STL algorithm算法lower_bound和upper_bound(31)
lower_bound原型:
function template
<algorithm>
std::lower_bound
| default (1) | template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val);
|
|---|---|
| custom (2) | template <class ForwardIterator, class T, class Compare>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val, Compare comp); |
假设序列中的值都小于val,则返回last.
序列应该已经有序!
使用operator<来比較两个元素的大小。
该函数优化了比較非连续存储序列的比較次数。
其行为类似于:
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = distance(first,last);
while (count>0)
{
it = first; step=count/2; advance (it,step);
if (*it<val) { // or: if (comp(*it,val)), for version (2)
first=++it;
count-=step+1;
}
else count=step;
}
return first;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(int argv,char **argc)
{
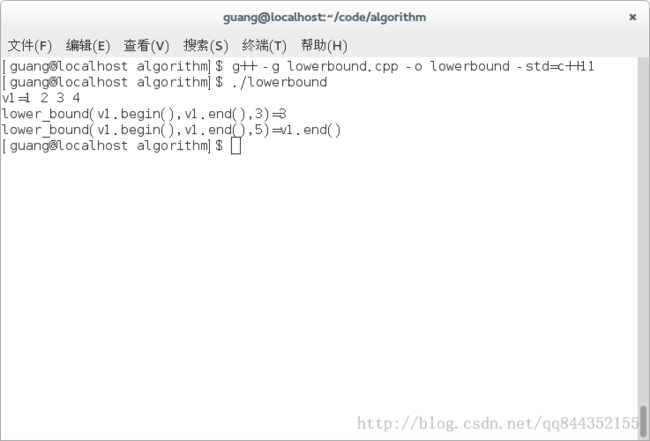
vector<int> v1{1,2,3,4};
cout<<"v1=";
for(int i:v1)
cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<endl;
auto it=lower_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),3);
cout<<"lower_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),3)="<<*it<<endl;
auto it2=lower_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),5);
if(it2==v1.end())
cout<<"lower_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),5)=v1.end()"<<endl;
else
cout<<"lower_bound(v1.begin(),v1.end(),5)="<<*it2<<endl;
}
执行截图:
upper_bound原型:
function template
<algorithm>
std::upper_bound
| default (1) | template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val);
|
|---|---|
| custom (2) | template <class ForwardIterator, class T, class Compare>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val, Compare comp); |
该函数返回范围内第一个大于指定val的值。
假设序列中的值都小于val,则返回last.
序列应该已经有序!
使用operator<来比較两个元素的大小。
该函数优化了比較非连续存储序列的比較次数。
其行为类似于:
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = std::distance(first,last);
while (count>0)
{
it = first; step=count/2; std::advance (it,step);
if (!(val<*it)) // or: if (!comp(val,*it)), for version (2)
{ first=++it; count-=step+1; }
else count=step;
}
return first;
}
// lower_bound/upper_bound example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::lower_bound, std::upper_bound, std::sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
int main () {
int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20};
std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20
std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30
std::vector<int>::iterator low,up;
low=std::lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
up= std::upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^
std::cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << '\n';
std::cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << '\n';
return 0;
}执行结果:
lower_bound和upper_bound返回的值刚好是equal_range相应的两个值!
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//写的错误或者不好的地方请多多指导,能够在以下留言或者点击左上方邮件地址给我发邮件,指出我的错误以及不足,以便我改动,更好的分享给大家,谢谢。
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq844352155
author:天下无双
Email:[email protected]
2014-9-17
于GDUT
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————