算法与数据结构--在顺序线性表L中查找第1个值与e满足compare()的元素的为序--算法2.5
/* (程序头部注释开始)
* 程序的版权和版本声明部分
* Copyright (c) 2011, 烟台大学计算机学院学生
* All rights reserved.
* 文件名称:在顺序线性表L中查找第1个值与e满足compare()的元素的为序
* 作 者: 雷恒鑫
* 完成日期: 2012 年 09 月 18 日
* 版 本 号: V1.0
* 对任务及求解方法的描述部分
* 输入描述: 在顺序线性表L中查找第1个值与e满足compare()的元素的为序
若找到,则返回其在L中的位序,否则返回0
* 问题描述:
* 程序输出:
* 程序头部的注释结束
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100 //线性表存储空间的初始分配量
#define LISTINCREMENT 10 //线性表存储空间的分配增量
typedef int ElemType; //定义别名
typedef int Status; //定义别名
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //存储空间基址
int length; //当前长度
int listsize; //当前分配的存储容量(以sizeof(ElemType)为单位)
}SqList;
Status InitList_Sq(SqList &L){
//构造一个空的线性表L
L.elem = (ElemType *)malloc(LIST_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
if(!L.elem)
exit(1); //存储分配失败
L.length = 0; //空表长度为0
L.listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE; //初始存储容量
return true;
}
Status ListInsert_Sq(SqList &L,int i,ElemType e)
{
//在顺序线性表L中第i个位置之前插入新的元素e
//i的合法值为1<=i<=ListLength_Sq(L)+1
if(i <1 || i> L.length + 1)
return false; //i值不合法
if(L.length >= L.listsize) //当前存储空间已满,增加分配
{
ElemType *newbase = (ElemType *)realloc(L.elem,(L.listsize + LISTINCREMENT )* sizeof(ElemType));
if(!newbase)
exit(1); //存储分配失败
L.elem = newbase;//新基址
L.listsize += LISTINCREMENT; //增加存储容量
}
ElemType *q = &(L.elem[i-1]);//q为插入位置
for(ElemType *p = &(L.elem[L.length-1]);p>=q;--p)
*(p+1) = *p; //插入位置及之后的元素右移
*q = e; //插入e
++L.length; //表长增1
return true;
}
Status ListDelete_Sq(SqList &L,int i)
{
//在顺序线性表L中删除第i个元素,并用e返回其值
//i的合法值为 1<= i<=ListLength_Sq(L)
if((i<1)||(i>L.length))
return false; //i值不合法
ElemType *p = &(L.elem[i-1]); //p为被删除元素的位置
ElemType e = *p; //被删除元素的值赋值给e
ElemType *q = L.elem + L.length-1; //表尾元素的位置
for(++p;p<=q;++p)
*(p-1) = *p; //被删除元素之后的元素左移
--L.length; //表长减1
return e;
}
Status compare(ElemType e1,ElemType e2)
{
if(e1==e2)
return true;
return false;
}
int LocateElem_sq(SqList L,ElemType e,Status (*compare)(ElemType,ElemType))
{
//在顺序线性表L中查找第1个值与e满足compare()的元素的为序
//若找到,则返回其在L中的位序,否则返回0
int i = 1;//i的初值为第1个元素的位序
ElemType *p = L.elem; //p的初值为为第1个元素的存储位置
while(i<=L.length &&!(*compare)(*p++,e))
{
++i;
}
if(i<=L.length)
{
return i;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void input(SqList L)
{
int i = 1;//i的初值为第1个元素的位序
ElemType *p = L.elem; //p的初值为为第1个元素的存储位置
while(i<=L.length)
{
cout<<*(p++)<<" ";
++i;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
SqList L;
InitList_Sq(L);
ListInsert_Sq(L,1,2);//在顺序线性表L中第i个位置之前插入新的元素e
ListInsert_Sq(L,2,3);//在顺序线性表L中第i个位置之前插入新的元素e
ListInsert_Sq(L,3,4);//在顺序线性表L中第i个位置之前插入新的元素e
ListInsert_Sq(L,4,5);//在顺序线性表L中第i个位置之前插入新的元素e
//ElemType e = ListDelete_Sq(L,1);
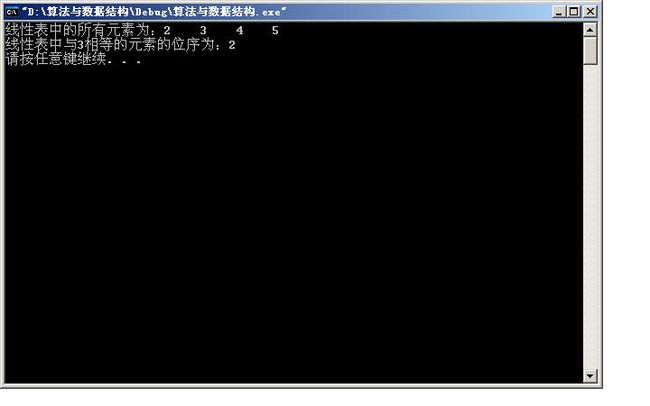
cout<<"线性表中的所有元素为:";
input(L);
int e = LocateElem_sq(L,3,(*compare));//在顺序线性表L中查找第1个值与e满足compare()的元素的为序
cout<<"线性表中与3相等的元素的位序为:"<<e<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return;
}
运行结果: