Netty的ByteBuf主要用于网络传输,有读写两个index。
* +-------------------+------------------+------------------+
* | discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes |
* | | (CONTENT) | |
* +-------------------+------------------+------------------+
* | | | |
* 0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity
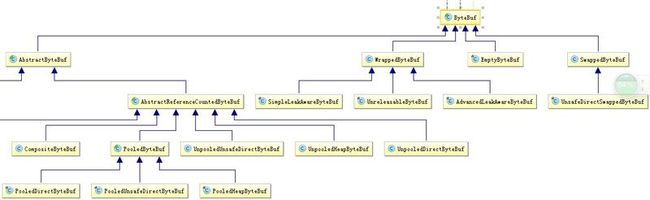
我们可以看出,大致分为几类ByteBuf,一类是Pooled,UnPooled。另一个是Heap,Direct。
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
static final ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf> leakDetector = new ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf>(ByteBuf.class);
int readerIndex; //读的索引
int writerIndex;//写的索引
private int markedReaderIndex;//标记读的索引
private int markedWriterIndex;//标记写的索引
private int maxCapacity;//最大容量
}
PooledByteBuf,通过capacity和deallocate方法我们可以发现都是用 chunk.arena来分配内存和释放内存的
abstract class PooledByteBuf<T> extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
private final Recycler.Handle recyclerHandle;
protected PoolChunk<T> chunk;
protected long handle;
protected T memory;
protected int offset;
protected int length;
int maxLength;
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;
@Override
public final ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
ensureAccessible();
// If the request capacity does not require reallocation, just update the length of the memory.
if (chunk.unpooled) {
if (newCapacity == length) {
return this;
}
} else {
if (newCapacity > length) {
if (newCapacity <= maxLength) {
length = newCapacity;
return this;
}
} else if (newCapacity < length) {
if (newCapacity > maxLength >>> 1) {
if (maxLength <= 512) {
if (newCapacity > maxLength - 16) {
length = newCapacity;
setIndex(Math.min(readerIndex(), newCapacity), Math.min(writerIndex(), newCapacity));
return this;
}
} else { // > 512 (i.e. >= 1024)
length = newCapacity;
setIndex(Math.min(readerIndex(), newCapacity), Math.min(writerIndex(), newCapacity));
return this;
}
}
} else {
return this;
}
}
// Reallocation required.
chunk.arena.reallocate(this, newCapacity, true);
return this;
}
@Override
protected final void deallocate() {
if (handle >= 0) {
final long handle = this.handle;
this.handle = -1;
memory = null;
chunk.arena.free(chunk, handle, maxLength);
recycle();
}
}
}
PooledDirectByteBuf 是缓存的DirectByteBuf. 用RECYCLER来做回收重复利用。调用memory的get方法获取数据。memory是一个DirectByteBuffer对象。
final class PooledDirectByteBuf extends PooledByteBuf<ByteBuffer> {
private static final Recycler<PooledDirectByteBuf> RECYCLER = new Recycler<PooledDirectByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected PooledDirectByteBuf newObject(Handle handle) {
return new PooledDirectByteBuf(handle, 0);
}
};
static PooledDirectByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledDirectByteBuf buf = RECYCLER.get();
buf.setRefCnt(1);
buf.maxCapacity(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}
@Override
protected byte _getByte(int index) {
return memory.get(idx(index));
}
@Override
protected short _getShort(int index) {
return memory.getShort(idx(index));
}
}
PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf和PooledDirectByteBuf的区别是没有使用DirectByteBuffer的接口方法去获取数据,而是直接用PlatformDependent的方法获取数据
final class PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf extends PooledByteBuf<ByteBuffer> {
private static final boolean NATIVE_ORDER = ByteOrder.nativeOrder() == ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN;
private static final Recycler<PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf> RECYCLER = new Recycler<PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf newObject(Handle handle) {
return new PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(handle, 0);
}
};
static PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf buf = RECYCLER.get();
buf.setRefCnt(1);
buf.maxCapacity(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}
private long memoryAddress;
private void initMemoryAddress() {
memoryAddress = PlatformDependent.directBufferAddress(memory) + offset;
}
@Override
protected byte _getByte(int index) {
return PlatformDependent.getByte(addr(index));
}
@Override
protected short _getShort(int index) {
short v = PlatformDependent.getShort(addr(index));
return NATIVE_ORDER? v : Short.reverseBytes(v);
}
}
PooledHeapByteBuf是直接用堆内分配的byte数组来存储数据,因此可以直接通过偏移量来读取数据
final class PooledHeapByteBuf extends PooledByteBuf<byte[]> {
private static final Recycler<PooledHeapByteBuf> RECYCLER = new Recycler<PooledHeapByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected PooledHeapByteBuf newObject(Handle handle) {
return new PooledHeapByteBuf(handle, 0);
}
};
static PooledHeapByteBuf newInstance(int maxCapacity) {
PooledHeapByteBuf buf = RECYCLER.get();
buf.setRefCnt(1);
buf.maxCapacity(maxCapacity);
return buf;
}
@Override
protected byte _getByte(int index) {
return memory[idx(index)];
}
@Override
protected short _getShort(int index) {
index = idx(index);
return (short) (memory[index] << 8 | memory[index + 1] & 0xFF);
}
}
UnpooledHeapByteBuf和PooledHeapByteBuf的区别是UnpooledHeapByteBuf不会用RECYCLER回收器
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
private byte[] array;
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;
/**
* Creates a new heap buffer with a newly allocated byte array.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the underlying byte array
* @param maxCapacity the max capacity of the underlying byte array
*/
protected UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
this(alloc, new byte[initialCapacity], 0, 0, maxCapacity);
}
}
Netty会调用PoolArea的allocate方法创建ByteBuf对象
abstract class PoolArena<T> {
static final int numTinySubpagePools = 512 >>> 4;
final PooledByteBufAllocator parent;
private final int maxOrder;
final int pageSize;
final int pageShifts;
final int chunkSize;
final int subpageOverflowMask;
final int numSmallSubpagePools;
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] tinySubpagePools;
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] smallSubpagePools;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q050;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q025;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q000;
private final PoolChunkList<T> qInit;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q075;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q100;
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity) {
final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity);
if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { // capacity < pageSize
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage<T>[] table;
if (isTiny(normCapacity)) { // < 512
if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity);
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity);
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
synchronized (this) {
final PoolSubpage<T> head = table[tableIdx];
final PoolSubpage<T> s = head.next;
if (s != head) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity;
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
return;
}
}
} else if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) {
if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
} else {
// Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge
allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity);
return;
}
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
}
}