上一篇介绍了一些有数学公式实现分型的例子,下面将介绍一些由递归实现的分形。
由递归实现分形是应该注意:1.一定要用一个标志来结束循环,不然会系统会抛出堆溢出错误
2.尽量把思路理清,把代码简化
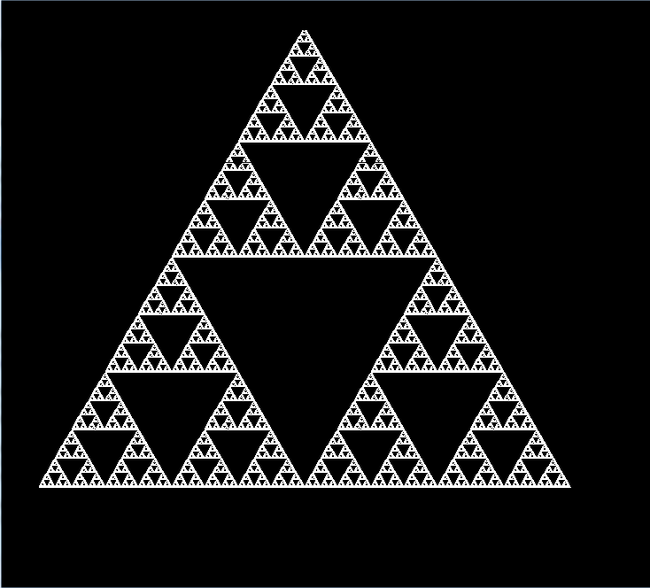
谢宾斯基三角形
谢宾斯基地毯
科赫曲线
科赫雪花
package cn.kml.递归20130706;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class Triangle extends JFrame{
//窗体可见后,获取窗体上的画布对象
private Graphics g;
//程序的入口主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Triangle tr = new Triangle();
tr.unitUI();
}
public void unitUI(){
this.setTitle("Recursion");
this.setSize(900,700);
//在窗体上实例化一个面板对象
JPanel jp = new JPanel();
//设置面板的大小
jp.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(150,0));
//在面板上加一个按钮对象
JButton bu = new JButton("Sierpinske");
JButton bu1 = new JButton("Rectangle");
JButton bu3 = new JButton("Koch-Snow");
JButton bu2 = new JButton("Koch Curve");
JButton bu4 = new JButton("Tree");
jp.add(bu);
jp.add(bu1);
jp.add(bu2);
jp.add(bu3);
jp.add(bu4);
bu.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bu1.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bu2.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bu3.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bu4.setForeground(Color.BLUE);
bu.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
bu1.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
bu2.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
bu3.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
bu4.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
//把面板加到窗体上
this.add(jp,BorderLayout.EAST);
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
this.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.BLACK);//设置背景颜色
this.setVisible(true);
//窗体可见后,获取画布对象
g= this.getGraphics();
RecuesionListener rl = new RecuesionListener(g);
bu.addActionListener(rl);
bu1.addActionListener(rl);
bu2.addActionListener(rl);
bu3.addActionListener(rl);
bu4.addActionListener(rl);
}
}
package cn.kml.递归20130706;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class RecuesionListener implements ActionListener{
private Graphics g;
static int state=10;
static int state1=6;
static int state2=2;
static int state3=7;
static int state4=7;
static int state5=10;
public RecuesionListener(Graphics g){
this.g=g;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// g.clearRect(0, 0, 750, 690);
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("Sierpinske")){
g.setColor(Color.WHITE);
draw(350, 60, 50, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+10, 650, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+10, state);
// g.setColor(new Color(210,210,200));
// draw(340, 65, 40, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+15, 640, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+15, state);
// g.setColor(new Color(180,180,170));
// draw(330, 70, 30, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+20, 630, (int)(50+300*Math.sqrt(3))+20, state);
}
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("Rectangle")){
drawRec(50,50,650,state1);
}
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("Koch Curve")){
drawKoch(50,600,700,600,state3);
}
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("Koch-Snow")){
drawSnow(700,550,400,(int)(550-Math.sqrt(3)*300),100,550,state4);
}
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("Tree")){
drawTree1(300,600,100,5,1);
}
}
public void draw(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,int state){
state--;
if(state>0){
//画出最外面的三角形
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x3, y3);
g.drawLine(x2, y2, x3, y3);
//算出任意两点的中点坐标
int x12=(int)((x1+x2)/2);
int y12=(int)((y1+y2)/2);
int x23=(int)((x2+x3)/2);
int y23=(int)((y2+y3)/2);
int x13=(int)((x1+x3)/2);
int y13=(int)((y1+y3)/2);
g.drawLine(x12, y12, x13, y13);
g.drawLine(x12, y12, x23, y23);
g.drawLine(x13, y13, x23, y23);
//递归调用
draw(x1,y1,x12,y12,x13,y13,state);
draw(x12,y12,x2,y2,x23,y23,state);
draw(x13,y13,x23,y23,x3,y3,state);
}else{
return;
}
}
public void drawRec(int x1,int y1,int x2,int state1){
state1--;
//先画出最外围的正方形
g.drawLine(50,50,650,50);
g.drawLine(50,50,50,650);
g.drawLine(650,50,650,650);
g.drawLine(50,650,650,650);
//循环化出里面的正方形
if(state1>0){
int x11=(int)((x2-x1)/3+x1);
int x22=(int)(2*(x2-x1)/3+x1);
int y11=(int)((x2-x1)/3+y1);
int y22=(int)(2*(x2-x1)/3+y1);
g.fillRect(x11, y11, x22-x11,x22-x11);
//递归调用函数
drawRec(x1,y1,x11,state1);
drawRec(x22,y1,x2,state1);
drawRec(x1,y22,x11,state1);
drawRec(x22,y22,x2,state1);
drawRec(x11,y1,x22,state1);
drawRec(x22,y11,x2,state1);
drawRec(x11,y22,x22,state1);
drawRec(x1,y11,x11,state1);
}else{
return;
}
}
public void drawKoch(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int state3){
int x3 = (2*x1+x2)/3;
int x4 = (x1+2*x2)/3;
int y3 = (2*y1+y2)/3;
int y4 = (y1+2*y2)/3;
int x5=0,y5=0;
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
if(y1 == y2){
x5 = (x3+x4)/2;
y5 = (int)(y1-Math.sqrt(3)*(x4-x3)/2);
}else if(y1>y2){
if(x1<x2){
x5 = x1;
y5 = y4;
}else if(x1>x2){
x5 = x2;
y5 = y3;
}
}else if(y1<y2){
if(x1>x2){
x5 = x1;
y5 = y4;
}else if(x1<x2){
x5 = x2;
y5 = y3;
}
}
if(state3==1){
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
if(state3<=0){
return;
}
drawKoch(x1,y1,x3,y3,state3-1);
drawKoch(x3,y3,x5,y5,state3-1);
drawKoch(x5,y5,x4,y4,state3-1);
drawKoch(x4,y4,x2,y2,state3-1);
}
public void drawSnow(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,int state4){
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
if(state4>0){
drawKoch(x2,y2,x1,y1,state4-1);
drawKoch(x3,y3,x2,y2,state4-1);
drawKoch(x1,y1,x3,y3,state4-1);
}else{
return;
}
}
}