Storm拓扑,组件之spout、bolt,并行策略
软件版本:Storm:0.9.3 ,Redis:2.8.19;jedis:2.6.2;
参考:http://storm.apache.org/documentation/Understanding-the-parallelism-of-a-Storm-topology.html
一、Storm原理
Storm简述:Storm中有两个组件:nimbus和supervisor,nimbus主要负责分配资源和schedule和协调任务,supervisor主要启动worker,每个worker可以启动一个到多个executor,一个executor可以启动一个到多个task,(默认一个executor对应一个task)实际执行任务的是task。
二、Storm编程
1. Topology (拓扑)
1.1 定义spout、bolt以及其关系
//Topology definition
TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder();
builder.setSpout("wc-spout",new WCSpout(),Integer.parseInt(args[2]));
builder.setBolt("split-bolt", new SplitBolt(),Integer.parseInt(args[3]))
.shuffleGrouping("wc-spout");
builder.setBolt("count-bolt", new CountBolt(),Integer.parseInt(args[4]))
.fieldsGrouping("split-bolt", new Fields("word"));
在设置spout和bolt的时候还可以设置并行的个数,即executor的个数,当然也可以设置task的个数,如下代码,两个executor,四个task,则每个executor配置两个task。
topologyBuilder.setBolt("green-bolt", new GreenBolt(), 2)
.setNumTasks(4)
.shuffleGrouping("blue-spout);<代码来自:
http://storm.apache.org/documentation/Understanding-the-parallelism-of-a-Storm-topology.html>
1.2 配置参数项(在spout和bolt中可通过此项设置获取参数值)
// 定义Configuration
Config conf = new Config();
conf.put("storeFrequent", Long.parseLong(args[0]));
conf.put("slow_fast", args[5]);
conf.put("printWC", args[6]);
conf.setNumWorkers(Integer.parseInt(args[1]));上面的代码除了设置三个变量值之外,还设置了worker的数量;
1.3 提交Topology
集群提交方式:
// 提交任务
StormSubmitter.submitTopology("wc-redis", conf,builder. createTopology());
其中的“wc-redis”是Topology的名字,后面两个是基本的模式写法,可以就按照上面的写即可。
单机提交方式:
LocalCluster cluster = new LocalCluster();
cluster. submitTopology("wc-redis", conf,
builder. createTopology());
2.1 继承BasiRichSpout
继承这个类后,定义一个域变量SpoutOutputCollector collector,这个用于输出;
2.2 覆写open方法
public void open(@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map conf, TopologyContext context,
SpoutOutputCollector collector) {在这里首先使用collector来初始化之前定义的域变量,如果有需要获取的参数值可以从conf中获取,context里面是当前的spout的相关信息上下文;
2.3 覆写nextTuple
在这个方法里面使用collector.emit方法即可进行输出,一般使用下面的方式即可:
public List<Integer> emit(List<Object> tuple) {
return emit(tuple, null);
}如果要求容错基本较高,可以使用一个streamid的方式进行输出,如下:
public List<Integer> emit(String streamId, List<Object> tuple) {
return emit(streamId, tuple, null);
}2.4 覆写declareOutputFields方法
一般定义一个field名字即可,如下:
@Override
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
declarer.declare(new Fields("line"));
}3. Bolt
3.1 继承BaseBasicBolt类
3.2 覆写prepare方法
public void prepare(@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map conf,TopologyContext context)这个方法类似Spout的open方法,进行一些初始化或获取参数值的操作;
3.3 覆写exec方法
public void execute(Tuple input, BasicOutputCollector collector)这个方法的input即是从Spout中输出的数据,通过对这个数据进行处理,然后使用collector.emit方法进行输出,可以是输出到下一个Bolt的处理,作为下一个Bolt的输入。
3.4 覆写declareOutputFields方法
这个方法和Spout的declareOutputFields方法类似,声明field的名字。
4. 提交运行
storm jar wc.jar test.TopologyMain
1. worker只是用来分配各个组件的,包括Spout和Bolt。
比如分配了一个worker,然后一个Spout S分配两个executor,一个Bolt A分配一个executor,另一个Bolt B分配一个executor,那么这些executor一共有4个task(使用默认一个executor对应一个task),就会全部分配在一个worker上。
如果分配了两个worker,还按上的组件分配,那么可能worker 1上面分配了一个Spout S的executor和Bolt A的executor,worker 2 上面分配了一个Spout S的另一个executor,和Bolt B的executor。
2. Spout executor并行
Spout如果单单设置executor的并行个数,那么其输出可能是有重复的,这样的并行策略是有问题的。
比如下面的Spout:
package wc.redis.spout;
import java.util.Map;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import wc.redis.util.RedisUtils;
import backtype.storm.spout.SpoutOutputCollector;
import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext;
import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseRichSpout;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Values;
public class WCSpout extends BaseRichSpout {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private SpoutOutputCollector collector;
private Jedis jedis;
Integer taskId;
String conponentId;
String slow_fast;
@Override
public void open(@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map conf, TopologyContext context,
SpoutOutputCollector collector) {
this.collector = collector;
slow_fast = (String)conf.get("slow_fast");
jedis = RedisUtils.connect(RedisUtils.HOSTNAME, RedisUtils.PORT, RedisUtils.INSERT_DB);
taskId = context.getThisTaskId();
conponentId = context.getThisComponentId();
context.getThisTaskIndex();
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(conponentId, taskId, " WCSpout初始化完成!"));
}
@Override
public void nextTuple() {
long interval =0;
while(true){// 获取数据
interval++;
String zero = getItem("0");
String one = getItem("1");
String two = getItem("2");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);// 每200毫秒发送一次数据
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(zero==null||one==null||two==null){
// do nothing
// 没有数据
if(interval%15==0){
// System.out.println(new java.util.Date()+":ConponentId:"+conponentId+",taskID:"+taskId+
// ",spout:No Data...");
// System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(conponentId, taskId, "spout:No data..."));
}
}else{
this.collector.emit(new Values(zero+","+one+","+two));
if(interval%15==0&&"fast".equals(slow_fast)){
// System.out.println(new java.util.Date()+":ConponentId:"+conponentId+",taskID:"+taskId+
// ",spout:["+zero+","+one+","+two+"]");
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(conponentId, taskId, "Spout:["+zero+","+one+","+two+"]"));
}else if("slow".equals(slow_fast)){
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(conponentId, taskId, "Spout:["+zero+","+one+","+two+"]"));
}else{
new RuntimeException("Wrong argument!");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
declarer.declare(new Fields("line"));
}
/**
* Redis中获取键值并删除对应的键
* @param index
*/
private String getItem(String index){
if(!jedis.exists(index)){
return null;
}
String val = jedis.get(index);
// if(val==null||"null".equals("null")){
// return ;
// }
jedis.del(index);
return val;
}
}
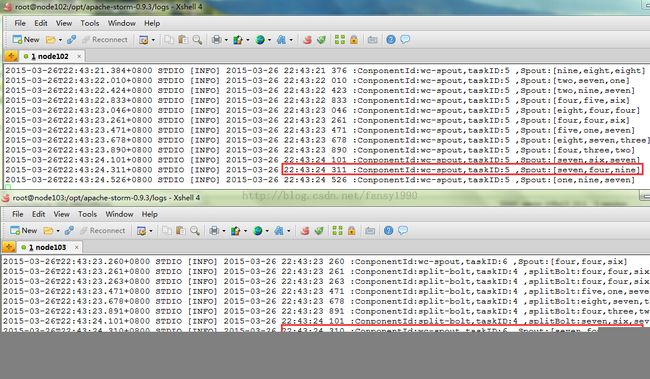
这个Spout从Redis服务器中获取数据,获取后把对应的数据删除。两个Spout都同时读取了数据,然后进行了输出,同时只能有一个Spout删除了Redis中的数据,这样就会有重复数据输出了,类似图1:
图1
从图1红色区域可以看到Spout的输出,从时间可以看出两个输出只相差了1毫秒;从蓝色的框也可以看出Spout的下一个Bolt获取了两条相同的数据,这就说明Spout输出了重复的数据;
所以Spout的并行策略应该是获取taskid,根据数据的特征来选择(可以随机)需要处理的executor,代码如下:
package wc.redis.spout;
import java.util.Map;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import wc.redis.util.RedisUtils;
import backtype.storm.spout.SpoutOutputCollector;
import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext;
import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseRichSpout;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields;
import backtype.storm.tuple.Values;
public class WCSpout extends BaseRichSpout {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private SpoutOutputCollector collector;
private Jedis jedis;
Integer taskId;
String componentId;
String slow_fast;
int numTasks ;
int thisTaskId;
@Override
public void open(@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Map conf, TopologyContext context,
SpoutOutputCollector collector) {
this.collector = collector;
slow_fast = (String)conf.get("slow_fast");
jedis = RedisUtils.connect(RedisUtils.HOSTNAME, RedisUtils.PORT, RedisUtils.INSERT_DB);
taskId = context.getThisTaskId();
componentId = context.getThisComponentId();
numTasks = context.getComponentTasks(componentId).size();
thisTaskId = context.getThisTaskIndex();
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(componentId, taskId, " WCSpout初始化完成!"));
}
@Override
public void nextTuple() {
long interval =0;
while(true){// 获取数据
interval++;
String zero = getItem("0");
String one = getItem("1");
String two = getItem("2");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);// 每200毫秒发送一次数据
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(zero==null||one==null||two==null){
// do nothing
// 没有数据
// if(interval%15==0){
// }
}else{
String tmpStr =zero+","+one+","+two;
if(thisTaskId==tmpStr.hashCode()%numTasks){ // spout负载均衡
this.collector.emit(new Values(tmpStr));
if(interval%15==0&&"fast".equals(slow_fast)){
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(String.valueOf(thisTaskId),
taskId, "Spout:["+zero+","+one+","+two+"]"));
}else if("slow".equals(slow_fast)){
System.out.println(RedisUtils.getCurrDateWithInfo(String.valueOf(thisTaskId),
taskId, "Spout:["+zero+","+one+","+two+"]"));
}else{
new RuntimeException("Wrong argument!");
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
declarer.declare(new Fields("line"));
}
/**
* Redis中获取键值并删除对应的键
* @param index
*/
private String getItem(String index){
if(!jedis.exists(index)){
return null;
}
String val = jedis.get(index);
// if(val==null||"null".equals("null")){
// return ;
// }
jedis.del(index);
return val;
}
}
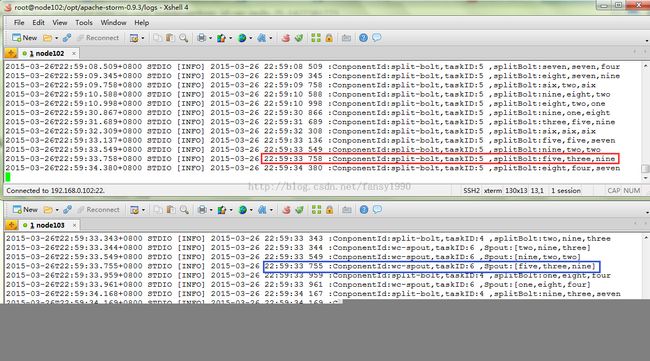
使用上面的代码后,Spout的输出就不会重复了,同时也达到了distribution的目的,如图2
从图2中红色框中可以看到从时间21:58 883 taskId5 Spout输出后,接着到了taskID6 21:59 494 Spout输出,然后又到taskID5 21:59 905 的Spout输出,并没有重复记录;
3. Bolt的并行
Bolt的并行只要设置了多个executor即可。
3.1 使用shuffle进行grouping
使用shuffle进行grouping,多个task的输入中同样的记录可能被分到了任何一个taskid中,如图3所示。
图3
从图3中的蓝色框中可以看到Spout输出了两条相同的记录,的那是一条记录被送到了taskID为5的Bolt中(红色框),一条被送到了taskID为6的Bolt中(红色框),当然从下面的描述中也可以知道,事实就是这样。
上图引自《Getting Started with Storm》
3.2 使用field进行grouping
使用field进行grouping其实是和shuffle一样的,但是有一点不一样,就是相同的记录只会被送往同一个taskid中,比如上面图3中,如果使用field进行grouping,那么Spout输出的两条相同的记录就只会被送往taskid为5的task中(或者为6)。
分享,成长,快乐
脚踏实地,专注
转载请注明blog地址:http://blog.csdn.net/fansy1990