分析函数调用过程栈的布局(stack frame layout)
int add(int x, int y)
{
int res = x + y;
return res;
}
int main()
{
add(1, 2);
return 0;
}
平台:x86,Ubuntu14.10
gcc -S -m32 -masm=intel add.c -o add.s
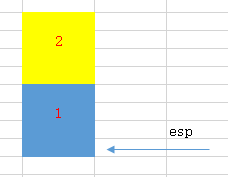
1. 将1和2推到栈中
push 2 push 1
注:图中上面的位置是内存高地址,是the bottom of stack;下面的位置是内存低地址,是the top of stack。栈增长的方向是从内存高地址到内存低地址。
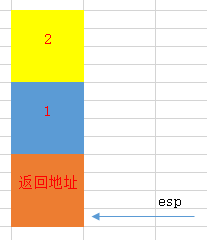
2. 调用函数add
call add
call指令会把call后的下一条指令的地址(eip)压入栈中,即add函数的返回地址压入栈中。
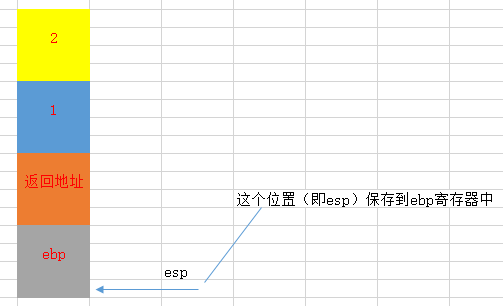
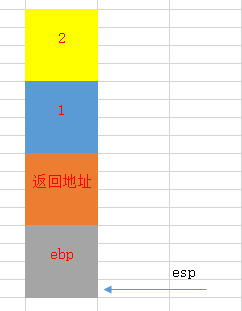
3. 保存上一个函数栈帧的开始位置到栈中,并保存当前esp位置到ebp中
push ebp mov ebp, esp
4. 若函数要用局部变量,则要在堆栈中开辟点空间
sub esp, 16
5. 具体的逻辑运算
; 将[ebp+8],即1送到edx寄存器 mov edx, DWORD PTR [ebp+8] ; 将[ebp+12],即2送到eax寄存器 mov eax, DWORD PTR [ebp+12] ; 将edx值加到eax中,eax的值变为3 add eax, edx ; 将eax的值送到[ebp-4],如下图所示 mov DWORD PTR [ebp-4], eax ; 将[ebp-4]中的值送到eax寄存器中,以便执行ret后还能访问 mov eax, DWORD PTR [ebp-4]
6. 恢复堆栈指针
leave
leave相当于:
mov esp, ebp pop ebp
步骤一、
步骤二、
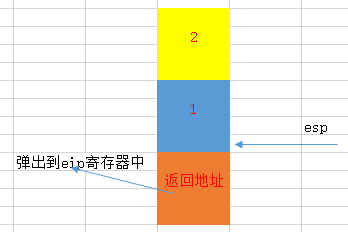
7. 执行return操作
ret
ret指令将call下一条指令的地址(调用call时存放在栈中)从栈中弹出到eip寄存器中。
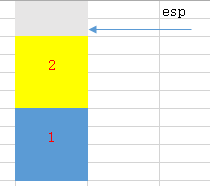
8. 收尾,保持堆栈平衡
add esp, 8
附:完整的汇编代码
.file "add.c" .intel_syntax noprefix .text .globl add .type add, @function add: .LFB0: .cfi_startproc push ebp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 8 .cfi_offset 5, -8 mov ebp, esp .cfi_def_cfa_register 5 sub esp, 16 mov edx, DWORD PTR [ebp+8] mov eax, DWORD PTR [ebp+12] add eax, edx mov DWORD PTR [ebp-4], eax mov eax, DWORD PTR [ebp-4] leave .cfi_restore 5 .cfi_def_cfa 4, 4 ret .cfi_endproc .LFE0: .size add, .-add .globl main .type main, @function main: .LFB1: .cfi_startproc push ebp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 8 .cfi_offset 5, -8 mov ebp, esp .cfi_def_cfa_register 5 push 2 push 1 call add add esp, 8 mov eax, 0 leave .cfi_restore 5 .cfi_def_cfa 4, 4 ret .cfi_endproc .LFE1: .size main, .-main .ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 4.9.1-16ubuntu6) 4.9.1" .section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
来自为知笔记(Wiz)
附件列表