EF里查看/修改实体的当前值、原始值和数据库值以及重写SaveChanges方法记录实体状态
EF里查看/修改实体的当前值、原始值和数据库值以及重写SaveChanges方法记录实体状态
本文目录
- 查看实体当前、原始和数据库值:DbEntityEntry
- 查看实体的某个属性值:GetValue<TValue>方法
- 拷贝DbPropertyValues到实体:ToObject方法
- 修改DbPropertyValues当前值:索引器
- 克隆实体:Clone方法
- 设置实体的值:SetValues方法
- 克隆实体:SetValues
- 获取和设置实体的单个属性:Property方法
- 查询实体的属性是否被修改:IsModified方法
- 修改导航属性
- 重新加载实体:Reload方法
- 读取相关联的实体和状态:DbContext.ChangeTracker.Entries方法
- EF里如何解决更新时的冲突
- 重写上下文的SaveChanges方法记录结果集里实体的各种增/删/改
- 本源源码和系列文章导航
文章开始前建议大家为了更好的记忆最好自己实现文中的所有方法。如果非要直接运行我的demo,必要的时候需要恢复下数据库数据,否则找不到记录。
之前的章节已经演示了context.Entry方法可以拿到实体的状态(EntityState),我们看一个方法:
/// <summary> /// 单个实体的状态 /// </summary> private static void PrintState() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Grand Canyon" select d).Single(); DbEntityEntry<DbContexts.Model.Destination> entry = context.Entry(canyon); Console.WriteLine("Before Edit:{0}", entry.State); //Unchaged canyon.TravelWarnings = "Take a lot of Water!"; DbEntityEntry<DbContexts.Model.Destination> entrys = context.Entry(canyon);
Console.WriteLine("After Edit:{0}", entrys.State); //Modified } }
context.Entry方法有两个重载,分别返回泛型DbEntityEntry<TEntity>和非泛型的DbEntityEntry,它们都可以监测到实体的状态,并且通过DbEntityEntry还可以操作实体的当前值、原始值和数据库值。他们分别是:
- 当前值(Current Value):当前设置实体属性的值;
- 原始值(Original Value):刚被数据库上下文跟踪到时的值;
- 数据库值(Database Value):存在数据库里的值
来看一个例子:
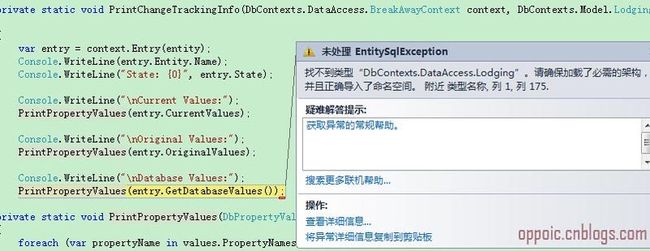
/// <summary> /// 打印实体当前、原始和数据库值 /// </summary> private static void PrintLodgingInfo() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); hotel.Name = "Super Grand Hotel"; context.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(@"UPDATE Lodgings SET Name = 'Not-So-Grand Hotel' WHERE Name = 'Grand Hotel'"); PrintChangeTrackingInfo(context, hotel); } } private static void PrintChangeTrackingInfo(DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext context, DbContexts.Model.Lodging entity) { var entry = context.Entry(entity); Console.WriteLine(entry.Entity.Name); Console.WriteLine("State: {0}", entry.State); Console.WriteLine("\nCurrent Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues); Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.OriginalValues); Console.WriteLine("\nDatabase Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.GetDatabaseValues()); } private static void PrintPropertyValues(DbPropertyValues values) { foreach (var propertyName in values.PropertyNames) { Console.WriteLine(" - {0}: {1}", propertyName, values[propertyName]); } }
方法分析:先从数据库取出一个实体,然后修改其Name属性,这个时候当前值(Current)和原始值(Original)都有了,分别是:修改后的值(还没提交,在内存中)和从库里取出来时实体的值。再使用Database.ExecuteSqlCommand执行了一段修改此对象在数据库中的值,这个时候数据库值(Database)也有了变化,这个实体的三个值都不相同了。还没看到打印结果,在执行entry.GetDatabaseValues()方法时报了一个EntitySqlException错:
找不到类型DbContexts.DataAccess.Lodging,项目的Lodging实体明明在DbContexts.Model.Lodging命名空间下,反复检查代码没发现任何问题,报这个错真是很疑惑。最后通过搜索引擎才知道这是EF4.1版本的一个bug,解决办法:修改实体和上下文到一个命名空间,或者使用EF4.3 release。看看本书作者Julie Lerman在msdn论坛上关于此bug的回复
换成4.3版本的EF问题就立马解决了(源码的libs目录下提供了EF4.3)。看下打印的结果:
结果分析:当前值为方法里修改的值、原始值是从数据库取出未做任何操作的值、数据库值是此时数据库里的值。当然新添加的实体不会有原始值和数据库值、删除的实体也不会有当前值,我们利用EntityState完善下方法:
private static void PrintChangeTrackingInfo(DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext context, DbContexts.Model.Lodging entity) { var entry = context.Entry(entity); Console.WriteLine(entry.Entity.Name); Console.WriteLine("State: {0}", entry.State); if (entry.State != EntityState.Deleted) //标记删除的实体不会有当前值 { Console.WriteLine("\nCurrent Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues); } if (entry.State != EntityState.Added) //新添加的时候不会有原始值和数据库值 { Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.OriginalValues); Console.WriteLine("\nDatabase Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.GetDatabaseValues()); } }
为了测试,我们重写下PrintLodgingInfo方法:
/// <summary> /// 测试打印添加和删除时实体当前、原始和数据库值 /// </summary> private static void PrintLodgingInfoAddAndDelete() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); PrintChangeTrackingInfo(context, hotel); //默认 var davesDump = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Dave's Dump" select d).Single(); context.Lodgings.Remove(davesDump); PrintChangeTrackingInfo(context, davesDump); //测试删除实体 var newMotel = new DbContexts.Model.Lodging { Name = "New Motel" }; context.Lodgings.Add(newMotel); PrintChangeTrackingInfo(context, newMotel); //测试新添加实体 } }
当然上面打印实体类型的方法并不通用,我们修改第二个参数为object类型:
/// <summary> /// 通用的打印实体方法 /// </summary> private static void PrintChangeTrackingInfo(DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext context, object entity) { var entry = context.Entry(entity); Console.WriteLine("Type:{0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); //打印实体类型 Console.WriteLine("State: {0}", entry.State); if (entry.State != EntityState.Deleted) //标记删除的实体不会有当前值 { Console.WriteLine("\nCurrent Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues); } if (entry.State != EntityState.Added) //新添加的时候不会有原始值和数据库值 { Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.OriginalValues); Console.WriteLine("\nDatabase Values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.GetDatabaseValues()); } }
看看打印结果:
之前打印实体的各种属性都是通过遍历的形式(PrintPropertyValues方法)打印出来,如果仅取某个字段当然没必要这么麻烦,可以使用GetValue<TValue>:
/// <summary> /// 打印实体单个属性 /// </summary> private static void PrintOriginalName() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); hotel.Name = "Super Grand Hotel"; string originalName = context.Entry(hotel).OriginalValues.GetValue<string>("Name"); Console.WriteLine("Current Name: {0}", hotel.Name); //Super Grand Hotel Console.WriteLine("Original Name: {0}", originalName); //Grand Hotel } }
拷贝DbPropertyValues到实体:ToObject方法
/// <summary> /// 拷贝DbPropertyValues到实体:ToObject方法 /// </summary> private static void TestPrintDestination() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var reef = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Great Barrier Reef" select d).Single(); reef.TravelWarnings = "Watch out for sharks!"; Console.WriteLine("Current Values"); PrintDestination(reef); Console.WriteLine("\nDatabase Values"); DbPropertyValues dbValues = context.Entry(reef).GetDatabaseValues(); PrintDestination((DbContexts.Model.Destination)dbValues.ToObject()); //ToObject方法创建Destination实例 } } private static void PrintDestination(DbContexts.Model.Destination destination) { Console.WriteLine("-- {0}, {1} --", destination.Name, destination.Country); Console.WriteLine(destination.Description); if (destination.TravelWarnings != null) { Console.WriteLine("WARNINGS!: {0}", destination.TravelWarnings); } }
方法分析:从Destination表里取出Name为Great Barrier Reef的实体并修改其TravelWarnings字段,然后调用PrintDestination方法打印当前实体的各属性,再查出此实体在数据库里的值,并且通过ToObject方法把数据库取出来的这个对象也转换成了实体对象。这么转有什么好处呢?这个通过ToObject转换的Destination实例不会被数据库上下文追踪,所以对其做的任何改变都不会提交数据库。看看打印结果:
修改DbPropertyValues当前值:
调用上下文的Entry方法,传入要操作的实体对象,再打点就可以拿到实体的当前值(CurrentValues)、原始值(OriginalValues)、数据库值(GetDatabaseValues()),返回类型是DbPropertyValues,直接遍历就可以输出实体的所有属性。当然DbPropertyValues并不是只读的。写个方法修改试试:
/// <summary> /// 修改DbPropertyValues当前值 /// </summary> private static void ChangeCurrentValue() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); context.Entry(hotel).CurrentValues["Name"] = "Hotel Pretentious"; Console.WriteLine("Property Value: {0}", hotel.Name); Console.WriteLine("State: {0}", context.Entry(hotel).State); //Modified } }
类似于索引器的方式赋值即可,赋值后实体的状态已经是Modified了,显然已经被上下文追踪到了,这个时候调用上下文的SaveChanges方法将会提交到数据库。那么如果只是想打印和修改实体状态以供查看,并不像被提交到数据库怎么办呢?
/// <summary> /// 克隆实体:Clone /// </summary> private static void CloneCurrentValues() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); var values = context.Entry(hotel).CurrentValues.Clone(); //Clone方法 values["Name"] = "Simple Hotel"; Console.WriteLine("Property Value: {0}", hotel.Name); Console.WriteLine("State: {0}", context.Entry(hotel).State); //Unchanged } }
设置实体的值:SetValues方法
当然实体的当前值、原始值和数据库值都是可以相互复制的:
/// <summary> /// 设置实体的值:SetValues方法 /// </summary> private static void UndoEdits() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Grand Canyon" select d).Single(); canyon.Name = "Bigger & Better Canyon"; var entry = context.Entry(canyon); entry.CurrentValues.SetValues(entry.OriginalValues); entry.State = EntityState.Unchanged; //标记未修改 Console.WriteLine("Name: {0}", canyon.Name); //Grand Canyon } }
上面的方法演示了拷贝原始值到当前值,最终保存的是当前值。很方便,不需要挨个赋值。
我们看看如何使用SetValues方法实现之前说的克隆实体:
/// <summary> /// 克隆实体:SetValues /// </summary> private static void CreateDavesCampsite() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var davesDump = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Dave's Dump" select d).Single(); var clone = new DbContexts.Model.Lodging(); context.Lodgings.Add(clone); context.Entry(clone).CurrentValues.SetValues(davesDump); //克隆davesDump的值到新对象clone里 clone.Name = "Dave's Camp"; //修改Name属性 context.SaveChanges(); //最后提交修改 Console.WriteLine("Name: {0}", clone.Name); //Dave's Camp Console.WriteLine("Miles: {0}", clone.MilesFromNearestAirport); //32.65 Console.WriteLine("Contact Id: {0}", clone.PrimaryContactId); //1 } }
exec sp_executesql N'insert [dbo].[Lodgings]([Name], [Owner], [MilesFromNearestAirport], [destination_id], [PrimaryContactId], [SecondaryContactId], [Entertainment], [Activities], [MaxPersonsPerRoom], [PrivateRoomsAvailable], [Discriminator]) values (@0, null, @1, @2, @3, null, null, null, null, null, @4) select [LodgingId] from [dbo].[Lodgings] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [LodgingId] = scope_identity()',N'@0 nvarchar(200),@1 decimal(18,2),@2 int,@3 int,@4 nvarchar(128)',@0=N'Dave''s Camp',@1=32.65,@2=1,@3=1,@4=N'Lodging'
很明显实体已经被克隆了。
获取和设置实体的单个属性:Property方法
/// <summary> /// 获取和设置实体的单个属性:Property方法 /// </summary> private static void WorkingWithPropertyMethod() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var davesDump = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Dave's Dump" select d).Single(); var entry = context.Entry(davesDump); entry.Property(d => d.Name).CurrentValue = "Dave's Bargain Bungalows"; //设置Name属性 Console.WriteLine("Current Value: {0}", entry.Property(d => d.Name).CurrentValue); //Dave's Bargain Bungalows Console.WriteLine("Original Value: {0}", entry.Property(d => d.Name).OriginalValue); //Dave's Dump Console.WriteLine("Modified?: {0}", entry.Property(d => d.Name).IsModified); //True } }
同样可以查询出实体的哪些属性被修改了:IsModified方法
/// <summary> /// 查询实体被修改字段:IsModified方法 /// </summary> private static void FindModifiedProperties() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Grand Canyon" select d).Single(); canyon.Name = "Super-Size Canyon"; canyon.TravelWarnings = "Bigger than your brain can handle!!!"; var entry = context.Entry(canyon); var propertyNames = entry.CurrentValues.PropertyNames; //获取所有的Name列 IEnumerable<string> modifiedProperties = from name in propertyNames where entry.Property(name).IsModified select name; foreach (var propertyName in modifiedProperties) { Console.WriteLine(propertyName); //Name、TravelWarnings } } }
前面的章节已经讲解了如何查询一对一、一对多等关系的导航属性了,还不了解的点这里。现在讲讲如何修改导航属性:
/// <summary> /// 修改导航属性(Reference):CurrentValue方法 /// </summary> private static void WorkingWithReferenceMethod() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var davesDump = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Dave's Dump" select d).Single(); var entry = context.Entry(davesDump); entry.Reference(l => l.Destination).Load(); //显示加载 var canyon = davesDump.Destination; Console.WriteLine("Current Value After Load: {0}", entry.Reference(d => d.Destination).CurrentValue.Name); var reef = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Great Barrier Reef" select d).Single(); entry.Reference(d => d.Destination).CurrentValue = reef; //修改 Console.WriteLine("Current Value After Change: {0}", davesDump.Destination.Name); } }
打印结果:
Current Value After Load: Grand Canyon
Current Value After Change: Great Barrier Reef
注:上面的方法并没有调用上下文的SaveChanges方法,故程序跑完数据也不会保存到数据库,本文所有方法仅作演示都未提交数据库。
有Reference找单个属性的,那么自然也有Collection找集合属性的:
/// <summary> /// 修改导航属性(Collection):CurrentValue方法 /// </summary> private static void WorkingWithCollectionMethod() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var res = (from r in context.Reservations where r.Trip.Description == "Trip from the database" select r).Single(); var entry = context.Entry(res); entry.Collection(r => r.Payments).Load(); Console.WriteLine("Payments Before Add: {0}", entry.Collection(r => r.Payments).CurrentValue.Count); var payment = new DbContexts.Model.Payment { Amount = 245 }; context.Payments.Add(payment); entry.Collection(r => r.Payments).CurrentValue.Add(payment); //修改 Console.WriteLine("Payments After Add: {0}", entry.Collection(r => r.Payments).CurrentValue.Count); } }
打印结果:
Payments Before Add: 1
Payments After Add: 2
我们从数据库取出实体加载到内存中,可能并不立马就展示给用户看。在进行一系列的排序、筛选等操作再展示出来。但是怎么确定展示的时候这些实体没有被修改过呢?我们可以使用Reload方法重新加载:
/// <summary> /// 取当前最新的数据库值:Reload方法 /// </summary> private static void ReloadLodging() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var hotel = (from d in context.Lodgings where d.Name == "Grand Hotel" select d).Single(); //取出实体 context.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(@"UPDATE dbo.Lodgings SET Name = 'Le Grand Hotel' WHERE Name = 'Grand Hotel'"); //立马修改实体值(这个时候数据库中的值已改变,但是取出来放在内存中的值并没改变) Console.WriteLine("Name Before Reload: {0}", hotel.Name); Console.WriteLine("State Before Reload: {0}", context.Entry(hotel).State); context.Entry(hotel).Reload(); Console.WriteLine("Name After Reload: {0}", hotel.Name); Console.WriteLine("State After Reload: {0}", context.Entry(hotel).State); } }
打印结果:
Name Before Reload: Grand Hotel
State Before Reload: Unchanged
Name After Reload: Le Grand Hotel
State After Reload: Unchanged
可以看出Reload方法已经帮我们重新取出了数据库中的最新值。来看看Reload方法生成的sql:
SELECT [Extent1].[Discriminator] AS [Discriminator], [Extent1].[LodgingId] AS [LodgingId], [Extent1].[Name] AS [Name], [Extent1].[Owner] AS [Owner], [Extent1].[MilesFromNearestAirport] AS [MilesFromNearestAirport], [Extent1].[destination_id] AS [destination_id], [Extent1].[PrimaryContactId] AS [PrimaryContactId], [Extent1].[SecondaryContactId] AS [SecondaryContactId], [Extent1].[Entertainment] AS [Entertainment], [Extent1].[Activities] AS [Activities], [Extent1].[MaxPersonsPerRoom] AS [MaxPersonsPerRoom], [Extent1].[PrivateRoomsAvailable] AS [PrivateRoomsAvailable] FROM [dbo].[Lodgings] AS [Extent1] WHERE ([Extent1].[Discriminator] IN ('Resort','Hostel','Lodging')) AND ([Extent1].[LodgingId] = 1)
当然Reload方法也会保存内存中修改的数据,这个并不会冲突。在方法里的linq查询后面加上:hotel.Name = "A New Name"; 打印结果就是这样的了:
Name Before Reload: A New Name
State Before Reload: Modified
Name After Reload: Le Grand Hotel
State After Reload: Unchanged
注意,代码里修改的Name已经显示了,并且标记实体状态为Modified了,Modified会在调用上下文的SaveChanges方法的时候提交到数据库。这个过程是这样的:
加载实体到内存中 - 在内存中对实体的某个属性进行修改 - 使用ExecuteSqlCommand方法执行sql修改数据库里该实体的值 - 调用Reload取出数据库里本实体的最新值 - 调用SaveChanges方法的话,在内存中对实体的修改也会被提交到数据库
之前我们操作了单个实体,现在看看如何读取关联实体和状态。使用DbContext.ChangeTracker.Entries方法:
/// <summary> /// 读取相关联的实体和状态:DbContext.ChangeTracker.Entries方法 /// </summary> private static void PrintChangeTrackerEntries() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var res = (from r in context.Reservations where r.Trip.Description == "Trip from the database" select r).Single(); context.Entry(res).Collection(r => r.Payments).Load();
res.Payments.Add(new DbContexts.Model.Payment { Amount = 245 }); var entries = context.ChangeTracker.Entries(); foreach (var entry in entries) { Console.WriteLine("Entity Type: {0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); Console.WriteLine(" - State: {0}", entry.State); } } }
添加了一个从表实体,并读取所有关联实体和其状态,打印结果:
Entity Type: DbContexts.Model.Payment
- State: Added
Entity Type: DbContexts.Model.Reservation
- State: Unchanged
Entity Type: DbContexts.Model.Payment
- State: Unchanged
EF里如何解决更新数据时的冲突
正常根据实体的主键修改实体的时候,EF是不会判断数据修改之前有没有被别的人修改过,但是如果做了并发控制,EF在更新某条记录的时候才会抛错。这个系列文章的demo里有两个实体做了并发控制:Person类的SocialSecurityNumber字段被标记了ConcurrencyCheck;Trip类的RowVersion字段被标记了Timestamp。我们来写一个触发DbUpdateConcurrencyException异常的方法并处理这个异常:
/// <summary> /// 修改实体 /// </summary> private static void ConcurrencyDemo() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var trip = (from t in context.Trip.Include(t => t.Destination) where t.Description == "Trip from the database" select t).Single(); trip.Description = "Getaway in Vermont"; context.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(@"UPDATE dbo.Trips SET CostUSD = 400 WHERE Description = 'Trip from the database'"); SaveWithConcurrencyResolution(context); } } /// <summary> /// 尝试保存 /// </summary> private static void SaveWithConcurrencyResolution(DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext context) { try { context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException ex) { ResolveConcurrencyConflicts(ex); SaveWithConcurrencyResolution(context); } }
方法分析:取出实体 - 修改实体Description属性(此时实体状态为Modified)- 使用ExecuteSqlCommand执行sql修改了CostUSD和Description字段(修改后时间戳已经不同了,PS:使用ExecuteSqlCommand执行sql不需要调用SaveChanges方法)- 调用上下文的SaveChanges方法保存之前被标记为Modified的实体,这个时候就会报一个DbUpdateConcurrencyException的异常,因为时间戳列已经找不到了,这个更新的where条件根本找不到记录了。有时间戳的列更新都是双条件,时间戳详细用法点这里了解。
我们尝试写个方法解决这个冲突:
/// <summary> /// 解决冲突 /// </summary> private static void ResolveConcurrencyConflicts(DbUpdateConcurrencyException ex) { foreach (var entry in ex.Entries) { Console.WriteLine("Concurrency conflict found for {0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); Console.WriteLine("\nYou are trying to save the following values:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues); //用户修改的值 Console.WriteLine("\nThe values before you started editing were:"); PrintPropertyValues(entry.OriginalValues); //从库里取出来时的值 var databaseValues = entry.GetDatabaseValues(); //即时数据库的值 Console.WriteLine("\nAnother user has saved the following values:"); PrintPropertyValues(databaseValues); Console.WriteLine("[S]ave your values, [D]iscard you changes or [M]erge?"); var action = Console.ReadKey().KeyChar.ToString().ToUpper(); //读取用户输入的字母 switch (action) { case "S": entry.OriginalValues.SetValues(databaseValues); //拷贝数据库值到当前值(恢复时间戳) break; case "D": entry.Reload(); //重新加载 break; case "M": var mergedValues = MergeValues(entry.OriginalValues, entry.CurrentValues, databaseValues);//合并 entry.OriginalValues.SetValues(databaseValues); //拷贝数据库值到当前值(恢复时间戳) entry.CurrentValues.SetValues(mergedValues); //拷贝合并后的值到当前值,最终保存的是当前值 break; default: throw new ArgumentException("Invalid option"); } } }
捕获到异常后告知用户要修改实体的原始值(用户修改前从数据库取出来的值)、现在的值(用户修改的值)、数据库里的值(此时数据库里的值,这个值已被修改,不是用户修改前取出来的值了),打印出来的结果显示已经有人修改了这条记录了。最后是问用户是否保存修改。分别是保存、放弃、合并修改。
用户输入"S"表示“保存”,case语句块里执行的操作是拷贝数据库值到原始值,这里该有疑惑了,调用SaveChanges方法保存的也是currentValues当前值,跟databaseValues数据库值还有OriginalValues原始值没有任何关系啊。其实这里这么操作的原因是恢复一下时间戳的值,之前说过timestamp的列更新条件是两个,任何一个不对都更新不了。看看sql:
exec sp_executesql N'update [dbo].[Trips] set [Description] = @0, [CostUSD] = @1 where (([Identifier] = @2) and ([RowVersion] = @3)) select [RowVersion] from [dbo].[Trips] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [Identifier] = @2',N'@0 nvarchar(max) ,@1 decimal(18,2),@2 uniqueidentifier,@3 binary(8)',@0=N'Getaway in Vermont',@1=1000.00,@2='CF2E6BD3-7393-440C-941A- 9124C61CE04A',@3=0x00000000000007D2
结果只保存了自己的修改:
用户输入“D”表示“放弃”,case语句块里执行的是Reload方法,这个方法之前已经介绍过了,是重新加载数据库里的最新值(Latest Value)。恢复下数据库数据再执行下方法,看看sql:
SELECT [Extent1].[Identifier] AS [Identifier], [Extent1].[StartDate] AS [StartDate], [Extent1].[EndDate] AS [EndDate], [Extent1].[Description] AS [Description], [Extent1].[CostUSD] AS [CostUSD], [Extent1].[RowVersion] AS [RowVersion], [Extent1].[DestinationId] AS [DestinationId] FROM [dbo].[Trips] AS [Extent1] WHERE [Extent1].[Identifier] = cast('cf2e6bd3-7393-440c-941a-9124c61ce04a' as uniqueidentifier)
取了下数据库里该实体最新的值(使用ExecuteSqlCommand更新后的值),没有其他任何更新语句,就是放弃本次修改的意思,但是之前ExecuteSqlCommand方法执行的修改是有效的,看看结果:
上面的“保存修改”和“放弃修改”都是最能达到一般的效果,如果让用户修改的和ExecuteSqlCommand的修改同时生效呢,我们选择M,意为合并。看看合并方法:
/// <summary> /// 合并 /// </summary> private static DbPropertyValues MergeValues(DbPropertyValues original, DbPropertyValues current, DbPropertyValues database) { var result = original.Clone(); //拷贝原始值并存放合并后的值 foreach (var propertyName in original.PropertyNames) //遍历原始值的所有列 { if (original[propertyName] is DbPropertyValues) //判断当前列是否复杂类型(很少) { var mergedComplexValues = MergeValues((DbPropertyValues)original[propertyName], (DbPropertyValues)current[propertyName], (DbPropertyValues)database[propertyName]); //是复杂类型的话就使用递归合并复杂类型的值 ((DbPropertyValues)result[propertyName]).SetValues(mergedComplexValues); } else //是普通里的话就和当前值、数据库值、原始值各种对比。修改了就赋值 { if (!object.Equals(current[propertyName], original[propertyName])) result[propertyName] = current[propertyName]; else if (!object.Equals(database[propertyName], original[propertyName])) result[propertyName] = database[propertyName]; } } return result; }
看看sql:
exec sp_executesql N'update [dbo].[Trips] set [Description] = @0, [CostUSD] = @1 where (([Identifier] = @2) and ([RowVersion] = @3)) select [RowVersion] from [dbo].[Trips] where @@ROWCOUNT > 0 and [Identifier] = @2',N'@0 nvarchar(max) ,@1 decimal(18,2),@2 uniqueidentifier,@3 binary(8)',@0=N'Getaway in Vermont',@1=400.00,@2='CF2E6BD3-7393-440C-941A-9124C61CE04A',@3=0x00000000000007DC
看看结果:
用户修改和ExecuteSqlCommand都保存上了。
最后讲一个更实用的东西:重写上下文的SaveChanges方法记录结果集里实体的各种增/删/改。
先到BreakAwayContext类里添加一个属性标识使用数据库上下文的SaveChanges方法还是使用自定义的SaveChanges方法:public bool LogChangesDuringSave { get; set; }
来看一个方法:
/// <summary> /// 记录结果集的各种:增 / 删 /改 /// </summary> private static void TestSaveLogging() { using (var context = new DbContexts.DataAccess.BreakAwayContext()) { var canyon = (from d in context.Destinations where d.Name == "Grand Canyon" select d).Single();//加载主表数据 context.Entry(canyon).Collection(d => d.Lodgings).Load();//显示加载出从表相关数据 canyon.TravelWarnings = "Take a hat!";//修改主表字段 context.Lodgings.Remove(canyon.Lodgings.First());//删除相关联从表的第一条数据 context.Destinations.Add(new DbContexts.Model.Destination { Name = "Seattle, WA" });//添加一条主表数据 context.LogChangesDuringSave = true; //设置标识,使用自定义的SaveChanges方法 context.SaveChanges(); } }
增加、修改、删除操作等都有。运行这个方法前需要在BreakAwayContext类里添加记录的帮助类方法:
/// <summary> /// 记录帮助类方法 /// </summary> private void PrintPropertyValues(DbPropertyValues values, IEnumerable<string> propertiesToPrint, int indent = 1) { foreach (var propertyName in propertiesToPrint) { var value = values[propertyName]; if (value is DbPropertyValues) { Console.WriteLine("{0}- Complex Property: {1}", string.Empty.PadLeft(indent), propertyName); var complexPropertyValues = (DbPropertyValues)value; PrintPropertyValues(complexPropertyValues, complexPropertyValues.PropertyNames, indent + 1); } else { Console.WriteLine("{0}- {1}: {2}", string.Empty.PadLeft(indent), propertyName, values[propertyName]); } } } private IEnumerable<string> GetKeyPropertyNames(object entity) { var objectContext = ((IObjectContextAdapter)this).ObjectContext; return objectContext.ObjectStateManager.GetObjectStateEntry(entity).EntityKey.EntityKeyValues.Select(k => k.Key); }
再在BreakAwayContext类里重写下上下文的SaveChanges方法:
/// <summary> /// 重写SaveChanges方法 /// </summary> public override int SaveChanges() { if (LogChangesDuringSave) //根据表示判断用重写的SaveChanges方法,还是普通的上下文SaveChanges方法 { var entries = from e in this.ChangeTracker.Entries() where e.State != EntityState.Unchanged select e; //过滤所有修改了的实体,包括:增加 / 修改 / 删除 foreach (var entry in entries) { switch (entry.State) { case EntityState.Added: Console.WriteLine("Adding a {0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues, entry.CurrentValues.PropertyNames); break; case EntityState.Deleted: Console.WriteLine("Deleting a {0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); PrintPropertyValues(entry.OriginalValues, GetKeyPropertyNames(entry.Entity)); break; case EntityState.Modified: Console.WriteLine("Modifying a {0}", entry.Entity.GetType()); var modifiedPropertyNames = from n in entry.CurrentValues.PropertyNames where entry.Property(n).IsModified select n; PrintPropertyValues(entry.CurrentValues, GetKeyPropertyNames(entry.Entity).Concat(modifiedPropertyNames)); break; } } } return base.SaveChanges(); //返回普通的上下文SaveChanges方法 }
运行结果为:
所有添加/修改/删除都记录下来了,这个可以方便我们做更细微的控制,毕竟EF对实体操作的依据就是实体的各种状态。
EF DbContext 系列文章导航: