Topology and Geometry in OpenCascade
Location and Orientaion
eryar@163.com
摘要Abstract:本文简要介绍了几何造型中的边界表示法(BRep),并结合程序说明OpenCascade中的边界表示的具体实现,即拓朴与几何的联系。拓朴结构中的位置(Location)和朝向(Orientation)进行了详细说明。
关键字Key Words:OpenCascade、BRep、Topology、Geometry、Location、Orientation
一、引言 Introduction
OpenCascade中的拓朴(topology)是根据STEP标准ISO-10303-42设计的。也许读一下这个标准中的有关概念还是很有帮助的。STEP ISO-10303-42的相关资源:
http://www.steptools.com/support/stdev_docs/express/step_irs/index.html
Figure 2.1 Topology data structure in OpenCascade
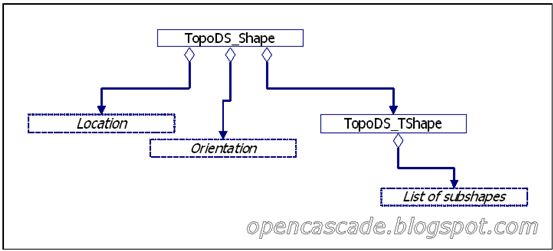
TopoDS_Shape由值控制,包含三个成员变量:myLocation、myOrient、myTShape。
Figure 2.2 TopoDS_Shape member fields
2.2 拓朴与几何的联系 Connection with Geometry
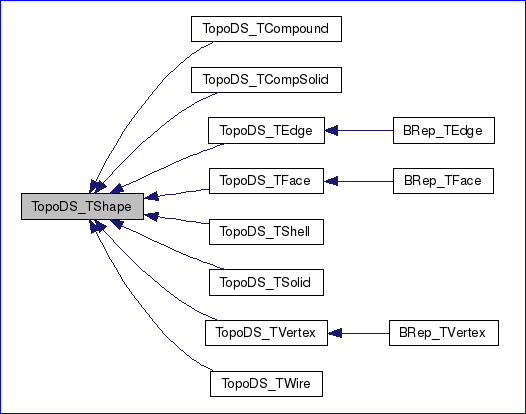
现在我们来考虑一下拓朴结构与几何的关系。通过继承TopoDS包中的抽象的拓朴类实现了边界表示模型。如下图所示:
Figure 2.3 Topology data structure in OpenCascade
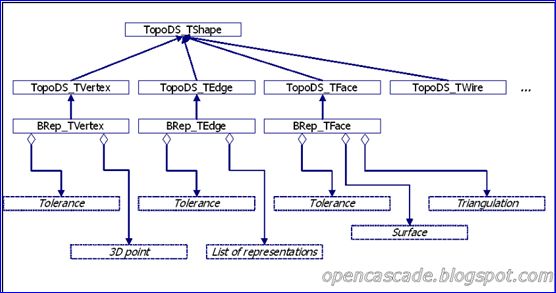
从上面的类图可以看出只有三种拓朴对象有几何表示:顶点(vertex)、边(edge)、面(face),分别为BRep_TVertex、BRep_TEdge、BRep_TFace。
Figure 2.4 TopoDS_TShape class diagram
二、位置 Location
ToposDS_Shape有个TopLoc_Location的成员变量myLocation,该变量定义了子形状相对于该形状的偏移量。例如,环(wire)有一个位置变量,该变量沿着向量{0,0,10}移动,意味着环所有的边都沿着Z轴移动10个单位。下面以一个程序来具体说明:
2 * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved.
3 *
4 * File : Main.cpp
5 * Author : eryar@163.com
6 * Date : 2013-09-26
7 * Version : V1.0
8 *
9 * Description : Shape location.
10 *
11 */
12
13 #define WNT
14 #include < Geom_Circle.hxx >
15
16 #include < TopoDS_Edge.hxx >
17 #include < TopoDS_Wire.hxx >
18 #include < TopoDS_Iterator.hxx >
19
20 #include < BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx >
21 #include < BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire.hxx >
22
23 #pragma comment(lib, " TKernel.lib " )
24 #pragma comment(lib, " TKMath.lib " )
25 #pragma comment(lib, " TKG3d.lib " )
26 #pragma comment(lib, " TKBRep.lib " )
27 #pragma comment(lib, " TKTopAlgo.lib " )
28
29 const std:: string dumpShapeType( const TopAbs_ShapeEnum & type)
30 {
31 std:: string strType( " Shape " );
32
33 switch (type)
34 {
35 case TopAbs_COMPOUND:
36 strType = " COMPOUND " ;
37 break ;
38
39 case TopAbs_COMPSOLID:
40 strType = " COMPSOLID " ;
41 break ;
42
43 case TopAbs_SOLID:
44 strType = " SOLID " ;
45 break ;
46
47 case TopAbs_SHELL:
48 strType = " SHELL " ;
49 break ;
50
51 case TopAbs_FACE:
52 strType = " FACE " ;
53 break ;
54
55 case TopAbs_WIRE:
56 strType = " WIRE " ;
57 break ;
58
59 case TopAbs_EDGE:
60 strType = " EDGE " ;
61 break ;
62
63 case TopAbs_VERTEX:
64 strType = " VERTEX " ;
65 break ;
66
67 default :
68 break ;
69 }
70
71 return strType;
72 }
73
74 void dumpShapeLocation( const TopoDS_Shape & shape)
75 {
76 std::cout << " Shape Type: " << dumpShapeType(shape.ShapeType()) << std::endl;
77 shape.Location().ShallowDump(std::cout);
78
79 TopoDS_Iterator anItr(shape);
80
81 for (; anItr.More(); anItr.Next())
82 {
83 const TopoDS_Shape & aChild = anItr.Value();
84
85 dumpShapeLocation(aChild);
86 }
87 }
88
89 int main( void )
90 {
91 Handle_Geom_Curve aCircle = new Geom_Circle(gp::XOY(), 5.0 );
92
93 TopoDS_Edge anEdge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(aCircle);
94 TopoDS_Wire aWire = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire(anEdge);
95
96 std::cout << " Before transformation: " << std::endl;
97 dumpShapeLocation(aWire);
98
99 gp_Trsf trsf;
100 trsf.SetTranslation(gp_Vec( 0 , 0 , 10 ));
101 TopLoc_Location location(trsf);
102
103 aWire.Location(location);
104
105 std::cout << " After transformation: " << std::endl;
106 dumpShapeLocation(aWire);
107
108 return 0 ;
109 }
程序结果如下所示:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
三、朝向 Orientation
朝向(orientation)与位置(location)的工作原理相同。当将子对象从实体中分离出来时,父对象的朝向会影响到子对象的朝向。但是有个很重要的例外就是面(Face)上边(Edge)的朝向不遵守这个规则。在讨论面的朝向时,讨论过边的参数空间曲线(pcurve)的material问题。这个例外说的是计算面上边的朝向时不应该受到面的朝向的影响。即若要使用边的参数空间曲线(pcurve)就按下面的方式:
2 for (; aFaceExp.More(); aFaceExp.Next())
3 {
4 const TopoDS_Edge & anEdge = TopoDS::Edge (aFaceExp.Current());
5 }
假如你研究得更为深入,这个例外也是可以理解的。让我们以一个具体例子来理解这个例外,从底层一步步的创建一个面:
2 // anti-clockwise circles if to look from surface normal
3 Handle(Geom_Curve) anExtC = new Geom_Circle (gp::XOY(), 10 .);
4 Handle(Geom_Curve) anIntC = new Geom_Circle (gp::XOY(), 5 .);
5 TopoDS_Edge anExtE = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge (anExtC);
6 TopoDS_Edge anIntE = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge (anExtC);
7 TopoDS_Wire anExtW = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire (anExtE);
8 TopoDS_Wire anIntW = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeWire (anIntE);
9 BRep_Builder aB;
10 TopoDS_Face aFace;
11 aB.MakeFace (aFace, aSurf, Precision::Confusion());
12 aB.Update (aFace, aSurf);
13 aB.Add (aFace, anExtW);
14 // material should lie on the right of the inner wire
15 aB.Add (aFace, anIntW.Reversed());
面默认的朝向是向前的(forward),让我们来遍历面的边(edge)和参数空间曲线(pcurve)。尽管我们没有显示地来添加它们,从原来的讨论中可知平面上的参数空间曲线可以默认计算(be computed on the fly):
2 {
3 TopExp_Explorer anExp (theFace, TopAbs_EDGE);
4 for (; anExp.More(); anExp.Next())
5 {
6 Standard_Real aF = 0.0 ;
7 Standard_Real aL = 0.0 ;
8 const TopoDS_Edge & anEdge = TopoDS::Edge (anExp.Current());
9
10 Handle(Geom2d_Curve) aPCurve = BRep_Tool::CurveOnSurface (anEdge, theFace, aF, aL);
11 }
12 }
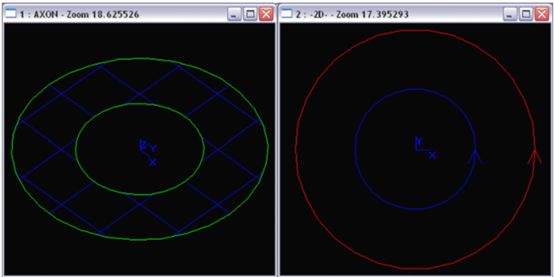
得到的参数空间曲线(pcurves)如下图所示,material在红线的左侧,在蓝线的右侧:
一切都很正确。现在设想一下,如果把面的朝向反向(reverse),然后再遍历边和参数空间曲线,会发生什么呢?
2
3 TraversePCurves (aRFace);
所有的边将会具有相反的朝向,对应边的参数空间曲线(pcurve)的material在外环的外侧,在内环的内侧,这明显是错误的!在前面讨论面的朝向时就说过面的朝向仅仅是面的逻辑朝向,而与其底层的曲面(surface)没有关系。在上面的例子中反转面aRFace只是一个法向为{0, 0, -1}的面。所以,要获得边的正确朝向,必须使用下面的方法来访问面中的边:
这样就确保面上的边具有正确的朝向,而与曲面(surface,注意在此不是face!)的法向没有关系。OpenCASCADE的算法对这种特殊的情况都做了处理,你也一定记得这样做。
四、结论 Conclusion
对拓朴形状(TopoDS_Shape)的位置(location)和朝向(orientation)进行深入理解,整个拓朴结构就变得清晰了,因为一个拓朴形状中除了子对象外,剩下就是位置和朝向成员变量了。
理解了拓朴结构后,对OpenCascade的模块ModelingData就有个较深刻地认识了。
五、参考资料 Reference
1. Roman Lygin, OpenCascade notes, opencascade.blogspot.com
2. 孙家广等. 计算机图形学. 清华大学出版社
3. OpenCascade source code.
PDF Version: Topology and Geometry in OpenCascade-Location and Orientation