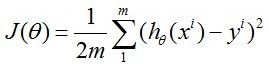Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
本讲内容:
Matlab 实现各种回归函数
=========================
基本模型
Y=θ0+θ1X1型---线性回归(直线拟合)
解决过拟合问题---Regularization
Y=1/(1+e^X)型---逻辑回归(sigmod 函数拟合)
在解决拟合问题的解决之前,我们首先回忆一下线性回归和逻辑回归的基本模型。
设待拟合参数 θn*1 和输入参数[ xm*n, ym*1 ] 。
对于各类拟合我们都要根据梯度下降的算法,给出两部分:
① cost function(指出真实值y与拟合值h<hypothesis>之间的距离):给出cost function 的表达式,每次迭代保证cost function的量减小;给出梯度gradient,即cost function对每一个参数θ的求导结果。
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction ( theta )
② Gradient_descent(主函数):用来运行梯度下降算法,调用上面的cost function进行不断迭代,直到最大迭代次数达到给定标准或者cost function返回值不再减小。
function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
线性回归:拟合方程为hθ(x)=θ0x0+θ1x1+…+θnxn,当然也可以有xn的幂次方作为线性回归项(如![]() ),这与普通意义上的线性不同,而是类似多项式的概念。
),这与普通意义上的线性不同,而是类似多项式的概念。
逻辑回归:拟合方程为hθ(x)=1/(1+e^(θTx)),其cost function 为:
cost function对各θj的求导请自行求取,看第三章最后一图,或者参见后文代码。
后面,我们分别对几个模型方程进行拟合,给出代码,并用matlab中的fit函数进行验证。
在Matlab 线性拟合 & 非线性拟合中我们已经讲过如何用matlab自带函数fit进行直线和曲线的拟合,非常实用。而这里我们是进行ML课程的学习,因此研究如何利用前面讲到的梯度下降法(gradient descent)进行拟合。
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction2( theta ) %COSTFUNCTION2 Summary of this function goes here % linear regression -> y=theta0 + theta1*x % parameter: x:m*n theta:n*1 y:m*1 (m=4,n=1) % %Data x=[1;2;3;4]; y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8]; m=size(x,1); hypothesis = h_func(x,theta); delta = hypothesis - y; jVal=sum(delta.^2); gradient(1)=sum(delta)/m; gradient(2)=sum(delta.*x)/m; end
function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta) %H_FUNC Summary of this function goes here % Detailed explanation goes here %cost function 2 res= theta(1)+theta(2)*inputx;function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta) end
function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
%GRADIENT_DESCENT Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',100);
initialTheta = zeros(2,1);
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction2,initialTheta,options);
end
result:
>> [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the default value of the function tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
optTheta =
0.3000
0.8600
functionVal =
0.0720
exitFlag =
1
function [ parameter ] = checkcostfunc( )
%CHECKC2 Summary of this function goes here
% check if the cost function works well
% check with the matlab fit function as standard
%check cost function 2
x=[1;2;3;4];
y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
EXPR= {'x','1'};
p=fittype(EXPR);
parameter=fit(x,y,p);
end
运行结果:
>> checkcostfunc()
ans =
Linear model:
ans(x) = a*x + b
Coefficients (with 95% confidence bounds):
a = 0.86 (0.4949, 1.225)
b = 0.3 (-0.6998, 1.3)
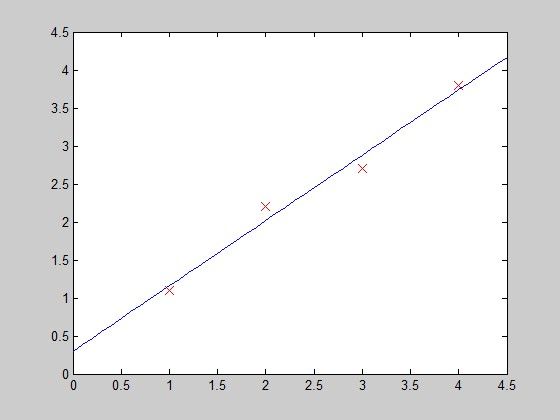
和我们的结果一样。下面画图:
function PlotFunc( xstart,xend ) %PLOTFUNC Summary of this function goes here % draw original data and the fitted %===================cost function 2====linear regression %original data x1=[1;2;3;4]; y1=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8]; %plot(x1,y1,'ro-','MarkerSize',10); plot(x1,y1,'rx','MarkerSize',10); hold on; %fitted line - 拟合曲线 x_co=xstart:0.1:xend; y_co=0.3+0.86*x_co; %plot(x_co,y_co,'g'); plot(x_co,y_co); hold off; end
在每次迭代中,按照gradient descent的方法更新参数θ:θ(i)-=gradient(i),其中gradient(i)是J(θ)对θi求导的函数式,在此例中就有gradient(1)=2*(theta(1)-5), gradient(2)=2*(theta(2)-5)。
函数costFunction, 定义jVal=J(θ)和对两个θ的gradient:
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction( theta ) %COSTFUNCTION Summary of this function goes here % Detailed explanation goes here jVal= (theta(1)-5)^2+(theta(2)-5)^2; gradient = zeros(2,1); %code to compute derivative to theta gradient(1) = 2 * (theta(1)-5); gradient(2) = 2 * (theta(2)-5); end
Gradient_descent,进行参数优化
function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
%GRADIENT_DESCENT Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',100);
initialTheta = zeros(2,1)
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction,initialTheta,options);
end
matlab主窗口中调用,得到优化厚的参数(θ1,θ2)=(5,5)
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
initialTheta =
0
0
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the default value of the function tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
optTheta =
5
5
functionVal =
0
exitFlag =
1
第四部分:Y=1/(1+e^X)型---逻辑回归(sigmod 函数拟合)
hypothesis function:function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta) %cost function 3 tmp=theta(1)+theta(2)*inputx;%m*1 res=1./(1+exp(-tmp));%m*1 end
cost function:
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction3( theta ) %COSTFUNCTION3 Summary of this function goes here % Logistic Regression x=[-3; -2; -1; 0; 1; 2; 3]; y=[0.01; 0.05; 0.3; 0.45; 0.8; 1.1; 0.99]; m=size(x,1); %hypothesis data hypothesis = h_func(x,theta); %jVal-cost function & gradient updating jVal=-sum(log(hypothesis+0.01).*y + (1-y).*log(1-hypothesis+0.01))/m; gradient(1)=sum(hypothesis-y)/m; %reflect to theta1 gradient(2)=sum((hypothesis-y).*x)/m; %reflect to theta 2 end
Gradient_descent:
function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',100);
initialTheta = [0;0];
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction3,initialTheta,options);
end
运行结果:
[optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the default value of the function tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
optTheta =
0.3526
1.7573
functionVal =
0.2498
exitFlag =
1
画图验证:
function PlotFunc( xstart,xend ) %PLOTFUNC Summary of this function goes here % draw original data and the fitted %===================cost function 3=====logistic regression %original data x=[-3; -2; -1; 0; 1; 2; 3]; y=[0.01; 0.05; 0.3; 0.45; 0.8; 1.1; 0.99]; plot(x,y,'rx','MarkerSize',10); hold on %fitted line x_co=xstart:0.1:xend; theta = [0.3526,1.7573]; y_co=h_func(x_co,theta); plot(x_co,y_co); hold off end
Reference:
1. http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7691571