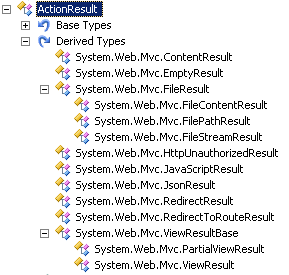
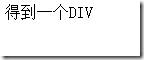MVC Controller与ActionResult的返回值
Action的要求
• 必须是一个公有方法
• 必须返回ActionResult类型
• 必须是实例方法
• 不能是范型方法
• 没有标注NonActionAttribute
• 不能被重载(overload)
Controller 提供了众多的方法让我们返回各种类型的 ActionResult。
1. View
最常用的一种,用于返回一个 "标准" 页面。
{
if (model != null)
{
base.ViewData.Model = model;
}
return new ViewResult
{
ViewName = viewName,
MasterName = masterName,
ViewData = base.ViewData,
TempData = base.TempData
};
}
public class ViewResult : ViewResultBase
{
protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context)
{
ViewEngineResult result = ViewEngineCollection.FindView(context, ViewName, MasterName);
if (result.View != null)
{
return result;
}
...
}
}
这个页面默认是 ViewPage,也可以是我们自己定义的其它模板引擎页面。
MVC 还提供了强类型的 ViewPage<TModel>。
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
public class TestController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["message"] = "Hello, World!";
var model = new User { Name = "Tom", Age = 13 };
return View(model);
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
Name: <%= Model.Name %>; Age: <%= Model.Age %>
</body>
</html>
在 WebForm 时代,我们就已经习惯了将一个页面分解成多个 UserControl,现在我们依然可以这么做。htmlHelper 专门提供了 RenderPartial 扩展方法,从当前视图目录(Views\xxx)下载入 .ascx 页面。
{
public static void RenderPartial(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, partialViewName, model, viewData)
{
htmlHelper.RenderPartialInternal(partialViewName, viewData, model, ViewEngines.Engines);
}
}
public class HtmlHelper
{
internal virtual void RenderPartialInternal(string partialViewName, ViewDataDictionary viewData,
object model, ViewEngineCollection viewEngineCollection)
{
...
ViewDataDictionary newViewData = null;
if (model == null)
{
if (viewData == null)
newViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(ViewData);
else
newViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(viewData);
}
else
{
if (viewData == null)
newViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(model);
else
newViewData = new ViewDataDictionary(viewData) { Model = model };
}
ViewContext newViewContext = new ViewContext(ViewContext, ViewContext.View,
newViewData, ViewContext.TempData);
IView view = FindPartialView(newViewContext, partialViewName, viewEngineCollection);
view.Render(newViewContext, ViewContext.HttpContext.Response.Output);
}
internal static IView FindPartialView(viewContext, partialViewName, viewEngineCollection)
{
ViewEngineResult result = viewEngineCollection.FindPartialView(viewContext, partialViewName);
if (result.View != null)
{
return result.View;
}
...
}
}
RenderPartialInternal 调用 FindParitialView 从视图引擎中载入 .ascx,同时将当前的环境参数传递给它。也就是说 RenderPartial 只是一种视图级别的行为,并不会再次触发 Controller Action 操作,这点要和 Controller.PartialView() 区别开来。
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
Name: <%= Model.Name %>; Age: <%= Model.Age %>
<br />
<% Html.RenderPartial("Part"); %>
</body>
</html>
Part.ascx
<%= ViewData["message"] %>
<br />
<%= Model.Name %>
2. Content
Content 用于输出(Response.Write) "静态" 片段。
{
return new ContentResult
{
Content = content,
ContentType = contentType,
ContentEncoding = contentEncoding
};
}
public class ContentResult : ActionResult
{
public string Content { get; set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(ContentType))
{
response.ContentType = ContentType;
}
if (ContentEncoding != null)
{
response.ContentEncoding = ContentEncoding;
}
if (Content != null)
{
response.Write(Content);
}
}
}
看看和 jQuery 的配合使用。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Part()
{
return Content("<a href=\"http://www.rainsts.net\">Q.yuhen</a>");
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
<script src="http://www.cnblogs.com/Scripts/jquery-1.3.1.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function()
{
$("#div1").load("/test/part");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
</div>
</body>
</html>
3. PartialView
Controller.PartialView() 和 HtmlHelper.RenderPartial() 的不同之处在于前者是再次执行 ActionInvoke 并返回一个 ActionResult 结果,后者只是使用现有的 ViewContext 显示一个视图片段。而与 Controller.Content() 的区别是 PartialView() 使用视图引擎输出一个 "动态" 的 ascx 结果。
{
if (model != null)
{
ViewData.Model = model;
}
return new PartialViewResult
{
ViewName = viewName,
ViewData = ViewData,
TempData = TempData
};
}
public class PartialViewResult : ViewResultBase
{
protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context)
{
ViewEngineResult result = ViewEngineCollection.FindPartialView(context, ViewName);
if (result.View != null)
{
return result;
}
...
}
}
和 Content() 一样,我们通常将其和 jQuery 等 Ajax 框架配合使用。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Part()
{
ViewData["time"] = DateTime.Now;
var model = new User { Name = "Tom", Age = 13 };
return PartialView(model);
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
<script src="http://www.cnblogs.com/Scripts/jquery-1.3.1.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function()
{
$("#div1").load("/test/part");
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
</div>
</body>
</html>
Part.ascx
<%= ViewData["time"] %> <br />
<%= Model.Name %>; <%= Model.Age %>
4. Redirect / RedirectToAction / RedirectToRoute
Controller 提供了几种方式,让我们在不同的 Action 之间进行跳转。
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
...
routes.MapRoute
(
"Test2",
"Test/T2/{name}/{age}",
new { controller = "Test", action = "T2", name = "", age = 0 }
);
...
}
}
方法1:
Redirect() 直接用 Response.Redirect() 完成 url 跳转。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return Redirect("/Test/T2/Tom/23");
}
public ActionResult T2(User user)
{
return Content(user.Name);
}
}
相关细节:
{
...
return new RedirectResult(url);
}
public class RedirectResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
string destinationUrl = UrlHelper.Content(Url, context.HttpContext);
context.HttpContext.Response.Redirect(destinationUrl, false /* endResponse */);
}
}
方法2:
RedirectToAction() 直接使用 Action Name 进行跳转。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return RedirectToAction("T2", new { name = "Tom", age = 23 });
}
public ActionResult T2(User user)
{
return Content(user.Name);
}
}
如果目标 Action 不在当前 Controller 类,则可以指定目标 Controller Name。
相关细节:
string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues)
{
RouteValueDictionary mergedRouteValues;
if (RouteData == null)
{
mergedRouteValues = RouteValuesHelpers.MergeRouteValues(actionName,
controllerName, null, routeValues, true /* includeImplicitMvcValues */);
}
else
{
mergedRouteValues = RouteValuesHelpers.MergeRouteValues(actionName,
controllerName, RouteData.Values, routeValues, true /* includeImplicitMvcValues */);
}
return new RedirectToRouteResult(mergedRouteValues);
}
public class RedirectToRouteResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
string destinationUrl = UrlHelper.GenerateUrl(RouteName, null /* actionName */,
null /* controllerName */, RouteValues, Routes, context.RequestContext,
false /* includeImplicitMvcValues */);
...
context.HttpContext.Response.Redirect(destinationUrl, false /* endResponse */);
}
}
可以看到 RedirectToRouteResult.ExecuteResult 中使用 Route 相关信息拼接成目标 Url 后进行跳转。
方法3:
RedirectToRoute() 则是直接用 MapRoute 时定义的 Route Name 进行跳转。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return RedirectToRoute("Test2", new { name = "Tom", age = 23 });
}
}
相关细节:
{
return new RedirectToRouteResult(routeName, RouteValuesHelpers.GetRouteValues(routeValues));
}
执行过程和 RedirectToAction() 相同。
5. Json
Json() 在编写 Ajax 时非常有用,可以将 Entity 等对象序列化成 JSON 格式供 Javascript 使用。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult GetUser(string name)
{
var user = new User { Name = name, Age = 23 };
return Json(user);
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
<script src="http://www.cnblogs.com/Scripts/jquery-1.3.1.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function()
{
$("#btnTest").click(function()
{
$.getJSON
(
"/Test/GetUser",
{ name: "Tom" },
function(json)
{
alert(json.Name + ";" + json.Age);
}
);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" id="btnTest" value="Test" />
</body>
</html>
很好用,不是吗?看看相关细节。
{
return new JsonResult
{
Data = data,
ContentType = contentType,
ContentEncoding = contentEncoding
};
}
public class JsonResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
if (Data != null)
{
JavaScriptSerializer serializer = new JavaScriptSerializer();
response.Write(serializer.Serialize(Data));
}
}
}
使用 System.Web.Script.Serialization.JavaScriptSerializer 完成 JSON 序列化操作,也就是说我们还可以用 ScriptIgnoreAttribute 排除某些属性。
6. Javascript
某些时候,我们需要根据一些逻辑判断来载入执行不同的 Javascript 代码。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult GetJs(int id)
{
switch (id)
{
case 1:
return JavaScript("alert('Hello, C#!');");
case 2:
return JavaScript("alert('Hello, MVC!');");
default:
return null;
}
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
<script src="http://www.cnblogs.com/Scripts/jquery-1.3.1.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function()
{
$("#btnTest").click(function()
{
var id = $("#txtId").val();
$.getScript("/Test/GetJs/" + id);
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="txtId" value="1" />
<input type="button" id="btnTest" value="Test" />
</body>
</html>
只是这种做法,似乎将 View 和 Controller 的耦合加大了…… 还不如直接用 Javascript 来处理这些。
{
return new JavaScriptResult { Script = script };
}
public class JavaScriptResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
response.ContentType = "application/x-javascript";
if (Script != null)
{
response.Write(Script);
}
}
}
7. File (Download / Upload)
File() 提供了 Download 功能。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Download(int id)
{
var filename = String.Format("~/Content/Download/{0}.rar", id);
var fileDownloadName = String.Format("{0}.rar", id);
return File(filename, "application/octet-stream", fileDownloadName);
}
}
当我们在浏览器请求 "/Test/Download/1" 是就会打开下载窗口,同时给出了保存文件名。
{
return new FileContentResult(fileContents, contentType) { FileDownloadName = fileDownloadName };
}
public abstract class FileResult : ActionResult
{
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
...
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
response.ContentType = ContentType;
...
WriteFile(response);
}
protected abstract void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response);
}
public class FileContentResult : FileResult
{
protected override void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response)
{
response.OutputStream.Write(FileContents, 0, FileContents.Length);
}
}
文件上传是另一个常用的 Web 应用。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Upload(HttpPostedFileBase file)
{
var filename = Server.MapPath("~/Content/Upload/" + Path.GetFileName(file.FileName));
file.SaveAs(filename);
return null;
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/Test/Upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="file" />
<input type="submit" name="upload" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
MVC 提供了一个 HttpPostedFileBaseModelBinder 将 Request.Files 的信息直接映射给 Action 同名参数。
{
public object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
...
HttpPostedFileBase theFile = controllerContext.HttpContext.Request.Files[bindingContext.ModelName];
// case 1: there was no <input type="file" ... /> element in the post
if (theFile == null)
{
return null;
}
// case 2: there was an <input type="file" ... /> element in the post, but it was left blank
if (theFile.ContentLength == 0 && String.IsNullOrEmpty(theFile.FileName))
{
return null;
}
// case 3: the file was posted
return theFile;
}
}
看看一次上传多个文件的演示。
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult Upload(HttpPostedFileBase file1, HttpPostedFileBase file2)
{
var html = String.Format("{0}:{1}<br />{2}:{3}",
file1.FileName, file1.InputStream.Length,
file2.FileName, file2.InputStream.Length);
return Content(html);
}
}
Index.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/Test/Upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input type="file" name="file1" />
<input type="file" name="file2" />
<input type="submit" name="upload" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
我们上边所看到的Action都是return View();我们可以看作这个返回值用于解析一个aspx文件。而它的返回类型是ActionResult如
public ActionResult Index() { return View(); }
除了View()之外那我们这里还能用于返回什么值呢?
一、ascx页面
场景:要返回代码片断,比如Ajax返回一个子页
我们先新建一个Action
public ActionResult Ascx() { return PartialView(); }
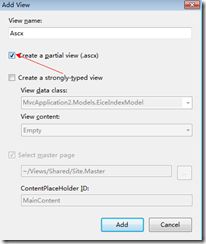
我们下面再建一个View,仍然是在Action中点右键,AddView。
于是新建了一个ascx页,我们将之少做改写一下
<%@ Control Language="C#" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewUserControl" %> <div> 得到一个DIV </div>
运行,得到页面
二、返回文本
除了上述情况,有时我们还会仅返回一段文本。
此时我们可以使用以下Action形式:
public ActionResult Text(){ return Content("这是一段文本"); }
三、返回Json
有时我们在调用Ajax时还会要求返回对象为Json序列化的结果,如:
public ActionResult ShowJson() { var m = new EiceIndexModel { Name = "邹健", Sex = true }; return Json(m); }
返回文本:
{"Name":"邹健","Sex":true}
四、输出JS文件
大多时候js文件都是静态的,但有时js文件可能也要动态生成这时我们可以这样输出
public ActionResult Js() { return JavaScript("var x=0;"); }
我们访问之,得到一个正常页面但其Content-Type:application/x-javascript; charset=utf-8
五、页面跳转
1.跳转到Url
public ActionResult rdurl() { return Redirect("http://www.baidu.com"); }
2.跳转到Action
public ActionResult rdaction() { return RedirectToAction("Index","Eice"); }
3.跳转到Routing规则
public ActionResult rdrouting() { return RedirectToRoute("Default",//Route名 new{ Controller = "Eice", Action = "Index" }); }
六、显示文件
public ActionResult fn() { return File( "/Content/site.css"//文件路径 , "text/css"//文件类型 ); }