匀速贝塞尔曲线运动的实现(转)
二次贝塞尔曲线通常以如下方式构建,给定二维平面上的固定点P0,P1,P2,用B(t)表示该条曲线
用一个动画来演示,可以更加清楚的表明这条曲线的构建过程

如果t变量本身线形变化的话,这条贝塞尔曲线本身的生成过程是并不是匀速的,通常都是两头快中间慢。

如果t变量本身线形变化的话,这条贝塞尔曲线本身的生成过程是并不是匀速的,通常都是两头快中间慢。
如何想要得到匀速的贝塞尔曲线运动呢?比如我们在某款游戏中设计了一条贝塞尔曲线的路径,如何实现玩家匀速在这条路径上运动呢?
思考这个算法颇费了一番脑筋,其间还得到数学牛人Charlesgao的帮助,非常感谢他(比较糗的是,我问问题的时候就把其中的一个公式搞错了,见笑了-_-!)。
首先需要求得B(t)相对于t的速度公式s(t)
![]()
为了简化公式,我们定义如下变量:
![]()
计算出的s(t)可以表达为:
![]()
其中A,B,C是根据P0,P1,P2计算出的常数:
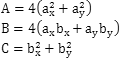
根据这个公式,求得贝塞尔曲线的长度公式L(t):

设t`就是能够使L实现匀速运动的自变量,那么显然L(t`)=L(1.0)*t,即:
![]()
由于L(t)函数非常复杂,直接求逆函数的表达式几乎不可能,还好我们可以知道它的导数为s(t),在实际使用中,可以使用牛顿切线法求出近似解。其迭代算法可以表达为:
![]()
我写了一个测试程序用于验证该算法,运算结果如下,可以看到,这条曲线已经是以匀速方式生成的了 ^_^:
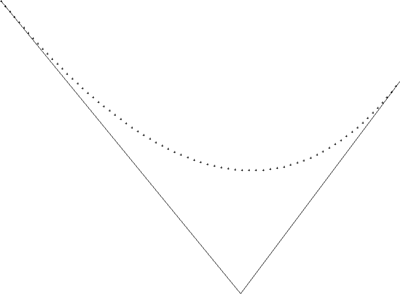
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <windows.h>
//三个控制点
POINT P0={50,50},P1={500,600},P2={800,200};
int ax = P0.x-2*P1.x+P2.x;
int ay = P0.y-2*P1.y+P2.y;
int bx = 2*P1.x-2*P0.x;
int by = 2*P1.y-2*P0.y;
double A = 4*(ax*ax+ay*ay);
double B = 4*(ax*bx+ay*by);
double C = bx*bx+by*by;
//曲线总长度
double total_length = 0.0;
//曲线分割的份数
const int STEP = 70;
//用于保存绘制点数据的数组
POINT pixels[STEP];
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//速度函数
/*
s(t_) = Sqrt[A*t*t+B*t+C]
*/
double s(double t)
{
return sqrt(A*t*t+B*t+C);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//长度函数
/*
L(t) = Integrate[s[t], t]
L(t_) = ((2*Sqrt[A]*(2*A*t*Sqrt[C + t*(B + A*t)] + B*(-Sqrt[C] + Sqrt[C + t*(B + A*t)])) +
(B^2 - 4*A*C) (Log[B + 2*Sqrt[A]*Sqrt[C]] - Log[B + 2*A*t + 2 Sqrt[A]*Sqrt[C + t*(B + A*t)]]))
/(8* A^(3/2)));
*/
double L(double t)
{
double temp1 = sqrt(C+t*(B+A*t));
double temp2 = (2*A*t*temp1+B*(temp1-sqrt(C)));
double temp3 = log(B+2*sqrt(A)*sqrt(C));
double temp4 = log(B+2*A*t+2*sqrt(A)*temp1);
double temp5 = 2*sqrt(A)*temp2;
double temp6 = (B*B-4*A*C)*(temp3-temp4);
return (temp5+temp6)/(8*pow(A,1.5));
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//长度函数反函数,使用牛顿切线法求解
/*
X(n+1) = Xn - F(Xn)/F'(Xn)
*/
double InvertL(double t, double l)
{
double t1=t, t2;
do
{
t2 = t1 - (L(t1)-l)/s(t1);
if(abs(t1-t2)<0.000001) break;
t1=t2;
}while(true);
return t2;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK _WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (message)
{
case WM_TIMER:
{
static nIndex = 0;
if(nIndex>=0 && nIndex<=STEP)
{
double t = (double)nIndex/STEP;
//如果按照线形增长,此时对应的曲线长度
double l = t*total_length;
//根据L函数的反函数,求得l对应的t值
t = InvertL(t, l);
//根据贝塞尔曲线函数,求得取得此时的x,y坐标
double x = (1-t)*(1-t)*P0.x +2*(1-t)*t*P1.x + t*t*P2.x;
double y = (1-t)*(1-t)*P0.y +2*(1-t)*t*P1.y + t*t*P2.y;
//取整
pixels[nIndex].x = (int)(x+0.5);
pixels[nIndex].y = (int)(y+0.5);
nIndex++;
InvalidateRect(hWnd, 0, 0);
}
else
{
KillTimer(hWnd, 101);
}
}
break;
case WM_PAINT:
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
::MoveToEx(hdc, P0.x, P0.y, 0);
LineTo(hdc, P1.x, P1.y);
LineTo(hdc, P2.x, P2.y);
for(int i=0; i<STEP; i++)
{
const POINT &pt = pixels[i];
if(pt.x==0 && pt.y==0) break;
::MoveToEx(hdc, pt.x-2, pt.y, 0);
::LineTo(hdc, pt.x+2, pt.y);
::MoveToEx(hdc, pt.x, pt.y-2, 0);
::LineTo(hdc, pt.x, pt.y+2);
}
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
}
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int APIENTRY WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPTSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
//注册窗口类
WNDCLASSEX wcex;
ZeroMemory(&wcex, sizeof(WNDCLASSEX));
wcex.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX);
wcex.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW;
wcex.lpfnWndProc = (WNDPROC)_WndProc;
wcex.hInstance = hInstance;
wcex.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
wcex.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1);
wcex.lpszClassName = "BezierClass";
RegisterClassEx(&wcex);
//创建窗口
HWND hWnd = CreateWindow("BezierClass", "BezierDemo", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,
CW_USEDEFAULT, 0, CW_USEDEFAULT, 0, NULL, NULL, hInstance, NULL);
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
//计算总长度
total_length = L(1);
//清空绘制点数据
ZeroMemory(&pixels, sizeof(pixels));
//设定定时刷新计时器
SetTimer(hWnd, 101, 10, 0);
//消息循环
MSG msg;
while(GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return (int) msg.wParam;
}