基于二叉树和数组实现限制长度的最优Huffman编码
具体介绍详见上篇博客:基于二叉树和双向链表实现限制长度的最优Huffman编码
基于数组和基于链表的实现方式在效率上有明显区别:
编码256个符号,符号权重为1...256,限制长度为16,循环编码1w次,Release模式下。基于链表的耗时为8972ms,基于数组的耗时为1793ms,速度是链表实现方式的5倍.
详细代码例如以下:
基于数组和基于链表的实现方式在效率上有明显区别:
编码256个符号,符号权重为1...256,限制长度为16,循环编码1w次,Release模式下。基于链表的耗时为8972ms,基于数组的耗时为1793ms,速度是链表实现方式的5倍.
详细代码例如以下:
//Reference:A fast algorithm for optimal length-limited Huffman codes.pdf,http://pan.baidu.com/s/1o6E19Bs
//author:by Pan Yumin.2014-06-18
//with the method of BinaryTree and linked-list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <memory.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSymbols 256 //the Maximum Number of Symbols
#define MaxHuffLen 16 //the Limited Length
typedef unsigned char boolean;
#ifndef FALSE //in case these macros already exist
#define FALSE 0 //values of boolean
#endif
#ifndef TRUE
#define TRUE 1
#endif
typedef struct __Node{
int width;
int weight;
int index;
int depth;
struct __Node *left; //left child
struct __Node *right; //right child
}Node;
typedef struct __HuffTable{
unsigned int index;
unsigned int len;
unsigned int code;
}HuffTable;
//Test memory leak
/*int g_malloc = 0,g_free = 0;
void* my_malloc(int size){
g_malloc++;
return malloc(size);
}
void my_free(void *ptr){
if(ptr){
g_free++;
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
}
}
#define malloc my_malloc
#define free my_free*/
//Get the smallest term in the diadic expansion of X
int GetSmallestTerm(int X)
{
int N=0;
while((X & 0x01) == 0){
X >>= 1;
N++;
}
return 1<<N;
}
void RemoveNodeMark(Node *tree,unsigned char *Flag,int Symbols)
{
if(tree->left == NULL && tree->right == NULL){
Flag[tree->depth*Symbols+tree->index] = 0; //set the nodemark zero
}
if(tree->left){
RemoveNodeMark(tree->left,Flag,Symbols);
}
if(tree->right){
RemoveNodeMark(tree->right,Flag,Symbols);
}
}
void PrintHuffCode(HuffTable Huffcode)
{
int i;
for(i=Huffcode.len-1;i>=0;i--){
printf("%d",(Huffcode.code>>i) & 0x01);
}
}
void GenerateHuffmanCode(HuffTable *HuffCode,unsigned char *Flag,int L,int Symbols,int *SortIndex)
{
char Code[17];
int Pre_L = 0;
int i=0,j=0;
unsigned int codes[MaxHuffLen+2]={0},rank[MaxHuffLen+1] = {0}; //rank: the number of symbols in every length
//find the first code
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
for(j=0;j<L;j++){
HuffCode[i].len += Flag[j*Symbols+i];
}
if(HuffCode[i].len != 0)
rank[HuffCode[i].len]++;
HuffCode[i].index = SortIndex[i];
}
for(i=0;i<=L;i++){
codes[i+1] = (codes[i]+rank[i])<<1;
rank[i] = 0;
}
//code
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
HuffCode[i].code = codes[HuffCode[i].len] + rank[HuffCode[i].len]++;
}
}
float BitsPerSymbol(HuffTable *HuffCode,int *weight,int Symbols,int WeightSum)
{
float bitspersymbol = 0.0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
bitspersymbol += (float)HuffCode[i].len*weight[i];
}
return bitspersymbol/WeightSum;
}
//ascending order
void FreqSort(int *Freq,int *SortIndex,int Symbols)
{
int i,j,tmp;
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
for(j=i+1;j<Symbols;j++){
if(Freq[i]>Freq[j]){
tmp = Freq[i];
Freq[i] = Freq[j];
Freq[j] = tmp;
tmp = SortIndex[i];
SortIndex[i] = SortIndex[j];
SortIndex[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
//ascending order, quick sort
void QuickSort(int *arr, int *SortIndex,int startPos,int endPos)
{
int i,j,key,index;
key=arr[startPos];
index = SortIndex[startPos];
i = startPos; j = endPos;
while(i < j){
while(arr[j]>=key && i<j)
--j;
arr[i]=arr[j]; SortIndex[i] = SortIndex[j];
while(arr[i]<=key && i<j)
++i;
arr[j]=arr[i]; SortIndex[j] = SortIndex[i];
}
arr[i]=key; SortIndex[i] = index;
if(i-1 > startPos)
QuickSort(arr,SortIndex,startPos,i-1);
if(endPos > i+1)
QuickSort(arr,SortIndex,i+1,endPos);
}
int GenLenLimitedOptHuffCode(int *Freq,int Symbols)
{
int i,j;
unsigned char *Flag = NULL; //record the state of the node
unsigned int rank[MaxHuffLen];
Node *tree = NULL, *base = NULL, *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
Node *start = NULL, *end = NULL, *Last = NULL; //start:the first(min weight) node of 2*r,end:the last(max weight) node of 2*r,Last:the last node of array.
Node *node = NULL;
HuffTable HuffCode[MaxSymbols];
float bitspersymbols = 0.0;
int WeightSum = 0;
int SortIndex[MaxSymbols];
int X = (Symbols-1)<<MaxHuffLen; //avoid float calculation
int minwidth,r,weight;
int r_Num = 0;
if(Symbols > (1<<MaxHuffLen)){
printf("Symbols > (1<<MaxHuffLen)\n");
return -1;
}
for(i=0;i<MaxSymbols;i++){
SortIndex[i] = i;
}
//FreqSort(Freq,SortIndex,Symbols); //sort
QuickSort(Freq,SortIndex,0,Symbols-1); //sort
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
WeightSum += Freq[i];
}
tree = (Node *)malloc(Symbols*MaxHuffLen*2*sizeof(Node));
memset(tree,0,Symbols*MaxHuffLen*2*sizeof(Node)); //2: for the optimize
Flag = (unsigned char*)malloc(MaxHuffLen*Symbols*sizeof(unsigned char));
memset(Flag,0x01,MaxHuffLen*Symbols*sizeof(unsigned char)); //mark every node 1
memset(HuffCode,0,sizeof(HuffCode));
for(i=0;i<MaxHuffLen;i++){
for(j=0;j<Symbols;j++){
tree[i*Symbols+j].depth = i;
tree[i*Symbols+j].index = j;
tree[i*Symbols+j].width = 1<<i; //avoid float calculation
tree[i*Symbols+j].weight = Freq[j];
}
}
//start code
base = tree; Last = tree+MaxHuffLen*Symbols-1;
while(X>0){
minwidth = GetSmallestTerm(X);
r = base->width;
if(r > minwidth){ //there is no optimal solution.
return -2;
}
else if(r == minwidth){
X -= minwidth;
base++;
}else{ //merge the smallest width and insert it into the original array
if(r < (1<<(MaxHuffLen-1))){
start = base+1; r_Num = 1;
//find start and end
while(start->width < 2*r && start <= Last){
r_Num++;
start++;
}
end = start;
while(end->width == 2*r && end <= Last){
end++;
}
end--;
//move back the (>=2*r)width node
node = Last; r_Num = r_Num/2;
while(node >= start){
*(node+r_Num) = *node;
node--;
}
//package and merge
node = start;
start = start + r_Num;
end = end + r_Num;
for(i=0;i<r_Num;i++){
left = base; base++;
right = base; base++;
weight = left->weight + right->weight;
while(start <= end && start->weight <= weight){
*node = *start;
start++;
node++;
}
node->weight = weight; node->width = 2*r;
node->left = left; node->right = right;
node++;
}
if(base->width == r){ //if r_Num is odd,remove the last r(width) Node.
RemoveNodeMark(base,Flag,Symbols);
base++;
}
Last += r_Num;
}else{ //r >= (1<<(MaxHuffLen-1))
while(base->width == r){
left = base; weight = base->weight;
if((*(base+1)).width == r){
base++;
right = base; weight += base->weight;
base++;
Last++;
Last->weight = weight; Last->width = 2*r;
Last->left = left; Last->right = right;
}else{
RemoveNodeMark(base,Flag,Symbols);
base++;
}
}
}
}
}
//output the HuffCode
GenerateHuffmanCode(HuffCode,Flag,MaxHuffLen,Symbols,SortIndex);
//print HuffCode
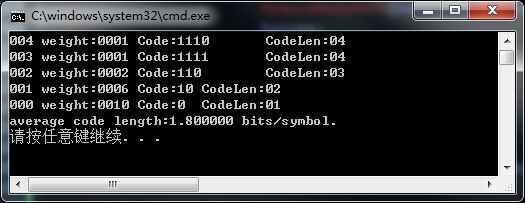
for(i=0;i<Symbols;i++){
printf("%03d weight:%04d Code:",HuffCode[i].index,Freq[i]);
PrintHuffCode(HuffCode[i]);
printf("\tCodeLen:%02d",HuffCode[i].len);
printf("\n");
}
bitspersymbols = BitsPerSymbol(HuffCode,Freq,Symbols,WeightSum);
printf("average code length:%f bits/symbol.\n",bitspersymbols);
free(tree); tree = NULL;
free(Flag); Flag = NULL;
return 0;
}
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
// int Freq[MaxSymbols] = {1,25,3,4,9,6,4,6,26,15,234,4578}; //weight is not zero.
int Freq[MaxSymbols] = {10,6,2,1,1}; //weight is not zero.
GenLenLimitedOptHuffCode(Freq,5); //5,12
return 0;
}输出结果例如以下所看到的:
