Struts2源码浅析-请求处理
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter doFilter方法为请求的入口
doFilter方法主要做以下几件事
一: 根据配置的常量 设置当前request 字符编码 response国际化Locale信息
二: 创建ActionContext数据对象
三: 请求处理
1.分析url 根据url 创建ActionMapping对象 这些操作主要由ActionMapper接口实现类完成
2. 执行请求逻辑动作
①.根据请求映射对象ActionMapping 创建ActionProxy 主要由ActionProxyFactory接口完成
②.执行Action 逻辑(拦截器,Action对应方法)
四:清理ActionContext数据对象
流程分析
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
//根据struts2常量配置 设置当前request Encoding 即request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding)
//当前 response 设置国际化Locale信息 即response.setLocale(locale);
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
//创建ActionContext数据对象 包括ValueStack
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
//将当前的Dispatcher保存到ThreadLocal中
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
if ( excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
//包装request 返回StrutsRequestWrapper
//StrutsRequestWrapper继承了HttpServletRequestWrapper
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
//创建ActionMapping
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
//真正执行Action的地方
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
//清除ActionContext
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
一:设置编码字符 国际化Locale信息,PrepareOperations#setEncodingAndLocale方法 调用了 Dispatcher#prepare方法 真正做事的还是Dispatcher
PrepareOperations类的setEncodingAndLocale 方法
public void setEncodingAndLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
dispatcher.prepare(request, response);
}
Dispatcher的prepare方法
public void prepare(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//struts.i18n.encoding 常量
String encoding = null;
if (defaultEncoding != null) {
encoding = defaultEncoding;
}
Locale locale = null;
if (defaultLocale != null) {
locale = LocalizedTextUtil.localeFromString(defaultLocale, request.getLocale());
}
if (encoding != null) {
try {
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("Error setting character encoding to '" + encoding + "' - ignoring.", e);
}
}
if (locale != null) {
response.setLocale(locale);
}
}
二:创建ActionContext数据对象 由PrepareOperations#createActionContext方法完成
public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ActionContext ctx;
Integer counter = 1;
Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER);
if (oldCounter != null) {
counter = oldCounter + 1;
}
//ActionContext与 ValueStack 是主从关系
//ActionContext中持有ValueStack
ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (oldContext != null) {
ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap<String, Object>(oldContext.getContextMap()));
} else {
//ValueStack是由ValueStackFactory 创建
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null, servletContext));
//将创建的ValueStack 保存到ActionContext
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
}
request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter);
//将当前ActionContext 保存到ThreadLocal中
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
return ctx;
}
三: 请求处理
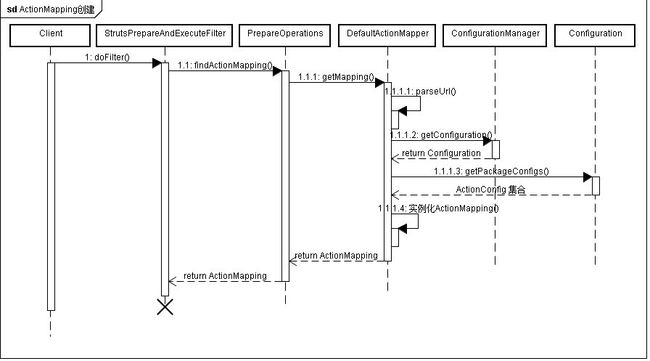
1.创建ActionMapping对象 一个ActionMapping对象 对应一次请求,
ActionMapping定义
public class ActionMapping {
private String name;
private String namespace;
private String method;
private String extension;
private Map<String, Object> params;
private Result result;
}
PrepareOperations findActionMapping方法 创建ActionMaping对象的动作转交给ActionMapper接口的getMapping方法完成
public ActionMapping findActionMapping(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, boolean forceLookup) {
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping) request.getAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY);
if (mapping == null || forceLookup) {
try {
//ActionMapper 默认实现DefaultActionMapper
//getMapping方法主要负责 查找对应的ActionConfig对象 根据ActionConfig对象创建 ActionMapping
mapping = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ActionMapper.class).getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
//错误信息
dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
}
}
return mapping;
}
ActionMapper 的实现类 DefaultActionMapper , getMapping方法 分析url ,根据url查找到的ActionConfig对象 创建ActionMapping
public ActionMapping getMapping(HttpServletRequest request,
ConfigurationManager configManager) {
//实例化ActionMapping
ActionMapping mapping = new ActionMapping();
String uri = getUri(request);
int indexOfSemicolon = uri.indexOf(";");
uri = (indexOfSemicolon > -1) ? uri.substring(0, indexOfSemicolon) : uri;
uri = dropExtension(uri, mapping);
if (uri == null) {
return null;
}
// name, namspace处理
parseNameAndNamespace(uri, mapping, configManager);
handleSpecialParameters(request, mapping);
if (mapping.getName() == null) {
return null;
}
//处理action!menthod 形式
parseActionName(mapping);
return mapping;
}
protected void parseNameAndNamespace(String uri, ActionMapping mapping,
ConfigurationManager configManager) {
String namespace, name;
int lastSlash = uri.lastIndexOf("/");
if (lastSlash == -1) {
namespace = "";
name = uri;
} else if (lastSlash == 0) {
namespace = "/";
name = uri.substring(lastSlash + 1);
} else if (alwaysSelectFullNamespace) {
// Simply select the namespace as everything before the last slash
namespace = uri.substring(0, lastSlash);
name = uri.substring(lastSlash + 1);
} else {
//配置元素管理器
Configuration config = configManager.getConfiguration();
String prefix = uri.substring(0, lastSlash);
namespace = "";
boolean rootAvailable = false;
//config.getPackageConfigs()
for (Object cfg : config.getPackageConfigs().values()) {
String ns = ((PackageConfig) cfg).getNamespace();
//匹配nameSpace
if (ns != null && prefix.startsWith(ns) && (prefix.length() == ns.length() || prefix.charAt(ns.length()) == '/')) {
if (ns.length() > namespace.length()) {
namespace = ns;
}
}
if ("/".equals(ns)) {
rootAvailable = true;
}
}
name = uri.substring(namespace.length() + 1);
if (rootAvailable && "".equals(namespace)) {
namespace = "/";
}
}
if (!allowSlashesInActionNames && name != null) {
int pos = name.lastIndexOf('/');
if (pos > -1 && pos < name.length() - 1) {
name = name.substring(pos + 1);
}
}
//TODO
mapping.setNamespace(namespace);
mapping.setName(name);
}
处理action!menthod 形式
protected ActionMapping parseActionName(ActionMapping mapping) {
if (mapping.getName() == null) {
return mapping;
}
if (allowDynamicMethodCalls) {
String name = mapping.getName();
int exclamation = name.lastIndexOf("!");
if (exclamation != -1) {
mapping.setName(name.substring(0, exclamation));
mapping.setMethod(name.substring(exclamation + 1));
}
}
return mapping;
}
ActionMapping创建 时序图
2.1根据请求映射对象ActionMapping 创建ActionProxy
回到StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter doFilter方法
//执行Action 方法入口 execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
ExecuteOperations 的 executeAction方法 把处理逻辑转交给了 Dispatcher的serviceAction方法
public void executeAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
}
Dispatcher的serviceAction方法主要完成 1.创建ActionProxy,ActionInvocation,Action对象 2.执行对应的方法
ActionProxy是个接口 接口定义
public interface ActionProxy {
/**
* 我们定义的Action
* ActionInvocation 中也持有Action引用
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
*/
Object getAction();
String getActionName();
/**
* 初始化阶段 包装的对象
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
*/
ActionConfig getConfig();
/**
* 该值决定 执行完Action对应的方法后 是否执行Result相关操作
*/
void setExecuteResult(boolean executeResult);
/**
*
* @return the status
*/
boolean getExecuteResult();
/**
* 执行器
*/
ActionInvocation getInvocation();
String getNamespace();
String execute() throws Exception;
/**
* Action 对应的方法
*/
String getMethod();
}
ActionInvocation 负责执行所有的拦截器Interceptor和我们定义的Action方法
ActionInvocation接口定义
/**
* Action 执行器
*/
public interface ActionInvocation extends Serializable {
/**
* 我们定义的Action
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
*/
Object getAction();
boolean isExecuted();
ActionContext getInvocationContext();
ActionProxy getProxy();
Result getResult() throws Exception;
/**
* Action 对应方法执行完成后 返回的Result
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
*/
String getResultCode();
void setResultCode(String resultCode);
ValueStack getStack();
void addPreResultListener(PreResultListener listener);
/**
* 执行所有操作
* 1.执行拦截器
* 2.调用invokeActionOnly方法执行 action对应方法
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
String invoke() throws Exception;
/**
* 执行我们定义的Action 方法 在invoke方法中调用
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
String invokeActionOnly() throws Exception;
void setActionEventListener(ActionEventListener listener);
/**
* 这个方法会创建我们定义的Action
* <br>------------------------------<br>
* @param proxy
*/
void init(ActionProxy proxy) ;
}
Dispatcher的serviceAction方法
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
//1.保存request, session, 等web元素到map中
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
// 省略
//TODO
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
//2.初始化完成之后 解析的xml数据对象 会保存到 Configuration#runtimeConfiguration变量中
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
//3.创建ActionProxy,ActionInvocation 返回StrutsActionProxy
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
//执行Action 对应方法入口
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
//StrutsActionProxy#execute()方法
//4.实际是转到了ActionInvocation#invoke方法
proxy.execute();
}
}
createContextMap 方法 保存web元素 最终已map的形式返回
public Map<String, Object> createContextMap(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping, ServletContext context) {
Map requestMap = new RequestMap(request);
Map params = new HashMap(request.getParameterMap());
Map session = new SessionMap(request);
Map application = new ApplicationMap(context);
//包装成map集合
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, params, session, application, request, response, context);
if (mapping != null) {
extraContext.put(ServletActionContext.ACTION_MAPPING, mapping);
}
return extraContext;
}
public HashMap<String, Object> createContextMap(Map requestMap, Map parameterMap, Map sessionMap, Map applicationMap, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext servletContext) {
HashMap<String, Object> extraContext = new HashMap<String, Object>();
extraContext.put(ActionContext.PARAMETERS, new HashMap(parameterMap));
extraContext.put(ActionContext.SESSION, sessionMap);
extraContext.put(ActionContext.APPLICATION, applicationMap);
Locale locale;
if (defaultLocale != null) {
locale = LocalizedTextUtil.localeFromString(defaultLocale, request.getLocale());
} else {
locale = request.getLocale();
}
extraContext.put(ActionContext.LOCALE, locale);
//extraContext.put(ActionContext.DEV_MODE, Boolean.valueOf(devMode));
// value为HttpServletRequest
//HttpServletRequest = extraContext.get('StrutsStatics.HTTP_REQUEST')
extraContext.put(StrutsStatics.HTTP_REQUEST, request);
extraContext.put(StrutsStatics.HTTP_RESPONSE, response);
extraContext.put(StrutsStatics.SERVLET_CONTEXT, servletContext);
//value为包装过的 元素map
//获取方式extraContext.get('request').requestMap.get('key')
extraContext.put("request", requestMap);
extraContext.put("session", sessionMap);
extraContext.put("application", applicationMap);
extraContext.put("parameters", parameterMap);
AttributeMap attrMap = new AttributeMap(extraContext);
extraContext.put("attr", attrMap);
return extraContext;
}
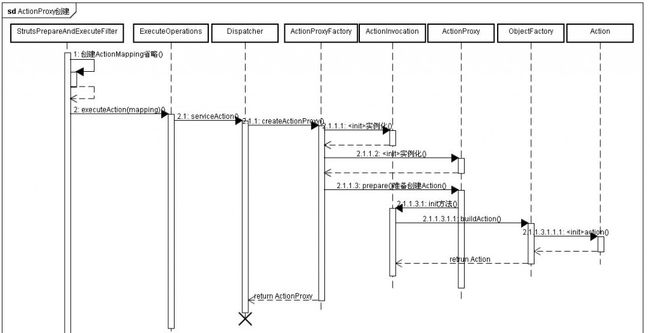
创建ActionProxy,ActionInvocation 是由ActionProxyFactory实现类完成
DefaultActionProxyFactory createActionProxy方法
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
//创建ActionInvocation
ActionInvocation inv = new DefaultActionInvocation(extraContext, true);
//对该ActionInvocation 实例 进行依赖注入 即引用了@Inject注解的 方法 变量..
container.inject(inv);
//创建ActionProxy
//ActionProxy,ActionInvocation都互相持有对方的引用
//子类StrutsActionProxyFactory 重写了该方法
return createActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
}
StrutsActionProxyFactory 的createActionProxy方法, StrutsActionProxyFactory是DefaultActionProxyFactory的子类
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(ActionInvocation inv, String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
StrutsActionProxy proxy = new StrutsActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
container.inject(proxy);
//这里会创建action
proxy.prepare();
return proxy;
}
StrutsActionProxyFactory 的prepare方法 主要完成调用ActionInvocation init方法 创建我们定义的Action 也可能是从Spring容器获得
protected void prepare() {
//从configuration runtimeConfiguration对象中获取ActionConfig
config = configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration().getActionConfig(namespace, actionName);
//...略
//ActionConfig method为空 默认设置为"execute"
resolveMethod();
//检查method 在Action是否存在
if (!config.isAllowedMethod(method)) {
throw new ConfigurationException("Invalid method: "+method+" for action "+actionName);
}
//创建Action 可能是从spring容器中获得
invocation.init(this);
}
DefaultActionInvocation init方法
public void init(ActionProxy proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
Map<String, Object> contextMap = createContextMap();
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (actionContext != null) {
actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
}
// 创建Action
createAction(contextMap);
if (pushAction) {
stack.push(action);
contextMap.put("action", action);
}
invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
//从当前mapping对应的ActionConfig获得拦截器
List<InterceptorMapping> interceptorList = new ArrayList<InterceptorMapping>(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();
}
protected void createAction(Map<String, Object> contextMap) {
//省略...
// load action
//Action的创建在此发生
action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);
//省略...
if (actionEventListener != null) {
action = actionEventListener.prepare(action, stack);
}
}
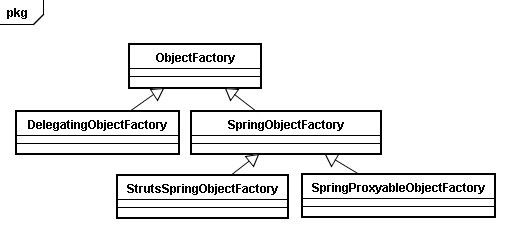
ObjectFactory 主要负责bean 的创建 继承关系:
以spring为例 StrutsSpringObjectFactory
ObjectFactory bulidAction方法 转到bulidBean方法
public Object buildAction(String actionName, String namespace, ActionConfig config, Map<String, Object> extraContext) throws Exception {
return buildBean(config.getClassName(), extraContext);
}
SpringObjectFactory 重写了ObjectFactory 的buildBean方法
主要从spring容器中获得bean 这里使用的是spring 的AutowireCapableBeanFactory容器 具有自动装配特性
public Object buildBean(Class clazz, Map<String, Object> extraContext) throws Exception {
Object bean;
try {
// Decide to follow autowire strategy or use the legacy approach which mixes injection strategies
if (alwaysRespectAutowireStrategy) {
// Leave the creation up to Spring
bean = autoWiringFactory.createBean(clazz, autowireStrategy, false);
injectApplicationContext(bean);
return injectInternalBeans(bean);
} else {
bean = autoWiringFactory.autowire(clazz, AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR, false);
bean = autoWiringFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, bean.getClass().getName());
// We don't need to call the init-method since one won't be registered.
bean = autoWiringFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, bean.getClass().getName());
return autoWireBean(bean, autoWiringFactory);
}
} catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException e) {
if (LOG.isErrorEnabled())
LOG.error("Error building bean", e);
// Fall back
return autoWireBean(super.buildBean(clazz, extraContext), autoWiringFactory);
}
}
ActionProxy, ActionInvocation创建过程结束了
当前的ActionInvocation对象中 持有当前映射匹配的拦截器集合interceptors,ActionProxy和我们定义的action对象
目前还没有执行Action对应方法 万事俱备只欠东风了。
ActionProxy创建时序图
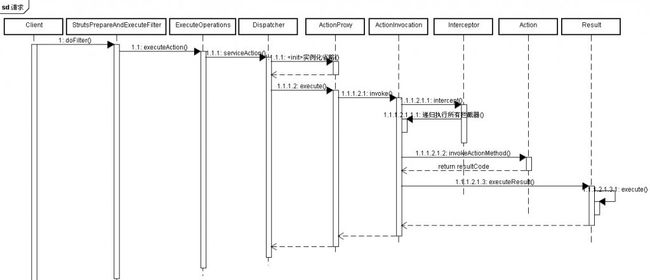
2.2 执行Action逻辑 真正执行逻辑是在ActionInvocation的invoke方法中发生
回到Dispatcher 的serviceAction方法
//StrutsActionProxy#execute()方法 //实际是转到了ActionInvocation#invoke方法 proxy.execute();
StrutsActionProxy的 execute方法调用ActionInvocation invoke方法
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext previous = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext());
try {
return invocation.invoke();
} finally {
if (cleanupContext)
ActionContext.setContext(previous);
}
}
ActionInvocation invoke方法
大致执行步骤1.执行所有的拦截器 2.执行Action对应的Method 3.根据Action执行结果 再执行Result
public String invoke() throws Exception {
//...省略
//1.先执行所有拦截器
if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
//这里类似一个递归调用
//intercept方法中 invocation.invoke();
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
} else {
//2.最后 执行Action对应方法 返回result字符串
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
//...省略
if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) {
//3.实例化Result对象
executeResult();
}
return resultCode;
}
拦截器的执行 interceptors为一个迭代器Iterator 当执行完一个拦截器 拦截器中又会回调 invoke方法执行下一个 例如:
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
String result = null;
//回调到DefaultActionInvocation#invoke方法
result = invocation.invoke();
return result;
}
拦截器执行完成 接着执行Action 对应方法 在invokeActionOnly发生
public String invokeActionOnly() throws Exception {
return invokeAction(getAction(), proxy.getConfig());
}
protected String invokeAction(Object action, ActionConfig actionConfig) throws Exception {
//要执行的方法
String methodName = proxy.getMethod();
try {
Object methodResult = null;
Method method = null;
//获得Method对象
method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(methodName, EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY);
//执行Action 方法
methodResult = method.invoke(action, new Object[0]);
if (methodResult instanceof Result) {
this.explicitResult = (Result) methodResult;
container.inject(explicitResult);
return null;
} else {
//返回 result Str
return (String) methodResult;
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The " + methodName + "() is not defined in action " + getAction().getClass() + "");
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getTargetException();
if (actionEventListener != null) {
//异常处理
String result = actionEventListener.handleException(t, getStack());
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
}
执行Result 根据ResultConfig 中的calssName创建result对象 在执行execute
private void executeResult() throws Exception {
//根据ResultConfig对象创建Result对象
result = createResult();
result.execute(this);
}
public Result createResult() throws Exception {
if (explicitResult != null) {
Result ret = explicitResult;
explicitResult = null;
return ret;
}
ActionConfig config = proxy.getConfig();
Map<String, ResultConfig> results = config.getResults();
ResultConfig resultConfig = null;
try {
resultConfig = results.get(resultCode);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
// swallow
}
if (resultConfig == null) {
// If no result is found for the given resultCode, try to get a wildcard '*' match.
resultConfig = results.get("*");
}
if (resultConfig != null) {
try {
//创建Result对象
//resultConfig中包含了 className 直
return objectFactory.buildResult(resultConfig, invocationContext.getContextMap());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("There was an exception while instantiating the result of type " + resultConfig.getClassName(), e);
throw new XWorkException(e, resultConfig);
}
} else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode) && unknownHandlerManager.hasUnknownHandlers()) {
return unknownHandlerManager.handleUnknownResult(invocationContext, proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getConfig(), resultCode);
}
return null;
}
执行Result execute方法 以ServletDispatcherResult为例
public void execute(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
lastFinalLocation = conditionalParse(location, invocation);
doExecute(lastFinalLocation, invocation);
}
public void doExecute(String finalLocation, ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
PageContext pageContext = ServletActionContext.getPageContext();
if (pageContext != null) {
pageContext.include(finalLocation);
} else {
//...省略
if (!insideActionTag && !response.isCommitted() && (request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.include.servlet_path") == null)) {
request.setAttribute("struts.view_uri", finalLocation);
request.setAttribute("struts.request_uri", request.getRequestURI());
//转向
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
} else {
dispatcher.include(request, response);
}
}
}
请求时序图: