Asp.net MVC 示例项目"Suteki.Shop"分析之---数据验证
在Suteki.Shop,实现了自己的数据校验机制,可以说其设计思路还是很有借鉴价值的。而使用这种机制也很容易在Model中对相应的实体对象(属性)添加校验操作方法。下面就来介绍一下其实现方式。
首先,看一下这样类图:
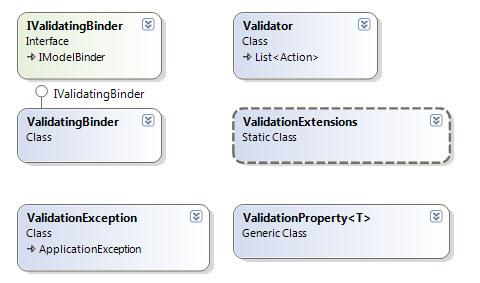
在Suteki.Shop定义一个“IValidatingBinder”接口,其派生自IModelBinder:
public
interface
IValidatingBinder : IModelBinder
{
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, string objectPrefix);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, ModelStateDictionary modelStateDictionary);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, ModelStateDictionary modelStateDictionary, string objectPrefix);
}
{
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, string objectPrefix);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, ModelStateDictionary modelStateDictionary);
void UpdateFrom( object target, NameValueCollection values, ModelStateDictionary modelStateDictionary, string objectPrefix);
}
其接口中定义了一个重载方法UpdateFrom,其要实现的功能与MVC中UpdateFrom一样,就是自动读取我们在form中定义的有些元素及其中所包含的内容。
实现IValidatingBinder接口的类叫做:ValidatingBinder,下面是其核心代码说明。
首先是BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)该方法是在IModelBinder接口中定义的,是其核心功能,用于将客户端数据转成我们希望Model类型。
///
<summary>
/// IModelBinder.BindModel
/// </summary>
/// <param name="controllerContext"></param>
/// <param name="bindingContext"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
if (bindingContext == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( " bindingContext " );
}
if (IsBasicType(bindingContext.ModelType))
{
return new DefaultModelBinder().BindModel(controllerContext, bindingContext);
}
var instance = Activator.CreateInstance(bindingContext.ModelType);
var request = controllerContext.HttpContext.Request;
var form = request.RequestType == " POST " ? request.Form : request.QueryString;
UpdateFrom(instance, form);
return instance;
}
/// IModelBinder.BindModel
/// </summary>
/// <param name="controllerContext"></param>
/// <param name="bindingContext"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
if (bindingContext == null )
{
throw new ArgumentNullException( " bindingContext " );
}
if (IsBasicType(bindingContext.ModelType))
{
return new DefaultModelBinder().BindModel(controllerContext, bindingContext);
}
var instance = Activator.CreateInstance(bindingContext.ModelType);
var request = controllerContext.HttpContext.Request;
var form = request.RequestType == " POST " ? request.Form : request.QueryString;
UpdateFrom(instance, form);
return instance;
}
上面代码第二个
if 用于判断bindingContext的Model类型是否是系统类型,比如decimal,string等。如果是则使用MVC自带的DefaultModelBinder来进行处理。否则就使用该类自己的UpdateFrom方法,从而实现对当前form中的数据与Model中相应类型的信息绑定,并返相应的 Model 实例(instance)。下面是其核心代码:
public
virtual
void
UpdateFrom(BindingContext bindingContext)
{
foreach (var property in bindingContext.Target.GetType().GetProperties())
{
try
{
foreach (var binder in propertyBinders)
{
binder.Bind(property, bindingContext);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
if (exception.InnerException is FormatException ||
exception.InnerException is IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, " Invalid value for {0} " .With(property.Name));
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else if (exception is ValidationException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, exception.Message);
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else if (exception.InnerException is ValidationException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, exception.InnerException.Message);
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else
{
throw ;
}
}
}
if ( ! bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.IsValid)
{
throw new ValidationException( " Bind Failed. See ModelStateDictionary for errors " );
}
}
{
foreach (var property in bindingContext.Target.GetType().GetProperties())
{
try
{
foreach (var binder in propertyBinders)
{
binder.Bind(property, bindingContext);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
if (exception.InnerException is FormatException ||
exception.InnerException is IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, " Invalid value for {0} " .With(property.Name));
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else if (exception is ValidationException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, exception.Message);
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else if (exception.InnerException is ValidationException)
{
string key = BuildKeyForModelState(property, bindingContext.ObjectPrefix);
bindingContext.AddModelError(key, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, exception.InnerException.Message);
bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.SetModelValue(key, new ValueProviderResult(bindingContext.AttemptedValue, bindingContext.AttemptedValue, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture));
}
else
{
throw ;
}
}
}
if ( ! bindingContext.ModelStateDictionary.IsValid)
{
throw new ValidationException( " Bind Failed. See ModelStateDictionary for errors " );
}
}
上面代码中的TRY部分就是其数据绑定的代码,而其Catch部分实现了在数据绑定过程中出现的错误异常(主要是数据验证等,会在后面提到)收集到ModelState(ModelStateDictionary)中以便于后续处理。而这里Suteki.Shop还定义了自己的验证异常类“ValidationException”(位于:Suteki.Common\Validation\ValidationException.cs,因为代码很简单,就不多做解释了。
有了ValidatingBinder之后,下面就来看一下Suteki.Shop是如何使用它的。这里以一个业务流程---“编辑用户”来进行说明。
下面就是UserController(Suteki.Shop\Controllers\UserController.cs) 中的Edit操作:
下面就是UserController(Suteki.Shop\Controllers\UserController.cs) 中的Edit操作:
[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post), UnitOfWork]
public ActionResult Edit([DataBind] User user, string password)
{
if ( ! string .IsNullOrEmpty(password))
{
user.Password = userService.HashPassword(password);
}
 ..
..
}
public ActionResult Edit([DataBind] User user, string password)
{
if ( ! string .IsNullOrEmpty(password))
{
user.Password = userService.HashPassword(password);
}
 ..
.. }
在该Action中,我们看到其定义并使用了DataBind这个ModelBinder进行绑定处理,所以我们要先看一下DataBinder(注:它是Suteki.Shop中关于数据绑定的“ModelBinder的基类)中倒底做了些什么,下面是其实现代码:
public
class
DataBinder : IModelBinder, IAcceptsAttribute
{
public virtual object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
object entity;
if (declaringAttribute == null || declaringAttribute.Fetch)
{
entity = FetchEntity(bindingContext, controllerContext);
}
else
{
entity = Activator.CreateInstance(bindingContext.ModelType);
}
try
{
validatingBinder.UpdateFrom(entity, controllerContext.HttpContext.Request.Form, bindingContext.ModelState, bindingContext.ModelName);
}
catch (ValidationException ex)
{}
return entity;
}


}
{
public virtual object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
object entity;
if (declaringAttribute == null || declaringAttribute.Fetch)
{
entity = FetchEntity(bindingContext, controllerContext);
}
else
{
entity = Activator.CreateInstance(bindingContext.ModelType);
}
try
{
validatingBinder.UpdateFrom(entity, controllerContext.HttpContext.Request.Form, bindingContext.ModelState, bindingContext.ModelName);
}
catch (ValidationException ex)
{}
return entity;
}


}
其BindModel方法中“获取当前要编辑的用户数据操作”就是通过下面这一行完成的:
FetchEntity(bindingContext, controllerContext)
而try中的代码 validatingBinder.UpdateFrom()就是对上面所说的“ValidatingBinder”中的“UpdateFrom”调用。通过UpdateFrom之后就会将绑定时出现的错误异常进行收集。
有了这种绑定,可以说设置上完成了,而如何将验证规则绑定到相应的Model对象上呢?
为了实现这个功能,Suteki.Shop提供了一个叫做ValidationProperty的泛型类,它提供了对于数字,是否为空, IsDecimal,最大值,最小值,IsEmail等验证功能。并以扩展方法的行式提供出来,相应代码如下:
为了实现这个功能,Suteki.Shop提供了一个叫做ValidationProperty的泛型类,它提供了对于数字,是否为空, IsDecimal,最大值,最小值,IsEmail等验证功能。并以扩展方法的行式提供出来,相应代码如下:
public static class ValidationExtensions
{
public static ValidationProperty<T> Label<T>(this T value, string label)
{
return new ValidationProperty<T>(value, label);
}
}
public class ValidationProperty<T>
{
T value;
string label;
public ValidationProperty(T value, string label)
{
this.value = value;
this.label = label;
}
public bool IsObject
{
get { return typeof (object).IsAssignableFrom(typeof (T)); }
}
public bool IsString
{
get { return (IsObject && typeof (string).IsAssignableFrom(typeof (T))); }
}
public string ValueAsString
{
get { return value as string; }
}
public T Value
{
get { return value; }
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsRequired()
{
if (value == null)
{
throw new ValidationException(label, StringExtensions.With("You must enter a value for {0}", label));
}
if (IsString && string.IsNullOrEmpty(ValueAsString))
{
throw new ValidationException(label, StringExtensions.With("You must enter a value for {0}", label));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsNumeric()
{
if(IsString)
{
// the obvious thing (int.Parse) doesn't work for very long strings of digits
if (ValueAsString.Trim().Any(c => !char.IsDigit(c)))
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must be a number e.g. 240".With(label));
}
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsDecimal()
{
if (IsString && ValueAsString.Trim().Any(c => !(char.IsDigit(c) || c == '.')))
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must be a decimal number e.g 12.30".With(label));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsNonZero()
{
int test;
if (!int.TryParse(value.ToString(), out test))
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must be a non-zero number".With(label));
}
if (test == 0)
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must be non-zero".With(label));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> WithMaxLength(int maxLength)
{
if (IsString && ValueAsString.Length > maxLength)
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must not exceed {1} characters".With(label, maxLength));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> WithLengthRange(IEnumerable<int> range)
{
if (IsString && ValueAsString.Length < range.Min() || ValueAsString.Length > range.Max())
{
throw new ValidationException(label,
"{0} length must be between {1} and {2} characters".With(label, range.Min(), range.Max()));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsEmail()
{
// ignore is null or empty, use IsRequired in parrallel to check this if needed
if (!IsString) return this;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(ValueAsString)) return this;
const string patternLenient = @"\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*";
if (!Regex.Match(ValueAsString, patternLenient).Success)
{
throw new ValidationException(label,"{0} must be a valid email address".With(label));
}
return this;
}
public ValidationProperty<T> IsCreditCard()
{
if (IsString)
{
var trimmedValue = Regex.Replace(value.ToString(), "[^0-9]", "");
trimmedValue.Label(label).IsNumeric().WithLengthRange(13.To(19));
var numbers = trimmedValue.Trim().Reverse().Select(c => int.Parse(c.ToString()));
var oddSum = numbers.AtOddPositions().Sum();
var doubleEvenSum = numbers.AtEvenPositions().SelectMany(i => new[] { (i * 2) % 10, (i * 2) / 10 }).Sum();
if ((oddSum + doubleEvenSum) % 10 != 0)
{
throw new ValidationException(label, "{0} is not a valid credit card number".With(label));
}
}
return this;
}
}
使用它就可以很方便的对Model中的相关属性添加验证规则了。以User为例,其验证规则添加内容如下(Suteki.Shop\Models\User.cs):
public
void
Validate()
{
Validator validator = new Validator
{
() => Email.Label( " Email " ).IsRequired().IsEmail(),
() => Password.Label( " Password " ).IsRequired(),
};
validator.Validate();
}
{
Validator validator = new Validator
{
() => Email.Label( " Email " ).IsRequired().IsEmail(),
() => Password.Label( " Password " ).IsRequired(),
};
validator.Validate();
}
在规则添加完成后,就把对获取到的信息进行验证了,下面是验证的实现方法:
public
class
Validator : List
<
Action
>
{
public void Validate()
{
var errors = new List < ValidationException > ();
foreach (Action validation in this )
{
try
{
validation();
}
catch (ValidationException validationException)
{
errors.Add(validationException);
}
}
if (errors.Count > 0 )
{
// backwards compatibility
string error = string .Join( "" , errors.Select(x => x.Message + " <br /> " ).ToArray());
throw new ValidationException(error, errors);
}
}
}
{
public void Validate()
{
var errors = new List < ValidationException > ();
foreach (Action validation in this )
{
try
{
validation();
}
catch (ValidationException validationException)
{
errors.Add(validationException);
}
}
if (errors.Count > 0 )
{
// backwards compatibility
string error = string .Join( "" , errors.Select(x => x.Message + " <br /> " ).ToArray());
throw new ValidationException(error, errors);
}
}
}
代码比较简单,大家看一下就可以了。
到这里,主要的代码就介绍完了,下面再后到UserController中看看Action是如何调用验证方法并发验证错误信息复制到ModelState中的,接着看一下编辑用户信息这个Action:
到这里,主要的代码就介绍完了,下面再后到UserController中看看Action是如何调用验证方法并发验证错误信息复制到ModelState中的,接着看一下编辑用户信息这个Action:
[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post), UnitOfWork]
public ActionResult Edit([DataBind] User user, string password)
{
if ( ! string .IsNullOrEmpty(password))
{
user.Password = userService.HashPassword(password);
}
try
{
user.Validate();
}
catch (ValidationException validationException)
{
validationException.CopyToModelState(ModelState, " user " );
return View( " Edit " , EditViewData.WithUser(user));
}
return View( " Edit " , EditViewData.WithUser(user).WithMessage( " Changes have been saved " ));
}
public ActionResult Edit([DataBind] User user, string password)
{
if ( ! string .IsNullOrEmpty(password))
{
user.Password = userService.HashPassword(password);
}
try
{
user.Validate();
}
catch (ValidationException validationException)
{
validationException.CopyToModelState(ModelState, " user " );
return View( " Edit " , EditViewData.WithUser(user));
}
return View( " Edit " , EditViewData.WithUser(user).WithMessage( " Changes have been saved " ));
}
大家看到了吧,Try中的user.Validate()就是启动验证的功能,而在Catch中使用CopyToModelState方法将错误信息Copy到当前Controller中的ModelState中,如下:
public
void
CopyToModelState(ModelStateDictionary dictionary,
string
prefix)
{
foreach (var error in errors)
{
string key = string .IsNullOrEmpty(prefix) ? error.propertyKey : prefix + " . " + error.propertyKey;
dictionary.AddModelError(key, error.Message);
}
}
{
foreach (var error in errors)
{
string key = string .IsNullOrEmpty(prefix) ? error.propertyKey : prefix + " . " + error.propertyKey;
dictionary.AddModelError(key, error.Message);
}
}
这样在前台View中,通过Html.ValidationSummary()方法来显示验证结果,现在我们看一下最终的运行效果:
以“输入错误的Email地址”为例:

好了,今天的内容就先到这里了。

好了,今天的内容就先到这里了。