详解 Android 的 Activity 组件——笔记
转载:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-android-actvt/
Activity 栈
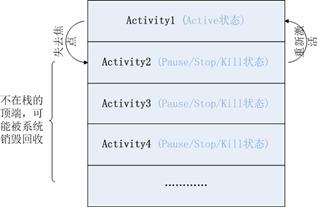
Android 是通过一种 Activity 栈的方式来管理 Activity 的,一个 Activity 的实例的状态决定它在栈中的位置。处于前台的 Activity 总是在栈的顶端,当前台的 Activity 因为异常或其它原因被销毁时,处于栈第二层的 Activity 将被激活,上浮到栈顶。当新的 Activity 启动入栈时,原 Activity 会被压入到栈的第二层。一个 Activity 在栈中的位置变化反映了它在不同状态间的转换。Activity 的状态与它在栈中的位置关系如下图所示:
图 2. Activity 的状态与它在栈中的位置关系如上所示,除了最顶层即处在 Active 状态的 Activity 外,其它的 Activity 都有可能在系统内存不足时被回收,一个 Activity 的实例越是处在栈的底层,它被系统回收的可能性越大。系统负责管理栈中 Activity 的实例,它根据 Activity 所处的状态来改变其在栈中的位置。
使用 SharedPreferences
SharedPreferences 使用 xml 格式为 Android 应用提供一种永久的数据存贮方式。对于一个 Android 应用,它存贮在文件系统的 /data/ data/your_app_package_name/shared_prefs/目录下,可以被处在同一个应用中的所有 Activity 访问。Android 提供了相关的 API 来处理这些数据而不需要程序员直接操作这些文件或者考虑数据同步问题。
// 写入 SharedPreferences
SharedPreferences preferences = getSharedPreferences("name", MODE_PRIVATE);
Editor editor = preferences.edit();
editor.putBoolean("boolean_key", true);
editor.putString("string_key", "string_value");
editor.commit();
// 读取 SharedPreferences
SharedPreferences preferences = getSharedPreferences("name", MODE_PRIVATE);
preferences.getBoolean("boolean_key", false);
preferences.getString("string_key", "default_value");
Activity 的 Intent Filter
Intent Filter 描述了一个组件愿意接收什么样的 Intent 对象,Android 将其抽象为 android.content.IntentFilter 类。在 Android 的 AndroidManifest.xml 配置文件中可以通过 <intent-filter >节点为一个 Activity 指定其 Intent Filter,以便告诉系统该 Activity 可以响应什么类型的 Intent。
当程序员使用 startActivity(intent) 来启动另外一个 Activity 时,如果直接指定 intent 了对象的 Component 属性,那么 Activity Manager 将试图启动其 Component 属性指定的 Activity。否则 Android 将通过 Intent 的其它属性从安装在系统中的所有 Activity 中查找与之最匹配的一个启动,如果没有找到合适的 Activity,应用程序会得到一个系统抛出的异常。这个匹配的过程如下:
图 4. Activity 种 Intent Filter 的匹配过程
Action 匹配
Action 是一个用户定义的字符串,用于描述一个 Android 应用程序组件,一个 Intent Filter 可以包含多个 Action。在 AndroidManifest.xml 的 Activity 定义时可以在其 <intent-filter >节点指定一个 Action 列表用于标示 Activity 所能接受的“动作”,例如:
<intent-filter > <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <action android:name="com.zy.myaction" /> …… </intent-filter>如果我们在启动一个 Activity 时使用这样的 Intent 对象:
Intent intent =new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.zy.myaction");
那么所有的 Action 列表中包含了“com.zy.myaction”的 Activity 都将会匹配成功。
Android 预定义了一系列的 Action 分别表示特定的系统动作。这些 Action 通过常量的方式定义在 android.content. Intent中,以“ACTION_”开头。我们可以在 Android 提供的文档中找到它们的详细说明。
URI 数据匹配
一个 Intent 可以通过 URI 携带外部数据给目标组件。在 <intent-filter >节点中,通过 <data/>节点匹配外部数据。
mimeType 属性指定携带外部数据的数据类型,scheme 指定协议,host、port、path 指定数据的位置、端口、和路径。如下:
<data android:mimeType="mimeType" android:scheme="scheme" android:host="host" android:port="port" android:path="path"/>如果在 Intent Filter 中指定了这些属性,那么只有所有的属性都匹配成功时 URI 数据匹配才会成功。
Category 类别匹配
<intent-filter >节点中可以为组件定义一个 Category 类别列表,当 Intent 中包含这个列表的所有项目时 Category 类别匹配才会成功
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/fundamentals/tasks-and-back-stack.html
关于