高性能web服务器nginx(三)之源码搭建LNMP
一、环境准备
1、关闭防火墙及selinux
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# iptables -F
[root@hpf-linux ~]# getenforce
Disabled
|
2、更改yum源(此步根据自身需要更改)
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-6.repo
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo{,.bak}
[root@hpf-linux ~]# yum repolist
|
3、同步时间
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# ntpdate 202.120.2.101
|
4、安装epel源
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# yum install -y epel-release
|
5、实验环境介绍
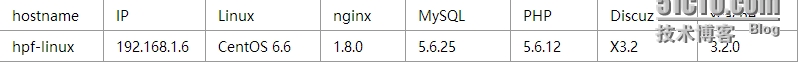
二、编译安装Nginx
1、下载nginx并解压
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz
[root@hpf-linux ~]# tar -xf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz
|
2、创建nginx运行用户
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# groupadd -g 108 -r nginx
[root@hpf-linux ~]# useradd -u 108 -r -g 108 nginx
[root@hpf-linux ~]# id nginx
uid=108(nginx) gid=108(nginx) 组=108(nginx)
|
3、安装依赖包
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# yum install -y gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel
|
4、编译安装nginx
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd nginx-1.8.0
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi --with-pcre
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# make && make install
|
5、查看nginx命令安装的路径
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# which nginx
/usr/sbin/nginx
|
查看nginx安装版本:
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.8.0
|
查看nginx编译选项:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.8.0
built by gcc 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-16) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.1e-fips 11 Feb 2013
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi --with-pcre
|
6、为nginx提供SysV init脚本:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# vim /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \
# proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
make_dirs() {
# make required directories
user=`nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed 's/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g' -`
options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep 'configure arguments:'`
for opt in $options; do
if [ `echo $opt | grep '.*-temp-path'` ]; then
value=`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2`
if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then
# echo "creating" $value
mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value
fi
fi
done
}
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
make_dirs
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest || return $?
stop
sleep 1
start
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit 2
esac
|
7、将脚本赋予执行权限并添加到服务启动列表
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# chkconfig --add nginx
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# chkconfig nginx on
|
8、启动nginx查看监听的端口
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# service nginx start
正在启动 nginx: [确定]
[root@hpf-linux nginx-1.8.0]# ss -tunlp |grep nginx
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* users:(("nginx",6177,6),("nginx",6179,6))
|
9、浏览器测试是否启动
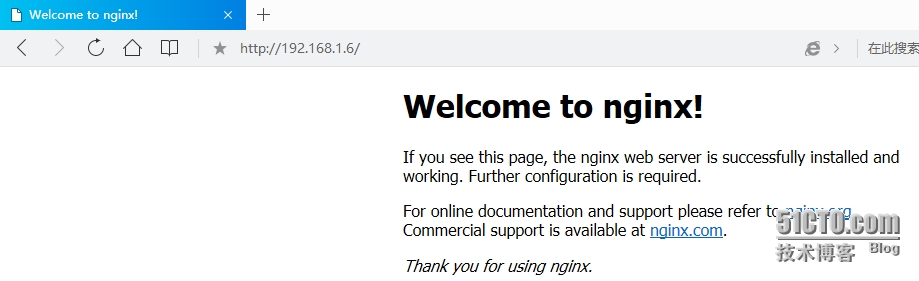
10、将在vim打开nginx配置文件时实现语句高亮显示
http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1886
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mkdir -pv .vim/syntax
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mv nginx.vim .vim/syntax
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim .vim/filetype.vim
au BufRead,BufNewFile /etc/nginx/*,/usr/local/nginx/conf/* if &ft == '' | setfiletype nginx | endif
|
三、安装与配置Mysql数据库
1、创建存放数据目录
正常情况实在有冗余raid上创建逻辑卷,这样既保证数据的扩展性,又有容灾的能力,这里节省步骤只是在系统中创建个目录。
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mkdir /data/mydata -pv
|
2、创建mysql用户
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# groupadd -r mysql
[root@hpf-linux ~]# useradd -g mysql -r -s /sbin/nologin -M -d /mydata/data mysql
[root@hpf-linux ~]# chown -R mysql.mysql /data/mydata/
|
3、安装初始化依赖的库
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# yum install -y libaio
|
4、安装并初始化mysql
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# tar -xf mysql-5.6.25-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd /usr/local/
[root@hpf-linux local]# ln mysql-5.6.25-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64 mysql -sv
"mysql" -> "mysql-5.6.25-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64"
[root@hpf-linux local]# cd mysql
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# chown -R mysql.mysql ./*
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mydata/
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# chown -R root ./*
|
5、为mysql提供主配置文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# cp /etc/my.cnf{,.bak}
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# grep -v '^#' /etc/my.cnf
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
port = 3306
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
skip-external-locking
key_buffer_size = 256M
max_allowed_packet = 1M
table_open_cache = 256
sort_buffer_size = 1M
read_buffer_size = 1M
read_rnd_buffer_size = 4M
myisam_sort_buffer_size = 64M
thread_cache_size = 8
query_cache_size= 16M
thread_concurrency = 2
datadir=/data/mydata
log-bin=mysql-bin
binlog_format=mixed
server-id = 1
[mysqldump]
quick
max_allowed_packet = 16M
[mysql]
no-auto-rehash
[myisamchk]
key_buffer_size = 128M
sort_buffer_size = 128M
read_buffer = 2M
write_buffer = 2M
[mysqlhotcopy]
interactive-timeout
|
6、为mysql提供sysv服务脚本并启动服务
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# chkconfig --add mysqld
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# chkconfig mysqld on ^C
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# service mysqld start
Starting MySQL............. SUCCESS!
|
7、查看mysql是否初始化和启动成功
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# ls /data/mydata/
auto.cnf hpf-linux.pid ib_logfile0 mysql mysql-bin.index test
hpf-linux.err ibdata1 ib_logfile1 mysql-bin.000001 performance_schema
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# ss -tunlp |grep mysql
tcp LISTEN 0 80 :::3306 :::* users:(("mysqld",6713,11))
|
8、后续配置
输出mysql的man手册至man命令的查找路径:
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# vim /etc/man.config
MANPATH /usr/local/mysql/man
|
输出mysql的头文件至系统头文件路径/usr/include:
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# ln -sv /usr/local/mysql/include/ /usr/include/mysql
"/usr/include/mysql" -> "/usr/local/mysql/include/"
|
输出mysql的库文件给系统库查找路径:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# vim /etc/ld.so.conf.d/mysql.conf
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# ldconfig -v
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# ldconfig -p |grep mysql
libtcmalloc_minimal.so.0 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/mysql/lib/libtcmalloc_minimal.so.0
libmysqlclient_r.so.16 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/lib64/mysql/libmysqlclient_r.so.16
libmysqlclient.so.18 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/mysql/lib/libmysqlclient.so.18
libmysqlclient.so.16 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/lib64/mysql/libmysqlclient.so.16
libmysqlclient.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/mysql/lib/libmysqlclient.so
|
修改PATH环境变量,让系统可以直接使用mysql的相关命令:
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# vim /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/mysql/bin
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# source /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
|
9、连接mysql将匿名用户删除并设置密码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' =PASSWORD('redhat');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'127.0.0.1' =PASSWORD('redhat');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'hpf-linux' =PASSWORD('redhat');
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop user 'root'@'::1';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop user ''@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop user ''@'hpf-linux';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select user,host,password from mysql.user;
+------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
| user | host | password |
+------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
| root | localhost | *84BB5DF4823DA319BBF86C99624479A198E6EEE9 |
| root | hpf-linux | *84BB5DF4823DA319BBF86C99624479A198E6EEE9 |
| root | 127.0.0.1 | *84BB5DF4823DA319BBF86C99624479A198E6EEE9 |
+------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
再次登录mysql就需要帐号密码了:
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux mysql]# mysql -uroot -hlocalhost -p
Enter password:
|
10、设置mysql不输入用户名密码直接登录数据库
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim .my.cnf
[mysql]
user = root
password = redhat
host = localhost
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Server version: 5.6.25-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
|
四、编译安装PHP
1、解决依赖关系
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# yum install -y libxml2-devel bzip2-devel libcurl-devel libmcrypt-devel
|
2、安装php
|
1
2
3
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd php-5.6.12
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php --with-mysql=/usr/local/mysql --with-openssl --enable-fpm --enable-sockets --enable-sysvshm --with-mysqli=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_config --enable-mbstring --with-freetype-dir --with-jpeg-dir --with-png-dir --with-zlib-dir --with-libxml-dir=/usr/ --enable-xml --with-mhash --with-mcrypt --with-config-file-path=/etc --with-config-file-scan-dir=/etc/php.d --with-bz2 --with-curl
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# make && make install
|
3、为php提供配置文件
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# cp php.ini-production /etc/php.ini
|
4、为php-fpm提供Sysv init脚本,并将其添加至服务列表
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# cp sapi/fpm/init.d.php-fpm /etc/init.d/php-fpm
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/php-fpm
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# chkconfig --add php-fpm
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# chkconfig php-fpm on
|
5、为php-fpm提供配置文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@hpf-linux php-5.6.12]# cd /usr/local/php/
[root@hpf-linux php]# ls
bin etc include lib php sbin var
[root@hpf-linux php]# cp etc/php-fpm.conf.default etc/php-fpm.conf
[root@hpf-linux php]# vim etc/php-fpm.conf
|
配置fpm的相关选项为你所需要的值,并启用pid文件(如下最后一行)
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
pm.max_children = 150
pm.start_servers = 8
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
pm.max_spare_servers = 10
pid = run/php-fpm.pid
|
6、启动php-fpm
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
[root@hpf-linux php]# service php-fpm start
Starting php-fpm done
[root@hpf-linux php]# ps aux |grep php-fpm
root 129929 0.5 0.5 112320 5296 ? Ss 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: master process (/usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf)
nobody 129930 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129931 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129932 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129933 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129934 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129935 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129936 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 129937 0.0 0.4 112320 4388 ? S 15:05 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
root 129939 0.0 0.0 103252 880 pts/0 S+ 15:05 0:00 grep php-fpm
[root@hpf-linux php]# ss -tunlp |grep php
tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:9000 *:* users:(("php-fpm",129929,7),("php-fpm",129930,0),("php-fpm",129931,0),("php-fpm",129932,0),("php-fpm",129933,0),("php-fpm",129934,0),("php-fpm",129935,0),("php-fpm",129936,0),("php-fpm",129937,0))
|
五、整合Nginx与PHP (FastCGI)
1、什么是 FastCGI
FastCGI是一个可伸缩地、高速地在HTTP server和动态脚本语言间通信的接口。多数流行的HTTP server都支持FastCGI,包括Apache、Nginx和lighttpd等。同时,FastCGI也被许多脚本语言支持,其中就有PHP。
FastCGI是从CGI发展改进而来的。传统CGI接口方式的主要缺点是性能很差,因为每次HTTP服务器遇到动态程序时都需要重新启动脚本解析器来执行解析,然后将结果返回给HTTP服务器。这在处理高并发访问时几乎是不可用的。另外传统的CGI接口方式安全性也很差,现在已经很少使用了。
FastCGI接口方式采用C/S结构,可以将HTTP服务器和脚本解析服务器分开,同时在脚本解析服务器上启动一个或者多个脚本解析守护进程。当HTTP服务器每次遇到动态程序时,可以将其直接交付给FastCGI进程来执行,然后将得到的结果返回给浏览器。这种方式可以让HTTP服务器专一地处理静态请求或者将动态脚本服务器的结果返回给客户端,这在很大程度上提高了整个应用系统的性能。
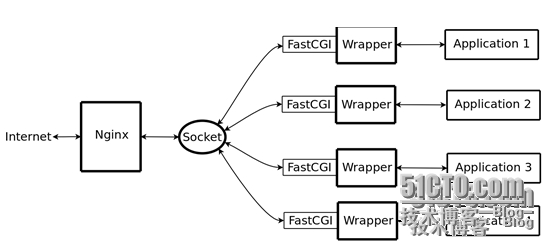
2、Nginx+FastCGI运行原理
Nginx不支持对外部程序的直接调用或者解析,所有的外部程序(包括PHP)必须通过FastCGI接口来调用。FastCGI接口在Linux下是socket(这个socket可以是文件socket,也可以是ip socket)。为了调用CGI程序,还需要一个FastCGI的wrapper(wrapper可以理解为用于启动另一个程序的程序),这个wrapper绑定在某个固定socket上,如端口或者文件socket。当Nginx将CGI请求发送给这个socket的时候,通过FastCGI接口,wrapper接收到请求,然后派生出一个新的线程,这个线程调用解释器或者外部程序处理脚本并读取返回数据;接着,wrapper再将返回的数据通过FastCGI接口,沿着固定的socket传递给Nginx;最后,Nginx将返回的数据发送给客户端。这就是Nginx+FastCGI的整个运作过程。如下图:
3、spawn-fcgi与PHP-FPM
前面介绍过,FastCGI接口方式在脚本解析服务器上启动一个或者多个守护进程对动态脚本进行解析,这些进程就是FastCGI进程管理器,或者称为FastCGI引擎。 spawn-fcgi与PHP-FPM就是支持PHP的两个FastCGI进程管理器。
下面简单介绍spawn-fcgi与PHP-FPM的异同。
spawn-fcgi是HTTP服务器lighttpd的一部分,目前已经独立成为一个项目,一般与lighttpd配合使用来支持PHP。但是ligttpd的spwan-fcgi在高并发访问的时候,会出现内存泄漏甚至自动重启FastCGI的问题。
Nginx是个轻量级的HTTP server,必须借助第三方的FastCGI处理器才可以对PHP进行解析,因此Nginx+spawn-fcgi的组合也可以实现对PHP的解析,这里不过多讲述。PHP-FPM也是一个第三方的FastCGI进程管理器,它是作为PHP的一个补丁来开发的(PHP从5.3.3以后已将PHP-FPM整合进PHP中,只要在./configure的时候带 --enable-fpm参数即可开启PHP-FPM),在安装的时候也需要和PHP源码一起编译,也就是说PHP-FPM被编译到PHP内核中,因此在处理性能方面更加优秀。同时PHP-FPM在处理高并发方面也比spawn-fcgi引擎好很多,因此,推荐使用Nginx+PHP/PHP-FPM这个组合对PHP进行解析。
FastCGI 的主要优点是把动态语言和HTTP Server分离开来,所以Nginx与PHP/PHP-FPM经常被部署在不同的服务器上,以分担前端Nginx服务器的压力,使Nginx专一处理静态请求和转发动态请求,而PHP/PHP-FPM服务器专一解析PHP动态请求。
4、整合Nginx与PHP (FastCGI)
修改nginx配置文件,启用如下选项。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf{,.bak}
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
location / {
root /www/a.com;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
root /www/a.com;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mkdir /www/a.com -pv
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim /www/a.com/index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
|
编辑/etc/nginx/fastcgi_params,将其内容更改为如下内容
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cp /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params{,.bak}
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params
fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1;
fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
|
重新加载一下nginx的配置文件:
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# service nginx reload
|
通过浏览器访问此测试页面:
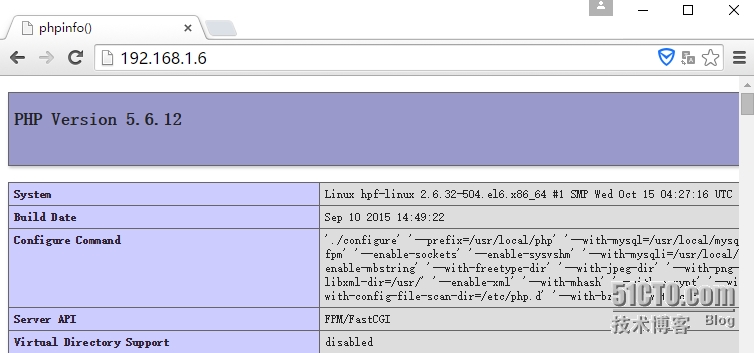
六、安装与配置xCache加速器
1、安装xcache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# tar -xf xcache-3.2.0.tar.gz
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd xcache-3.2.0
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# /usr/local/php/bin/phpize
Configuring for:
PHP Api Version: 20131106
Zend Module Api No: 20131226
Zend Extension Api No: 220131226
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# ./configure --enable-xcache --with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# make && make install
Installing shared extensions: /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20131226/
|
2、编辑php.ini,整合php和xcache
将xcache提供的样例配置导入php.ini :
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# mkdir /etc/php.d
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# cp xcache.ini /etc/php.d/
|
编辑/etc/php.d/xcache.ini,找到zend_extension开头的行,修改为如下行:
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# vim /etc/php.d/xcache.ini
extension = /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20131226/xcache.so
|
3、重新启动php-fpm
|
1
|
[root@hpf-linux xcache-3.2.0]# service php-fpm restart
|
4、浏览器验证是否加载xcache模块
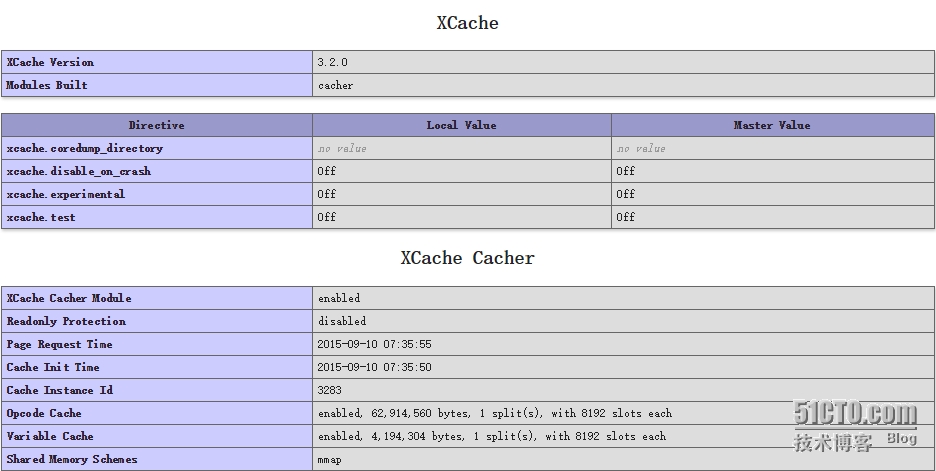
5、PHP连接Mysql测试
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
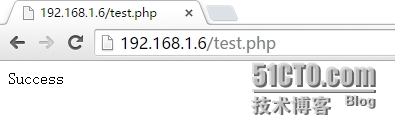
[root@hpf-linux ~]# vim /www/a.com/test.php
<?php
$conn=mysql_connect('localhost','root','redhat');
if ($conn)
echo "Success";
else
echo "Failure";
?>
|
浏览器测试:
七、安装phppMyAdmin工具
1、解压phppMyAdmin软件
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# unzip phpMyAdmin-4.1.4-all-languages.3715384168.zip
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mv phpMyAdmin-4.1.4-all-languages /www/a.com/pma
|
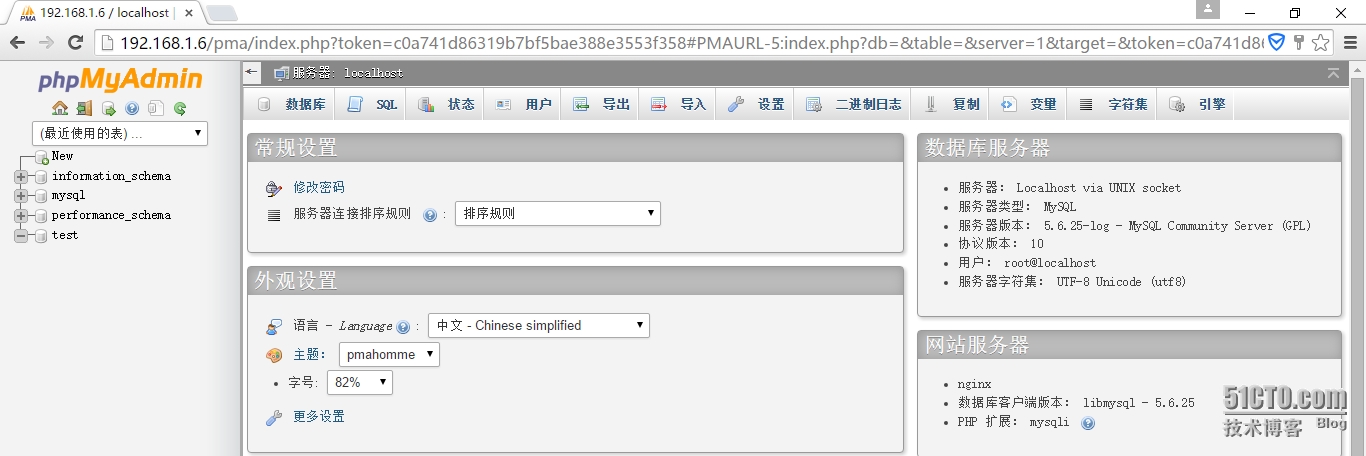
在浏览器输入IP/pma,后在输入mysql数据库的帐号密码就能登录phpMyAdmin了。
八、安装wordpress
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# unzip wordpress-4.2-zh_CN.zip
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cp wordpress /www/a.com/ -r
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd /www/a.com/wordpress/
[root@hpf-linux wordpress]# cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
[root@hpf-linux wordpress]# vim wp-config.php
/** WordPress数据库的名称 */
define('DB_NAME', 'wpdb');
/** MySQL数据库用户名 */
define('DB_USER', 'wpuser');
/** MySQL数据库密码 */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'redhat');
/** MySQL主机 */
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
root@hpf-linux wordpress]# mysql
mysql> create database wpdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.15 sec)
mysql> grant all privileges on wpdb.* to 'wpuser'@'localhost' identified by 'redhat';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
[root@hpf-linux wordpress]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.a.com;
location / {
root /www/a.com/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
root /www/a.com;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
[root@hpf-linux wordpress]# service nginx reload
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
重新载入 nginx: [确定]
|
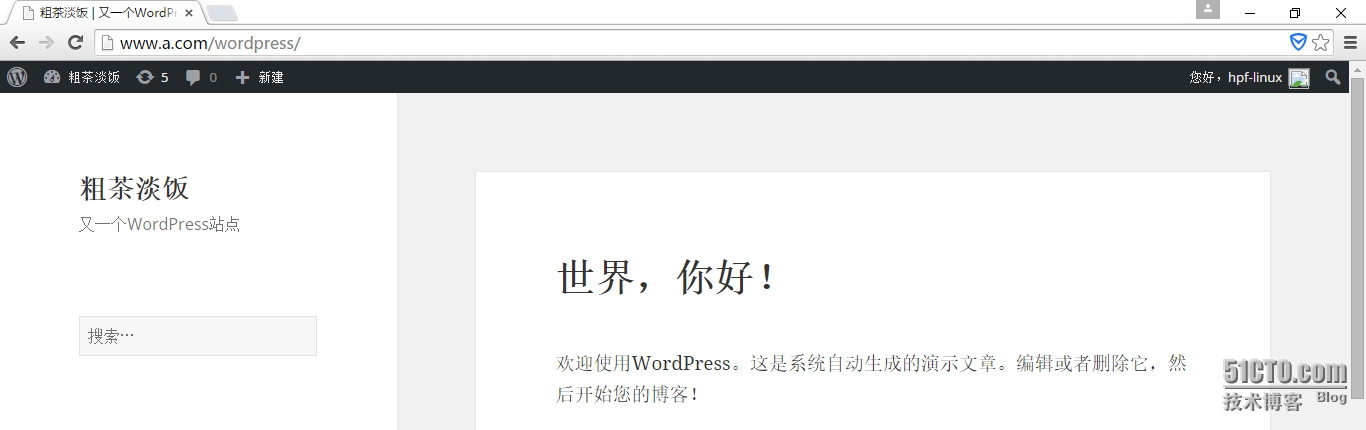
浏览器输入本地手动设置的域名/wordpress,之后按提示输入就好了。
九、安装并测试Discuz论坛
1、准备Discuz 3.2
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# unzip Discuz_X3.2_SC_UTF8.zip
[root@hpf-linux ~]# mv upload /www/a.com/
|
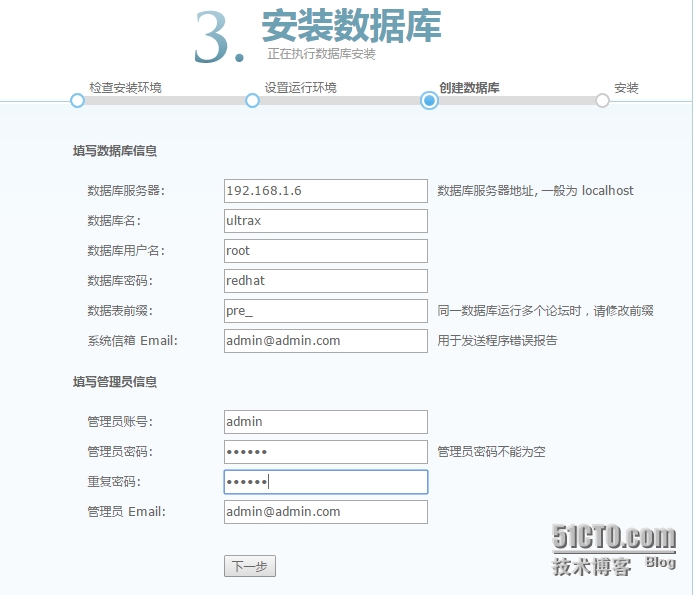
2、授权主机对mysql的访问
|
1
2
3
4
|
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'192.168.%.%' identified by 'redhat';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
|
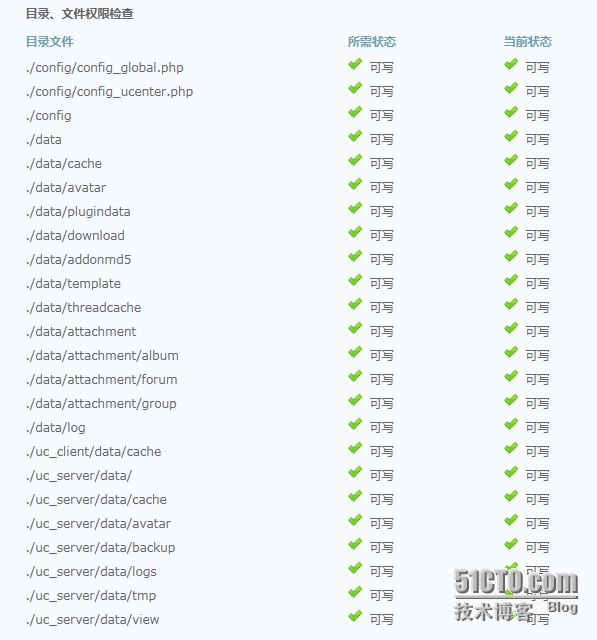
3、修改后目录权限
|
1
2
|
[root@hpf-linux ~]# cd /www/a.com/upload/
[root@hpf-linux upload]# chmod 777 ./data ./config/ ./data/cache/ ./data/avatar/ ./data/plugindata/ ./data/download/ ./data/addonmd5/ ./data/template/ ./ data/threadcache/ ./data/attachment/ ./data/attachment/album/ ./data/attachment/forum/ ./data/attachment/group/ ./data/log/ ./uc_client/data/cache/ ./uc_server/data ./uc_server/data/avatar/ ./uc_server/data/backup/ ./uc_server/data/logs/ ./uc_server/data/tmp/ ./uc_server/data/view/ ./uc_server/data/cache/
|
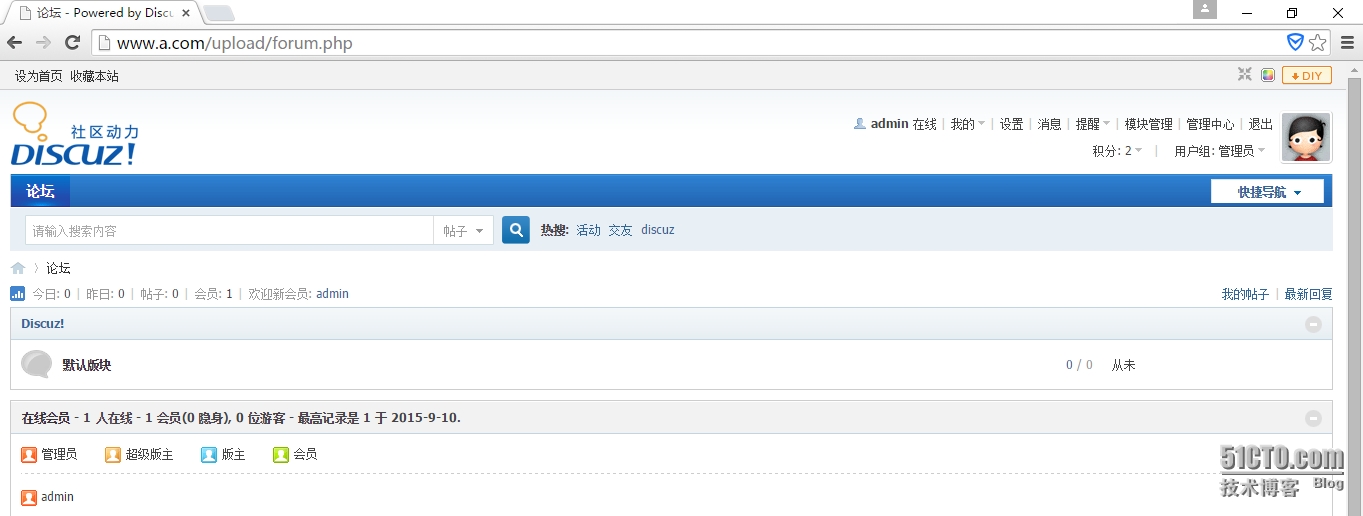
在浏览器输入(本地域名/upload),下载就是下一步啥的。