锁问题。 无奈此前没有接触过Sybase IQ12.7这套数据库产品,加之当时已属于下班时间无法求助于支持人员支持,因此只有借助搜索引擎强大的
- java异常处理机制
CrazyMizzz
java
java异常关键字有以下几个,分别为 try catch final throw throws
他们的定义分别为
try: Opening exception-handling statement.
catch: Captures the exception.
finally: Runs its code before terminating
- hive 数据插入DML语法汇总
daizj
hiveDML数据插入
Hive的数据插入DML语法汇总1、Loading files into tables语法:1) LOAD DATA [LOCAL] INPATH 'filepath' [OVERWRITE] INTO TABLE tablename [PARTITION (partcol1=val1, partcol2=val2 ...)]解释:1)、上面命令执行环境为hive客户端环境下: hive>l
- 工厂设计模式
dcj3sjt126com
设计模式
使用设计模式是促进最佳实践和良好设计的好办法。设计模式可以提供针对常见的编程问题的灵活的解决方案。 工厂模式
工厂模式(Factory)允许你在代码执行时实例化对象。它之所以被称为工厂模式是因为它负责“生产”对象。工厂方法的参数是你要生成的对象对应的类名称。
Example #1 调用工厂方法(带参数)
<?phpclass Example{
- mysql字符串查找函数
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
FIND_IN_SET(str,strlist)
假如字符串str 在由N 子链组成的字符串列表strlist 中,则返回值的范围在1到 N 之间。一个字符串列表就是一个由一些被‘,’符号分开的自链组成的字符串。如果第一个参数是一个常数字符串,而第二个是type SET列,则 FIND_IN_SET() 函数被优化,使用比特计算。如果str不在strlist 或st
- jvm内存管理
easterfly
jvm
一、JVM堆内存的划分
分为年轻代和年老代。年轻代又分为三部分:一个eden,两个survivor。
工作过程是这样的:e区空间满了后,执行minor gc,存活下来的对象放入s0, 对s0仍会进行minor gc,存活下来的的对象放入s1中,对s1同样执行minor gc,依旧存活的对象就放入年老代中;
年老代满了之后会执行major gc,这个是stop the word模式,执行
- CentOS-6.3安装配置JDK-8
gengzg
centos
JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_45
JRE_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre
PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin
CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JRE_HOME/lib
export JAVA_HOME
- 【转】关于web路径的获取方法
huangyc1210
Web路径
假定你的web application 名称为news,你在浏览器中输入请求路径: http://localhost:8080/news/main/list.jsp 则执行下面向行代码后打印出如下结果: 1、 System.out.println(request.getContextPath()); //可返回站点的根路径。也就是项
- php里获取第一个中文首字母并排序
远去的渡口
数据结构PHP
很久没来更新博客了,还是觉得工作需要多总结的好。今天来更新一个自己认为比较有成就的问题吧。 最近在做储值结算,需求里结算首页需要按门店的首字母A-Z排序。我的数据结构原本是这样的:
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[sid] => 2885842
[recetcstoredpay] =&g
- java内部类
hm4123660
java内部类匿名内部类成员内部类方法内部类
在Java中,可以将一个类定义在另一个类里面或者一个方法里面,这样的类称为内部类。内部类仍然是一个独立的类,在编译之后内部类会被编译成独立的.class文件,但是前面冠以外部类的类名和$符号。内部类可以间接解决多继承问题,可以使用内部类继承一个类,外部类继承一个类,实现多继承。
&nb
- Caused by: java.lang.IncompatibleClassChangeError: class org.hibernate.cfg.Exten
zhb8015
maven pom.xml关于hibernate的配置和异常信息如下,查了好多资料,问题还是没有解决。只知道是包冲突,就是不知道是哪个包....遇到这个问题的分享下是怎么解决的。。
maven pom:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<ar
- Spark 性能相关参数配置详解-任务调度篇
Stark_Summer
sparkcachecpu任务调度yarn
随着Spark的逐渐成熟完善, 越来越多的可配置参数被添加到Spark中来, 本文试图通过阐述这其中部分参数的工作原理和配置思路, 和大家一起探讨一下如何根据实际场合对Spark进行配置优化。
由于篇幅较长,所以在这里分篇组织,如果要看最新完整的网页版内容,可以戳这里:http://spark-config.readthedocs.org/,主要是便
- css3滤镜
wangkeheng
htmlcss
经常看到一些网站的底部有一些灰色的图标,鼠标移入的时候会变亮,开始以为是js操作src或者bg呢,搜索了一下,发现了一个更好的方法:通过css3的滤镜方法。
html代码:
<a href='' class='icon'><img src='utv.jpg' /></a>
css代码:
.icon{-webkit-filter: graysc