#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct _Node{
float data;
struct _Node *lchild;
struct _Node *rchild;
int huffmanCode[10],pos;//保存编码,在数组中从后往前存储,最多10位
} Node,*Tree;
/* 排序算法,从大到小 */
void Sort(float a[],int low,int high)
{
int i;
float temp;
if(low == high)return;
for(i=low; i<=high; i++){
if(a[i] > a[low]){
temp = a[low];
a[low] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
}
Sort(a,low+1,high);
}
/* 将一个字符型数组 char a[]转化为 Tree型数组,而且已经从大到小排序
* 为构建哈夫曼树做准备*/
Tree* InitHuffmanTree(float a[],int count)
{
int i,j;
Tree T ;
Sort(a,0,count-1);//先排序
Tree *HuffmanTrees = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
for(i=0; i<count; i++){
T = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
T->data = a[i];
T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL;
T->pos = 10;
HuffmanTrees[i] = T;
}
return HuffmanTrees;
}
/* 给一棵子树的节点赋哈夫曼编码 */
void Encoding(Tree head,int code)
{
if(!head)return;
head->huffmanCode[--(head->pos)] = code;
Encoding(head->lchild,code);
Encoding(head->rchild,code);
}
/* 构建哈夫曼树,打印哈夫曼编码
* huffmanTrees[]中存储的是所有huffman树的根,
* 而且已经从大到小排序*/
Tree CreateHuffmanTree(Tree *huffmanTrees,int count)
{
int i;
if(count <= 1)return huffmanTrees[0];
Node *newTree = NULL;
if(!(newTree=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node))))printf("overflow!\n");
newTree->data = huffmanTrees[count-1]->data + huffmanTrees[count-2]->data;
newTree->lchild = huffmanTrees[count-1];
Encoding(huffmanTrees[count-1],0);//修改子树的哈夫曼编码
newTree->rchild = huffmanTrees[count-2];
Encoding(huffmanTrees[count-2],1);
newTree->pos = 10;
count -= 2;
/*插入合适位置(从大到小顺序)*/
for(i=count; i>0 && newTree->data > huffmanTrees[i-1]->data; i--)
{
huffmanTrees[i] = huffmanTrees[i-1];
}
huffmanTrees[i] = newTree;
count++;
return CreateHuffmanTree(huffmanTrees,count);
}
/* 输出哈夫曼编码 : 左0右1*/
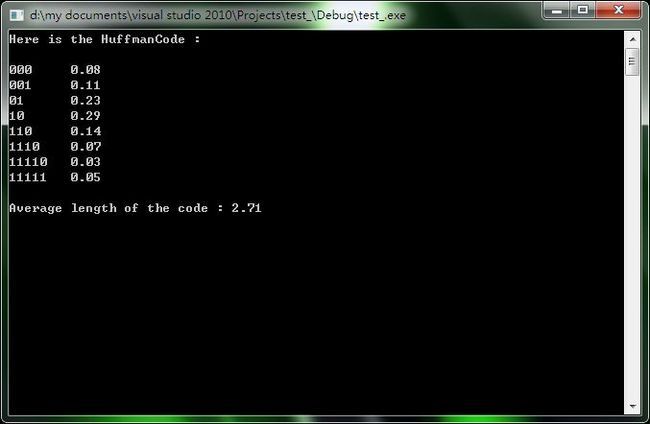
float printHuffmanCode(Tree head)
{
int i;
static float length = 0,TotLen=0,num=0;
if(!head)return length;
if (!head->lchild && !head->rchild)
{
for(i=head->pos; i<10; i++)printf("%d",head->huffmanCode[i]);
printf("\t%.2f\n",head->data);
TotLen += head->data * (10-head->pos);
num += head->data;
}
printHuffmanCode(head->lchild);
printHuffmanCode(head->rchild);
length = TotLen/num;
return length;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
float a[] = {.23,.11,.05,.03,.29,.14,.07,.08},length;
int count = 8;
Tree *huffmanTrees = InitHuffmanTree(a,count);
Tree huffmanTree = CreateHuffmanTree(huffmanTrees,count);
printf("Here is the HuffmanCode :\n\n");
length = printHuffmanCode(huffmanTree);
printf("\nAverage length of the code : %.2f\n",length);
getchar();
}
