PHP服务器文件管理器开发小结(五):获取文件属性信息
回顾第三节列出的基本代码框架,作者为枚举文件属性信息预留了不少的表头:
echo "<table>"; echo "<tr><th>Name</th><th>Type</th><th>Readable</th><th>Writable</th><th>Excutable</th><th>Size</th><th>Created</th><th>Modified</th><th>Access</th><th>Operation</th></tr>";
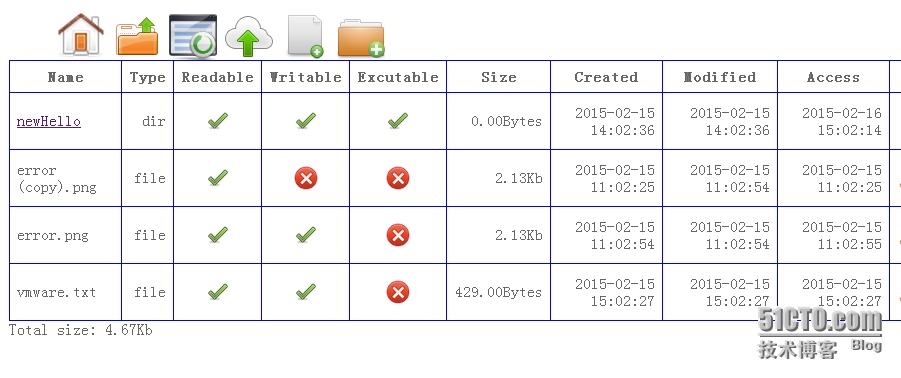
如下图:
从左至右分别为名称、类型、可读性、可写性、可执行性、大小、创建时间、修改时间、访问时间、操作。类型为文件夹、文件、连接等,可读、可写、可执行通过对号和错号图标标识True or False。大小提供一个约数,创建、修改、访问时间提供标准时间表示,操作栏则列出对该元素可执行的操作。
具体到文件,每一行的内容通过getFileElemInfo函数列出:
if (isset($fileList))
{
$isDirEmpty = false;
natsort($fileList);
foreach($fileList as $fileName)
{
echo getFileElemInfo($strDirName, $fileName);
}
}
使用natsort,可以为文件名提供比较合理的排序模式。如果需要更复杂的排序,可以使用usort,这里不做展开。
通过stat()函数可以得到文件比较多的属性了,而文件类型可以通过filetype得到。
下面是前两项的描述方法:
function getDirElemInfo($dirPath, $elemName)
{
$dirPath = rtrim($dirPath, "/");
$filePath = $dirPath."/".$elemName;
if (!($res = stat($filePath)))
return "";
$info = "<tr>";
$elemType = filetype($filePath)
$info.= "<td class=\"fileName\">".$elemName."</td>";
$info.= "<td>".$elemType."</td>";
$info变量保存着整个行的信息,下面会继续用到。
通过下面三个函数可以得到后面三栏的值:
可读:is_readable
可写:is_writable
可执行:is_executable
然而,这样得到的结果只是BOOL值,需要转化为具体的图像链接。下面用?:三元算子简洁的实现了这一功能。
$pathCorrect = "images/correct.png"; $pathError = "images/error.png"; $pathReadable = is_readable($filePath)?$pathCorrect:$pathError; $info.= "<td class=\"sig\"><img src=\"".$pathReadable."\" alt=\"\" class=\"tabmenu\"></td>"; $pathWritable = is_writable($filePath)?$pathCorrect:$pathError; $info.= "<td class=\"sig\"><img src=\"".$pathWritable."\" alt=\"\" class=\"tabmenu\"></td>"; $pathExcutable = is_executable($filePath)?$pathCorrect:$pathError; $info.= "<td class=\"sig\"><img src=\"".$pathExcutable."\" alt=\"\" class=\"tabmenu\"></td>";
注意其使用的样式类sig,对应的css为:
.sig{
text-align: center;
}
可以使图标居中显示。
使用filesize或stat()["size"]可以获取基于BYTE的文件大小,但是那样太冗余,因此笔者编写了下面的sizeToBytes函数用于给出文件的相对大小:
function sizeToBytes($size)
{
$listUnits = array("Bytes", "Kb", "Mb", "Gb", "Tb");
$index = 0;
$base = 1;
while ($size >= $base * 1024)
{
$base *= 1024;
$index ++;
}
return sprintf("%.2f%s", $size/$base, $listUnits[$index]);
}
$info.= "<td>".sizeToBytes($res["size"])."</td>";
文件的创建、修改、访问时间可以通过以下方式列出
$info.= "<td>".date("Y-m-d H:m:s",$res["ctime"])."</td>";
$info.= "<td>".date("Y-m-d H:m:s",$res["mtime"])."</td>";
$info.= "<td>".date("Y-m-d H:m:s",$res["atime"])."</td>";
实际上,上面的诸多函数除了文件大小外其他都适用于文件夹的属性。
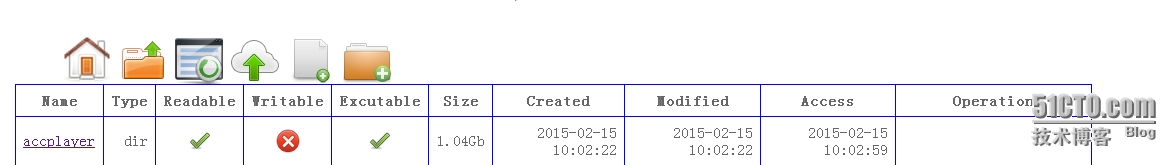
具体效果: