- 关于沟通这件事,项目经理不需要每次都面对面进行
流程大师兄
很多项目经理都会遇到这样的问题,项目中由于事情太多,根本没有足够的时间去召开会议,那在这种情况下如何去有效地管理项目中的利益相关者?当然,不建议电子邮件也不需要开会的话,建议可以采取下面几种方式来形成有效的沟通,这几种方式可以帮助你努力的通过各种办法来保持和各方面的联系。项目经理首先要问自己几个问题,项目中哪些利益相关者是必须要进行沟通的?可以列出项目中所有的利益相关者清单,同时也整理出项目中哪些
- 机器学习与深度学习间关系与区别
ℒℴѵℯ心·动ꦿ໊ོ꫞
人工智能学习深度学习python
一、机器学习概述定义机器学习(MachineLearning,ML)是一种通过数据驱动的方法,利用统计学和计算算法来训练模型,使计算机能够从数据中学习并自动进行预测或决策。机器学习通过分析大量数据样本,识别其中的模式和规律,从而对新的数据进行判断。其核心在于通过训练过程,让模型不断优化和提升其预测准确性。主要类型1.监督学习(SupervisedLearning)监督学习是指在训练数据集中包含输入
- element实现动态路由+面包屑
软件技术NINI
vue案例vue.js前端
el-breadcrumb是ElementUI组件库中的一个面包屑导航组件,它用于显示当前页面的路径,帮助用户快速理解和导航到应用的各个部分。在Vue.js项目中,如果你已经安装了ElementUI,就可以很方便地使用el-breadcrumb组件。以下是一个基本的使用示例:安装ElementUI(如果你还没有安装的话):你可以通过npm或yarn来安装ElementUI。bash复制代码npmi
- 10月|愿你的青春不负梦想-读书笔记-01
Tracy的小书斋
本书的作者是俞敏洪,大家都很熟悉他了吧。俞敏洪老师是我行业的领头羊吧,也是我事业上的偶像。本日摘录他书中第一章中的金句:『一个人如果什么目标都没有,就会浑浑噩噩,感觉生命中缺少能量。能给我们能量的,是对未来的期待。第一件事,我始终为了进步而努力。与其追寻全世界的骏马,不如种植丰美的草原,到时骏马自然会来。第二件事,我始终有阶段性的目标。什么东西能给我能量?答案是对未来的期待。』读到这里的时候,我便
- C语言如何定义宏函数?
小九格物
c语言
在C语言中,宏函数是通过预处理器定义的,它在编译之前替换代码中的宏调用。宏函数可以模拟函数的行为,但它们不是真正的函数,因为它们在编译时不会进行类型检查,也不会分配存储空间。宏函数的定义通常使用#define指令,后面跟着宏的名称和参数列表,以及宏展开后的代码。宏函数的定义方式:1.基本宏函数:这是最简单的宏函数形式,它直接定义一个表达式。#defineSQUARE(x)((x)*(x))2.带参
- c++ 的iostream 和 c++的stdio的区别和联系
黄卷青灯77
c++算法开发语言iostreamstdio
在C++中,iostream和C语言的stdio.h都是用于处理输入输出的库,但它们在设计、用法和功能上有许多不同。以下是两者的区别和联系:区别1.编程风格iostream(C++风格):C++标准库中的输入输出流类库,支持面向对象的输入输出操作。典型用法是cin(输入)和cout(输出),使用>操作符来处理数据。更加类型安全,支持用户自定义类型的输入输出。#includeintmain(){in
- Long类型前后端数据不一致
igotyback
前端
响应给前端的数据浏览器控制台中response中看到的Long类型的数据是正常的到前端数据不一致前后端数据类型不匹配是一个常见问题,尤其是当后端使用Java的Long类型(64位)与前端JavaScript的Number类型(最大安全整数为2^53-1,即16位)进行数据交互时,很容易出现精度丢失的问题。这是因为JavaScript中的Number类型无法安全地表示超过16位的整数。为了解决这个问
- LocalDateTime 转 String
igotyback
java开发语言
importjava.time.LocalDateTime;importjava.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;publicclassMain{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//获取当前时间LocalDateTimenow=LocalDateTime.now();//定义日期格式化器DateTimeFormatterformat
- mysql禁用远程登录
igotyback
mysql
去mysql库中的user表里,将host都改成localhost之后刷新权限FLUSHPRIVILEGES;
- Linux下QT开发的动态库界面弹出操作(SDL2)
13jjyao
QT类qt开发语言sdl2linux
需求:操作系统为linux,开发框架为qt,做成需带界面的qt动态库,调用方为java等非qt程序难点:调用方为java等非qt程序,也就是说调用方肯定不带QApplication::exec(),缺少了这个,QTimer等事件和QT创建的窗口将不能弹出(包括opencv也是不能弹出);这与qt调用本身qt库是有本质的区别的思路:1.调用方缺QApplication::exec(),那么我们在接口
- 30天风格练习-DAY2
黄希夷
Day2(重义)在一个周日/一周的最后一天,我来到位于市中心/市区繁华地带的一家购物中心/商场,中心内人很多/熙熙攘攘。我注意到/看见一个独行/孤身一人的年轻女孩/,留着一头引人注目/长过腰际的头发,上身穿一件暗红色/比正红色更深的衣服/穿在身体上的东西。走下扶梯的时候,她摔倒了/跌向地面,在她正要站起来/让身体离开地面的时候,过长/超过一般人长度的头发被支撑身体/躯干的手掌压/按在下面,她赶紧用
- 店群合一模式下的社区团购新发展——结合链动 2+1 模式、AI 智能名片与 S2B2C 商城小程序源码
说私域
人工智能小程序
摘要:本文探讨了店群合一的社区团购平台在当今商业环境中的重要性和优势。通过分析店群合一模式如何将互联网社群与线下终端紧密结合,阐述了链动2+1模式、AI智能名片和S2B2C商城小程序源码在这一模式中的应用价值。这些创新元素的结合为社区团购带来了新的机遇,提升了用户信任感、拓展了营销渠道,并实现了线上线下的完美融合。一、引言随着互联网技术的不断发展,社区团购作为一种新兴的商业模式,在满足消费者日常需
- 向内而求
陈陈_19b4
10月27日,阴。阅读书目:《次第花开》。作者:希阿荣博堪布,是当今藏传佛家宁玛派最伟大的上师法王,如意宝晋美彭措仁波切颇具影响力的弟子之一。多年以来,赴海内外各地弘扬佛法,以正式授课、现场开示、发表文章等多种方法指导佛学弟子修行佛法。代表作《寂静之道》、《生命这出戏》、《透过佛法看世界》自出版以来一直是佛教类书籍中的畅销书。图片发自App金句:1.佛陀说,一切痛苦的根源在于我们长期以来对自身及外
- 消息中间件有哪些常见类型
xmh-sxh-1314
java
消息中间件根据其设计理念和用途,可以大致分为以下几种常见类型:点对点消息队列(Point-to-PointMessagingQueues):在这种模型中,消息被发送到特定的队列中,消费者从队列中取出并处理消息。队列中的消息只能被一个消费者消费,消费后即被删除。常见的实现包括IBM的MQSeries、RabbitMQ的部分使用场景等。适用于任务分发、负载均衡等场景。发布/订阅消息模型(Pub/Sub
- 高级编程--XML+socket练习题
masa010
java开发语言
1.北京华北2114.8万人上海华东2,500万人广州华南1292.68万人成都华西1417万人(1)使用dom4j将信息存入xml中(2)读取信息,并打印控制台(3)添加一个city节点与子节点(4)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端输入城市ID,服务器响应相应城市信息(5)使用socketTCP协议编写服务端与客户端,客户端要求用户输入city对象,服务端接收并使用dom4j
- 水平垂直居中的几种方法(总结)
LJ小番茄
CSS_玄学语言htmljavascript前端csscss3
1.使用flexbox的justify-content和align-items.parent{display:flex;justify-content:center;/*水平居中*/align-items:center;/*垂直居中*/height:100vh;/*需要指定高度*/}2.使用grid的place-items:center.parent{display:grid;place-item
- 每日一题——第八十二题
互联网打工人no1
C语言程序设计每日一练c语言
题目:将一个控制台输入的字符串中的所有元音字母复制到另一字符串中#include#include#include#include#defineMAX_INPUT1024boolisVowel(charp);intmain(){charinput[MAX_INPUT];charoutput[MAX_INPUT];printf("请输入一串字符串:\n");fgets(input,sizeof(inp
- WPF中的ComboBox控件几种数据绑定的方式
互联网打工人no1
wpfc#
一、用字典给ItemsSource赋值(此绑定用的地方很多,建议熟练掌握)在XMAL中:在CS文件中privatevoidBindData(){DictionarydicItem=newDictionary();dicItem.add(1,"北京");dicItem.add(2,"上海");dicItem.add(3,"广州");cmb_list.ItemsSource=dicItem;cmb_l
- 直抒《紫罗兰永恒花园外传》
雷姆的黑色童话
没看过《紫罗兰永恒花园》的我莫名的看完了《紫罗兰永恒花园外传》,又莫名的被故事中的姐妹之情狠狠地感动了的一把。感动何在:困苦中相依为命的姐妹二人被迫分离,用一个人的自由换取另一个人的幸福。之后,虽相隔不知几许依旧心心念念彼此牵挂。这种深深的姐妹情谊就是令我为之动容的所在。贝拉和泰勒分别影片开始,海天之间一个孩童凭栏眺望,手中拿着折旧的信纸。镜头一转,挑灯伏案的薇尔莉特正在打字机前奋笔疾书。这些片段
- 将cmd中命令输出保存为txt文本文件
落难Coder
Windowscmdwindow
最近深度学习本地的训练中我们常常要在命令行中运行自己的代码,无可厚非,我们有必要保存我们的炼丹结果,但是复制命令行输出到txt是非常麻烦的,其实Windows下的命令行为我们提供了相应的操作。其基本的调用格式就是:运行指令>输出到的文件名称或者具体保存路径测试下,我打开cmd并且ping一下百度:pingwww.baidu.com>./data.txt看下相同目录下data.txt的输出:如果你再
- 直返最高等级与直返APP:无需邀请码的返利新体验
古楼
随着互联网的普及和电商的兴起,直返模式逐渐成为一种流行的商业模式。在这种模式下,消费者通过购买产品或服务,获得一定的返利,并可以分享给更多的人。其中,直返最高等级和直返APP是直返模式中的重要概念和工具。本文将详细介绍直返最高等级的概念、直返APP的使用以及与邀请码的关系。【高省】APP(高佣金领导者)是一个自用省钱佣金高,分享推广赚钱多的平台,百度有几百万篇报道,运行三年,稳定可靠。高省APP,
- 读《人世间》有感
一0一
这个寒假,就如同朋友圈中的一段话:一闭眼,一睁眼假期还有5天,在一闭眼一睁眼假期还有12天;再一闭眼一睁眼假期还有20天;不敢睡,不敢睡啊……受疫情影响,这个假期变得漫长又煎熬,我也无时无刻不关注着疫情的变化。当然这样的一个假期,我还真得要感谢周翔,因为他有个爱看书的习惯,所以家里有不少他看过的书,可以让我随意挑选,因此也让我的假期不至于那么无所事事。这次我选了一本梁晓声的《人世间》,作为一名语文
- SQL Server_查询某一数据库中的所有表的内容
qq_42772833
SQLServer数据库sqlserver
1.查看所有表的表名要列出CrabFarmDB数据库中的所有表(名),可以使用以下SQL语句:USECrabFarmDB;--切换到目标数据库GOSELECTTABLE_NAMEFROMINFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLESWHERETABLE_TYPE='BASETABLE';对这段SQL脚本的解释:SELECTTABLE_NAME:这个语句的作用是从查询结果中选择TABLE_NAM
- 【加密社】Solidity 中的事件机制及其应用
加密社
闲侃区块链智能合约区块链
加密社引言在Solidity合约开发过程中,事件(Events)是一种非常重要的机制。它们不仅能够让开发者记录智能合约的重要状态变更,还能够让外部系统(如前端应用)监听这些状态的变化。本文将详细介绍Solidity中的事件机制以及如何利用不同的手段来触发、监听和获取这些事件。事件存储的地方当我们在Solidity合约中使用emit关键字触发事件时,该事件会被记录在区块链的交易收据中。具体而言,事件
- 使用LLaVa和Ollama实现多模态RAG示例
llzwxh888
python人工智能开发语言
本文将详细介绍如何使用LLaVa和Ollama实现多模态RAG(检索增强生成),通过提取图像中的结构化数据、生成图像字幕等功能来展示这一技术的强大之处。安装环境首先,您需要安装以下依赖包:!pipinstallllama-index-multi-modal-llms-ollama!pipinstallllama-index-readers-file!pipinstallunstructured!p
- 如何部分格式化提示模板:LangChain中的高级技巧
nseejrukjhad
langchainjava服务器python
标题:如何部分格式化提示模板:LangChain中的高级技巧内容:如何部分格式化提示模板:LangChain中的高级技巧引言在使用大型语言模型(LLM)时,提示工程是一个关键环节。LangChain提供了强大的提示模板功能,让我们能更灵活地构建和管理提示。本文将介绍LangChain中一个高级特性-部分格式化提示模板,这个技巧可以让你的提示管理更加高效和灵活。什么是部分格式化提示模板?部分格式化提
- GitHub上克隆项目
bigbig猩猩
github
从GitHub上克隆项目是一个简单且直接的过程,它允许你将远程仓库中的项目复制到你的本地计算机上,以便进行进一步的开发、测试或学习。以下是一个详细的步骤指南,帮助你从GitHub上克隆项目。一、准备工作1.安装Git在克隆GitHub项目之前,你需要在你的计算机上安装Git工具。Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,用于跟踪和管理代码变更。你可以从Git的官方网站(https://git-scm.
- Day17笔记-高阶函数
~在杰难逃~
Python笔记python开发语言pycharm数据分析
高阶函数【重点掌握】函数的本质:函数是一个变量,函数名是一个变量名,一个函数可以作为另一个函数的参数或返回值使用如果A函数作为B函数的参数,B函数调用完成之后,会得到一个结果,则B函数被称为高阶函数常用的高阶函数:map(),reduce(),filter(),sorted()1.map()map(func,iterable),返回值是一个iterator【容器,迭代器】func:函数iterab
- 读书||陶新华《教育中的积极心理学》1—28
流水淙淙2022
读一本好书,尤如和一位高尚者对话,亦能对人的精神进行洗礼。但是若不能和实践结合起来,也只能落到空读书的状态。读书摘要与感想1、塞利格曼在《持续的幸福》一书中提出了幸福2.0理论,提出幸福由5个元素决定——积极情绪、投入的工作和生活、目标和意义、和谐的人际关系、成就感。2、人的大脑皮层在进行智力活动时,都伴有皮下中枢活动,对这些活动进行体验请假,并由此产生了情感解读。人的情绪情感体验总是优先于大脑的
- Python快速入门 —— 第三节:类与对象
孤华暗香
Python快速入门python开发语言
第三节:类与对象目标:了解面向对象编程的基础概念,并学会如何定义类和创建对象。内容:类与对象:定义类:class关键字。类的构造函数:__init__()。类的属性和方法。对象的创建与使用。示例:classStudent:def__init__(self,name,age,major):self.name&#
- apache 安装linux windows
墙头上一根草
apacheinuxwindows
linux安装Apache 有两种方式一种是手动安装通过二进制的文件进行安装,另外一种就是通过yum 安装,此中安装方式,需要物理机联网。以下分别介绍两种的安装方式
通过二进制文件安装Apache需要的软件有apr,apr-util,pcre
1,安装 apr 下载地址:htt
- fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别
Cb123456
match_parentfill_parent
fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别:
1)fill_parent
设置一个构件的布局为fill_parent将强制性地使构件扩展,以填充布局单元内尽可能多的空间。这跟Windows控件的dockstyle属性大体一致。设置一个顶部布局或控件为fill_parent将强制性让它布满整个屏幕。
2) wrap_conte
- 网页自适应设计
天子之骄
htmlcss响应式设计页面自适应
网页自适应设计
网页对浏览器窗口的自适应支持变得越来越重要了。自适应响应设计更是异常火爆。再加上移动端的崛起,更是如日中天。以前为了适应不同屏幕分布率和浏览器窗口的扩大和缩小,需要设计几套css样式,用js脚本判断窗口大小,选择加载。结构臃肿,加载负担较大。现笔者经过一定时间的学习,有所心得,故分享于此,加强交流,共同进步。同时希望对大家有所
- [sql server] 分组取最大最小常用sql
一炮送你回车库
SQL Server
--分组取最大最小常用sql--测试环境if OBJECT_ID('tb') is not null drop table tb;gocreate table tb( col1 int, col2 int, Fcount int)insert into tbselect 11,20,1 union allselect 11,22,1 union allselect 1
- ImageIO写图片输出到硬盘
3213213333332132
javaimage
package awt;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.imagei
- 自己的String动态数组
宝剑锋梅花香
java动态数组数组
数组还是好说,学过一两门编程语言的就知道,需要注意的是数组声明时需要把大小给它定下来,比如声明一个字符串类型的数组:String str[]=new String[10]; 但是问题就来了,每次都是大小确定的数组,我需要数组大小不固定随时变化怎么办呢? 动态数组就这样应运而生,龙哥给我们讲的是自己用代码写动态数组,并非用的ArrayList 看看字符
- pinyin4j工具类
darkranger
.net
pinyin4j工具类Java工具类 2010-04-24 00:47:00 阅读69 评论0 字号:大中小
引入pinyin4j-2.5.0.jar包:
pinyin4j是一个功能强悍的汉语拼音工具包,主要是从汉语获取各种格式和需求的拼音,功能强悍,下面看看如何使用pinyin4j。
本人以前用AscII编码提取工具,效果不理想,现在用pinyin4j简单实现了一个。功能还不是很完美,
- StarUML学习笔记----基本概念
aijuans
UML建模
介绍StarUML的基本概念,这些都是有效运用StarUML?所需要的。包括对模型、视图、图、项目、单元、方法、框架、模型块及其差异以及UML轮廓。
模型、视与图(Model, View and Diagram)
&
- Activiti最终总结
avords
Activiti id 工作流
1、流程定义ID:ProcessDefinitionId,当定义一个流程就会产生。
2、流程实例ID:ProcessInstanceId,当开始一个具体的流程时就会产生,也就是不同的流程实例ID可能有相同的流程定义ID。
3、TaskId,每一个userTask都会有一个Id这个是存在于流程实例上的。
4、TaskDefinitionKey和(ActivityImpl activityId
- 从省市区多重级联想到的,react和jquery的差别
bee1314
jqueryUIreact
在我们的前端项目里经常会用到级联的select,比如省市区这样。通常这种级联大多是动态的。比如先加载了省,点击省加载市,点击市加载区。然后数据通常ajax返回。如果没有数据则说明到了叶子节点。 针对这种场景,如果我们使用jquery来实现,要考虑很多的问题,数据部分,以及大量的dom操作。比如这个页面上显示了某个区,这时候我切换省,要把市重新初始化数据,然后区域的部分要从页面
- Eclipse快捷键大全
bijian1013
javaeclipse快捷键
Ctrl+1 快速修复(最经典的快捷键,就不用多说了)Ctrl+D: 删除当前行 Ctrl+Alt+↓ 复制当前行到下一行(复制增加)Ctrl+Alt+↑ 复制当前行到上一行(复制增加)Alt+↓ 当前行和下面一行交互位置(特别实用,可以省去先剪切,再粘贴了)Alt+↑ 当前行和上面一行交互位置(同上)Alt+← 前一个编辑的页面Alt+→ 下一个编辑的页面(当然是针对上面那条来说了)Alt+En
- js 笔记 函数
征客丶
JavaScript
一、函数的使用
1.1、定义函数变量
var vName = funcation(params){
}
1.2、函数的调用
函数变量的调用: vName(params);
函数定义时自发调用:(function(params){})(params);
1.3、函数中变量赋值
var a = 'a';
var ff
- 【Scala四】分析Spark源代码总结的Scala语法二
bit1129
scala
1. Some操作
在下面的代码中,使用了Some操作:if (self.partitioner == Some(partitioner)),那么Some(partitioner)表示什么含义?首先partitioner是方法combineByKey传入的变量,
Some的文档说明:
/** Class `Some[A]` represents existin
- java 匿名内部类
BlueSkator
java匿名内部类
组合优先于继承
Java的匿名类,就是提供了一个快捷方便的手段,令继承关系可以方便地变成组合关系
继承只有一个时候才能用,当你要求子类的实例可以替代父类实例的位置时才可以用继承。
在Java中内部类主要分为成员内部类、局部内部类、匿名内部类、静态内部类。
内部类不是很好理解,但说白了其实也就是一个类中还包含着另外一个类如同一个人是由大脑、肢体、器官等身体结果组成,而内部类相
- 盗版win装在MAC有害发热,苹果的东西不值得买,win应该不用
ljy325
游戏applewindowsXPOS
Mac mini 型号: MC270CH-A RMB:5,688
Apple 对windows的产品支持不好,有以下问题:
1.装完了xp,发现机身很热虽然没有运行任何程序!貌似显卡跑游戏发热一样,按照那样的发热量,那部机子损耗很大,使用寿命受到严重的影响!
2.反观安装了Mac os的展示机,发热量很小,运行了1天温度也没有那么高
&nbs
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-生成器模式-Builder
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* 生成器模式的意图在于将一个复杂的构建与其表示相分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示(GoF)
* 个人理解:
* 构建一个复杂的对象,对于创建者(Builder)来说,一是要有数据来源(rawData),二是要返回构
- JIRA与SVN插件安装
chenyu19891124
SVNjira
JIRA安装好后提交代码并要显示在JIRA上,这得需要用SVN的插件才能看见开发人员提交的代码。
1.下载svn与jira插件安装包,解压后在安装包(atlassian-jira-subversion-plugin-0.10.1)
2.解压出来的包里下的lib文件夹下的jar拷贝到(C:\Program Files\Atlassian\JIRA 4.3.4\atlassian-jira\WEB
- 常用数学思想方法
comsci
工作
对于搞工程和技术的朋友来讲,在工作中常常遇到一些实际问题,而采用常规的思维方式无法很好的解决这些问题,那么这个时候我们就需要用数学语言和数学工具,而使用数学工具的前提却是用数学思想的方法来描述问题。。下面转帖几种常用的数学思想方法,仅供学习和参考
函数思想
把某一数学问题用函数表示出来,并且利用函数探究这个问题的一般规律。这是最基本、最常用的数学方法
- pl/sql集合类型
daizj
oracle集合typepl/sql
--集合类型
/*
单行单列的数据,使用标量变量
单行多列数据,使用记录
单列多行数据,使用集合(。。。)
*集合:类似于数组也就是。pl/sql集合类型包括索引表(pl/sql table)、嵌套表(Nested Table)、变长数组(VARRAY)等
*/
/*
--集合方法
&n
- [Ofbiz]ofbiz初用
dinguangx
电商ofbiz
从github下载最新的ofbiz(截止2015-7-13),从源码进行ofbiz的试用
1. 加载测试库
ofbiz内置derby,通过下面的命令初始化测试库
./ant load-demo (与load-seed有一些区别)
2. 启动内置tomcat
./ant start
或
./startofbiz.sh
或
java -jar ofbiz.jar
&
- 结构体中最后一个元素是长度为0的数组
dcj3sjt126com
cgcc
在Linux源代码中,有很多的结构体最后都定义了一个元素个数为0个的数组,如/usr/include/linux/if_pppox.h中有这样一个结构体: struct pppoe_tag { __u16 tag_type; __u16 tag_len; &n
- Linux cp 实现强行覆盖
dcj3sjt126com
linux
发现在Fedora 10 /ubutun 里面用cp -fr src dest,即使加了-f也是不能强行覆盖的,这时怎么回事的呢?一两个文件还好说,就输几个yes吧,但是要是n多文件怎么办,那还不输死人呢?下面提供三种解决办法。 方法一
我们输入alias命令,看看系统给cp起了一个什么别名。
[root@localhost ~]# aliasalias cp=’cp -i’a
- Memcached(一)、HelloWorld
frank1234
memcached
一、简介
高性能的架构离不开缓存,分布式缓存中的佼佼者当属memcached,它通过客户端将不同的key hash到不同的memcached服务器中,而获取的时候也到相同的服务器中获取,由于不需要做集群同步,也就省去了集群间同步的开销和延迟,所以它相对于ehcache等缓存来说能更好的支持分布式应用,具有更强的横向伸缩能力。
二、客户端
选择一个memcached客户端,我这里用的是memc
- Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
hcx2013
search
Follow up for "Search in Rotated Sorted Array":What if duplicates are allowed?
Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
Write a function to determine if a given ta
- Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
jinnianshilongnian
spring4generic type
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- CentOS安装JDK
liuxingguome
centos
1、行卸载原来的:
[root@localhost opt]# rpm -qa | grep java
tzdata-java-2014g-1.el6.noarch
java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.65-2.5.1.2.el6_5.x86_64
java-1.6.0-openjdk-1.6.0.0-11.1.13.4.el6.x86_64
[root@localhost
- 二分搜索专题2-在有序二维数组中搜索一个元素
OpenMind
二维数组算法二分搜索
1,设二维数组p的每行每列都按照下标递增的顺序递增。
用数学语言描述如下:p满足
(1),对任意的x1,x2,y,如果x1<x2,则p(x1,y)<p(x2,y);
(2),对任意的x,y1,y2, 如果y1<y2,则p(x,y1)<p(x,y2);
2,问题:
给定满足1的数组p和一个整数k,求是否存在x0,y0使得p(x0,y0)=k?
3,算法分析:
(
- java 随机数 Math与Random
SaraWon
javaMathRandom
今天需要在程序中产生随机数,知道有两种方法可以使用,但是使用Math和Random的区别还不是特别清楚,看到一篇文章是关于的,觉得写的还挺不错的,原文地址是
http://www.oschina.net/question/157182_45274?sort=default&p=1#answers
产生1到10之间的随机数的两种实现方式:
//Math
Math.roun
- oracle创建表空间
tugn
oracle
create temporary tablespace TXSJ_TEMP
tempfile 'E:\Oracle\oradata\TXSJ_TEMP.dbf'
size 32m
autoextend on
next 32m maxsize 2048m
extent m
- 使用Java8实现自己的个性化搜索引擎
yangshangchuan
javasuperword搜索引擎java8全文检索
需要对249本软件著作实现句子级别全文检索,这些著作均为PDF文件,不使用现有的框架如lucene,自己实现的方法如下:
1、从PDF文件中提取文本,这里的重点是如何最大可能地还原文本。提取之后的文本,一个句子一行保存为文本文件。
2、将所有文本文件合并为一个单一的文本文件,这样,每一个句子就有一个唯一行号。
3、对每一行文本进行分词,建立倒排表,倒排表的格式为:词=包含该词的总行数N=行号
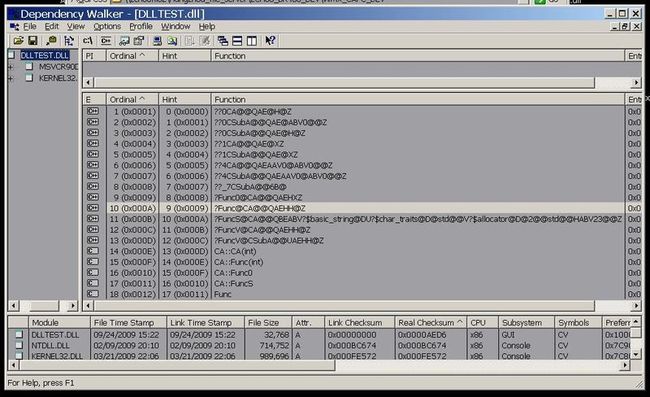
 #ifndef __DLLMAIN_H__
#ifndef __DLLMAIN_H__ #define
__DLLMAIN_H__
#define
__DLLMAIN_H__

 #include
<
string
>
#include
<
string
>

 #define
DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
#define
DllExport __declspec(dllexport)

 extern
"
C
"
int
DllExport Func(
int
x);
extern
"
C
"
int
DllExport Func(
int
x);
 extern
"
C
"
class
DllExport CA
extern
"
C
"
class
DllExport CA

 {
{ public:
public: CA(int x);
CA(int x); ~CA();
~CA();
 int Func0();
int Func0(); int Func(int x);
int Func(int x); const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const; protected:
protected: int _x;
int _x;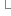 }
;
}
;

 #endif
#endif
 #include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
iostream
>

 #include
"
DllMain.h
"
#include
"
DllMain.h
"

 int
Func(
int
x)
int
Func(
int
x)

 {
{ return x * 10;
return x * 10;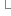 }
}

 CA::CA(
int
x)
CA::CA(
int
x) : _x(x)
: _x(x)

 {
{ std::cout << "contructor" << std::endl;
std::cout << "contructor" << std::endl;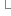 }
}

 CA::
~
CA()
CA::
~
CA()

 {
{ std::cout << "destructor" << std::endl;
std::cout << "destructor" << std::endl; }
}

 int
CA::Func0()
int
CA::Func0()

 {
{ return _x;
return _x; }
}

 int
CA::Func(
int
x)
int
CA::Func(
int
x)

 {
{ return _x * x;
return _x * x; }
}

 const
std::
string
&
CA::FuncS(
int
x,
const
std::
string
&
str)
const
const
std::
string
&
CA::FuncS(
int
x,
const
std::
string
&
str)
const


 {
{ return str;
return str; }
}

 LIBRARY TESTDLL
LIBRARY TESTDLL EXPORTS
EXPORTS Func
=
Func
Func
=
Func CA::CA(
int
)
=
??
0CA@@QAE@H@Z
CA::CA(
int
)
=
??
0CA@@QAE@H@Z CA::
~
CA
=
??
1CA@@QAE@XZ
CA::
~
CA
=
??
1CA@@QAE@XZ CA::Func0
=
?
Func0@CA@@QAEHXZ
CA::Func0
=
?
Func0@CA@@QAEHXZ CA::Func(
int
)
=
?
Func@CA@@QAEHH@Z
CA::Func(
int
)
=
?
Func@CA@@QAEHH@Z ;CA::FuncS(
int
,std::basic_string
<
char
>&
)
=
?
FuncS@CA@@QBEABV
?
$basic_string@DU
?
$char_traits@D@std@@V
?
$allocator@D@
2
@@std@@HABV23@@Z
;CA::FuncS(
int
,std::basic_string
<
char
>&
)
=
?
FuncS@CA@@QBEABV
?
$basic_string@DU
?
$char_traits@D@std@@V
?
$allocator@D@
2
@@std@@HABV23@@Z CA::FuncS
=
?
FuncS@CA@@QBEABV
?
$basic_string@DU
?
$char_traits@D@std@@V
?
$allocator@D@
2
@@std@@HABV23@@Z
CA::FuncS
=
?
FuncS@CA@@QBEABV
?
$basic_string@DU
?
$char_traits@D@std@@V
?
$allocator@D@
2
@@std@@HABV23@@Z

 #include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
iostream
>
 #include
<
string
>
#include
<
string
>

 #include
<
windows.h
>
#include
<
windows.h
>

 //
#include "DllMain.h"
//
#include "DllMain.h"

 #define
DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
#define
DllExport __declspec(dllexport)

 extern
"
C
"
int
DllExport Func(
int
x);
extern
"
C
"
int
DllExport Func(
int
x);
 extern
"
C
"
class
DllExport CA
extern
"
C
"
class
DllExport CA

 {
{ public:
public: CA(int x);
CA(int x); ~CA();
~CA();
 int Func0();
int Func0(); int Func(int x);
int Func(int x); const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
 private:
private: int _x;
int _x; }
;
}
;
 typedef
int
(
*
func)(
int
);
typedef
int
(
*
func)(
int
); typedef
void
(WINAPI
*
PCTOR)(
int
);
typedef
void
(WINAPI
*
PCTOR)(
int
); typedef
int
(WINAPI
*
func0)(
void
);
typedef
int
(WINAPI
*
func0)(
void
); typedef
int
(WINAPI
*
funcc)(
int
);
typedef
int
(WINAPI
*
funcc)(
int
); typedef
const
std::
string
&
(WINAPI
*
funcs)(
int
,
const
std::
string
&
);
typedef
const
std::
string
&
(WINAPI
*
funcs)(
int
,
const
std::
string
&
); typedef
void
(WINAPI
*
PDTOR)(
void
);
typedef
void
(WINAPI
*
PDTOR)(
void
);
 int
main()
int
main()

 {
{ HINSTANCE hdll;
HINSTANCE hdll; hdll = LoadLibraryA(("../DLLTEST/Debug/DLLTEST.dll"));
hdll = LoadLibraryA(("../DLLTEST/Debug/DLLTEST.dll")); if(hdll != NULL)
if(hdll != NULL)

 {
{ func pf = (func)GetProcAddress(hdll, "Func");
func pf = (func)GetProcAddress(hdll, "Func"); std::cout << pf(10) << std::endl;
std::cout << pf(10) << std::endl; CA* a = (CA*)malloc(sizeof(CA));
CA* a = (CA*)malloc(sizeof(CA)); PCTOR pc = (PCTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::CA(int)");
PCTOR pc = (PCTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::CA(int)");
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }  pc(5);
pc(5); func0 pf0 = (func0)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func0");
func0 pf0 = (func0)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func0");
 _asm
_asm  {MOV ECX, a }
{MOV ECX, a } std::cout << pf0() << std::endl;
std::cout << pf0() << std::endl; funcc pfc = (funcc)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func(int)");
funcc pfc = (funcc)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func(int)");
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a } std::cout << pfc(10) << std::endl;
std::cout << pfc(10) << std::endl; funcs pfs = (funcs)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::FuncS");
funcs pfs = (funcs)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::FuncS");
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a } std::cout << pfs(0, std::string("hello world")) << std::endl;
std::cout << pfs(0, std::string("hello world")) << std::endl; PDTOR pd = (PDTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::~CA");
PDTOR pd = (PDTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::~CA");
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }  pd();
pd();  free(a);
free(a);  }
} FreeLibrary(hdll);
FreeLibrary(hdll);
 return 0;
return 0; }
}
 100
100
 contructor
contructor 5
5
 50
50
 hello world
hello world destructor
destructor