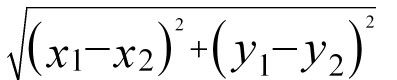Cocos2d-x 寻路算法之二 离目的地的距离优先
1.介绍:
接上一篇《Cocos2d-x 寻路算法之一 距离优先》,看这个图,我们发现这个寻路算法有点傻,明明终点在右侧却每个方向都找。难道没有其他办法了吗?从现实生活中我们知道东西如果在东边,当然是往东边搜索才是最好的办法。
2.开始动手
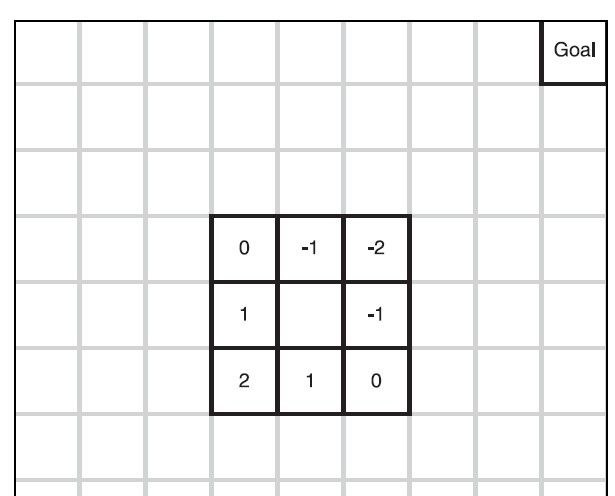
计算机中如何表示离目标近呢? 用图来解释就是这样的,目标在右上角,我们往右走,从X轴的角度来说离目标又近了一步,同理往上走是在Y轴上里目标近一步。最好的一步应该是图中-2的点,X轴和Y轴同时离目标近了一步。简单地转换成代码就是下面的这样:
bool comparebyWhichNearerGoalSimpleWay(Cell *c1, Cell *c2){
int distanceOfC1AndGoal = abs(g_goalX - c1->getX()) + abs(g_goalY - c1->getY());
int distanceOfC2AndGoal = abs(g_goalX - c2->getX()) + abs(g_goalY - c2->getY());
if(distanceOfC1AndGoal <= distanceOfC2AndGoal){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
扔到heap的比较条件中我们轻易地就实现了按照离目标距离优先的寻路算法,startPathFinding整个方法都不要改,只需要传进去上面提到的比较方法就行了。
typedef bool (*compareTwoCells)(Cell *c1, Cell *c2);
void HelloWorld::startPathFinding(compareTwoCells compareMethod, int startX,int startY,int goalX,int goalY){
Cell *startCell = _m_Map.Get(startX, startY);
vector<Cell*> vecCells;
vecCells.push_back(startCell);
make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
startCell->setMarked(true);
Cell *nowProcessCell;
while(vecCells.size() != 0){
pop_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
nowProcessCell = vecCells.back();
vecCells.pop_back();
if(nowProcessCell->getX() == _goalX && nowProcessCell->getY() == _goalY){//the goal is reach
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){ //check eight direction
int indexX = nowProcessCell->getX() + DIRECTION[i][0];
int indexY = nowProcessCell->getY() + DIRECTION[i][1];
if(indexX >= 0 && indexX < xLineCount && indexY >= 0 && indexY < yLineCount
&& _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY)->getPassable() == true){//check is a OK cell or not
Cell *cell = _m_Map.Get(indexX,indexY);
float beforeDistance = DISTANCE[i] * cell->getWeight() + _m_Map.Get(nowProcessCell->getX(),
nowProcessCell->getY())->getDistance();//calculate the distance
if(cell->getMarked() == false){
cell->setMarked(true);
cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
vecCells.push_back(cell);//only push the unmarked cell into the vector
push_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);
}else{// if find a lower distance, update it
if(beforeDistance < cell->getDistance()){
cell->setDistance(beforeDistance);
cell->setLastX(nowProcessCell->getX());
cell->setLastY(nowProcessCell->getY());
make_heap(vecCells.begin(),vecCells.end(),compareMethod);//distance change,so make heap again
}
}
}
}
}
}
startPathFinding(comparebyWhichNearerGoalSimpleWay,_playerX,_playerY,_goalX,_goalY);//demo
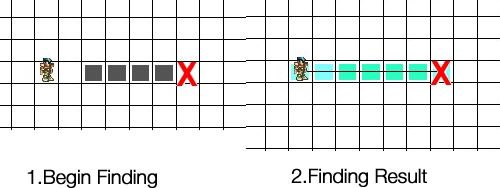
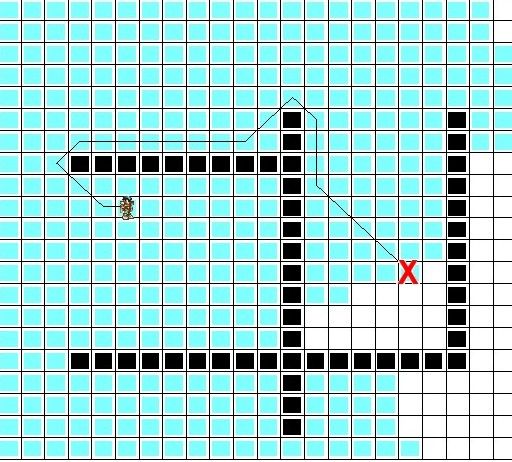
3.离目的地的距离优先效果图:
我们惊奇地发现似乎我们成功了,就用了9步就找到了目的地!
4.算法改进
从图2中我们用的是X轴和Y轴上的相对距离,并不是真正的物理距离,意识到这个问题我们马上修改了比较函数。物理距离当然容易算了,公式如下:
换成C++函数就是下面的样子:
float distanceBetweenTwoCells(float c1X,float c1Y, float c2X, float c2Y){
return sqrt(pow(c2X - c1X,2) + pow(c2Y - c1Y,2));
}
bool comparebyWhichNearerGoalPhysicWay(Cell *c1, Cell *c2){
float distanceOfC1AndGoal = distanceBetweenTwoCells((float)c1->getX(),(float)c1->getY(),(float)g_goalX,(float) g_goalY);
float distanceOfC2AndGoal = distanceBetweenTwoCells((float)c2->getX(),(float)c2->getY(),(float)g_goalX,(float) g_goalY);
if(distanceOfC1AndGoal <= distanceOfC2AndGoal){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
演示了下发现没有什么变化。但我们知道我们变的更好了。
5.该算法存在的问题
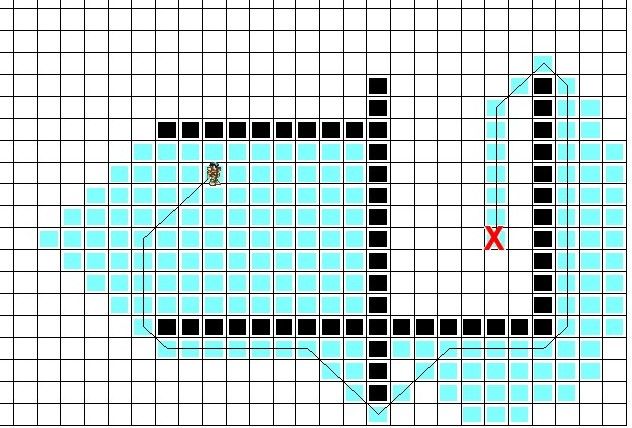
1.很容易想到的一个问题是,它没有考虑权重!如果目标在右侧,而右侧是一条非常难走的路,那么这个算法将毫无顾虑地走过去,丝毫不考虑就在不远处有条非常轻松的路。下面这个图就可以说明这个问题。
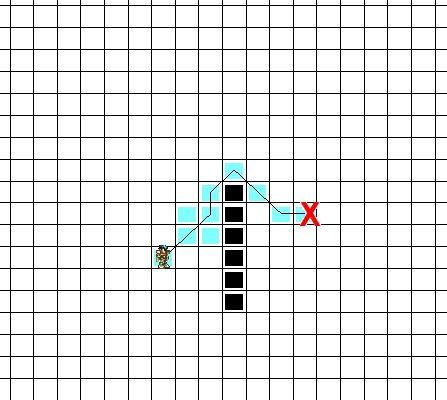
2.还有个问题,即使没有权重Cell的存在,只有可通过和不可通过Cell的存在,这个算法也有问题,我们可以人为地制造一个陷进,虽然目标在起点的下方,但是上面有条更近的路,这个算法应该会愚蠢地在往下找吧,这个就跟人一样,有时候目光短浅。下图是演示结果。
对比之前的算法发现其实上面的这条路更好的,虽然它查询了大量的Cell才发现这点(人家很努力的好不好)。
看看还有什么更好的办法没有?期待下篇的寻路算法吧。
6.项目下载
(请用7z解压,开发工具vs2010)
http://www.waitingfy.com/?attachment_id=828
A*算法应用可以看下这篇文章《 贪吃蛇 AI 的实现 snake AI》