自定义struts(一)--咱家自己写的struts--我对struts的理解
学习了几天struts2,拦截器什么的还没接触过,简要谈谈我对struts2的理解:
用了struts2,都不用写servlet了,完全被action替代了。web.xml文件干净多了,有用的东西全搬到了struts.xml这个配置文件中。
对于我来说,目前为止struts2最大的好处就是
1.struts.xml文件比web.xml可读性强多了
2.不用再写复杂的代码了,就连request中的参数都能自动注入了。
学到目前为止,感觉流程是这样的:
下面我来山寨一个我所理解的:
一、首先说下文件结构:
1.struts.xml配置文件与web.xml
2.用于读取xml的工具类
3.用于测试的action与jsp
4.充当前端控制器的filter,所有代码基本都在这个类里了。
二、贴上1.2.3中的代码
1.
fakestruts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <struts> <results name="/login" class="com.aii.struts.action.TestAction"> <result returnString="success" location="/index.jsp"></result> <result returnString="failed" location="/login.jsp"></result> </results> <results name="/test2" class="com.aii.struts.action.TestAction2"> <result returnString="success" location="/index.jsp"></result> <result returnString="failed" location="/login.jsp"></result> </results> </struts>这个测试用,只有第一个results被用到。
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> <display-name></display-name> <filter> <filter-name>fakeStruts</filter-name> <filter-class>com.aii.struts.filter.FakeFrontControllerFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>fakeStruts</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>login.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>只是加了一个过滤器
2.StrutsXmlReader
package com.aii.struts.utils;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.NamedNodeMap;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class StrutsXmlReader {
private static Document document = null;
static {
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory
.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
document = builder.parse(Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("fakestruts.xml"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 通过此方法,传入name,可以获取到对应的类名
* */
public static String getClassName(String tagname) {
try {
NodeList nl = document.getElementsByTagName("results");
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
NamedNodeMap map = nl.item(i).getAttributes();
if (tagname.equals(map.getNamedItem("name").getNodeValue())) {
return map.getNamedItem("class").getNodeValue();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 传入name与返回结果,获取需要定位到的页面
* */
public static String getLocation(String name, String returnString) {
try {
NodeList nl = document.getElementsByTagName("results");
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
NamedNodeMap map = nl.item(i).getAttributes();
if (name.equals(map.getNamedItem("name").getNodeValue())) {
// 找到对应的results
NodeList result = nl.item(i).getChildNodes();
// 遍历result
for (int j = 0; i < result.getLength(); j++) {
// 查找对应的returnString属性
if ("result".equals(result.item(j).getNodeName())) {
NamedNodeMap resultmap = result.item(j)
.getAttributes();
if (returnString.equals(resultmap.getNamedItem(
"returnString").getNodeValue())) {
return resultmap.getNamedItem("location")
.getNodeValue();
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
工具类没仔细整理过,基本功能有,将就着看把。。。
3.
TestAction.java
package com.aii.struts.action;
public class TestAction {
private String userName;
private String password;
public String execute() {
System.out.println("userName:" + userName + "\npassowrd:" + password);
if ("andy".equals(userName) && "tiger".equals(password)) {
return "success";
}
return "failed";
}
}
login.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> </head> <body> <form action="login.action" method="post"> userName:<input name="userName" type="text" /><br /> password:<input name="password" type="password" /><br /> <input type="submit" /> </form> </body> </html>
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> </head> <body> welcome </body> </html>
三、主要是这个filter这个类
package com.aii.struts.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import com.aii.struts.annotation.Transaction;
import com.aii.struts.utils.StrutsXmlReader;
public class FakeFrontControllerFilter implements Filter {
public void destroy() {
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 查看配置文件,查找相关的类
Class clazz = readTargetClass((HttpServletRequest) request);
// 根据class得到方法,这里简单用execute,正常的应该再次查找配置文件的配置
Method method = getTargetMethod(clazz);
// 如果配置文件中无记录,直接放行。
if (method == null) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
// doAction执行相应的操作,并且返回结果
String returnValue = doAction((HttpServletRequest) request, clazz,
method);
// 根据返回结果,查找配置文件,这里简单的用forward直接返回,正常的还应该考虑location的type
String location = getLocationByReturnValue(
(HttpServletRequest) request, returnValue);
request.getRequestDispatcher(location).forward(request, response);
return;
}
private Method getTargetMethod(Class clazz) {
try {
return clazz.getDeclaredMethod("execute", null);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return null;
}
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
/**
* 从配置文件中读取有无此类,无则返回null
* */
private Class readTargetClass(HttpServletRequest request) {
String target = getTargetLocation(request);
String className = StrutsXmlReader.getClassName(target);
if (className == null) {
return null;
}
try {
return Class.forName(className);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 读取目标请求位置
private String getTargetLocation(HttpServletRequest request) {
String target = request.getRequestURI().replace("/FakeStruts", "");
// 去除"action"
if (target.endsWith(".action")) {
target = target.substring(0, target.length() - ".action".length());
}
System.out.println("target->" + target);
return target;
}
// 通过返回值,查找配置,得到要定向的url
private String getLocationByReturnValue(HttpServletRequest request,
String returnValue) {
String target = getTargetLocation(request);
String location = StrutsXmlReader.getLocation(target, returnValue);
System.out.println("forword to " + location);
return location;
}
/**
* 1.将request中的参数注入到Action属性中 2.执行该方法。
*/
private String doAction(HttpServletRequest request, Class clazz,
Method method) {
// 调用newInstance方法,得到对象,这里简单的直接反射得到了,其实可以给他换个代理对象来处理。
Object object = this.newInstance(clazz);
this.setParameterToField(request, object);
try {
return (String) method.invoke(object, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 将request中的参数注入到Action属性中,其实就是遍历request中的name,找到field中对应名字的,尝试类型转化,放进去
*/
private void setParameterToField(HttpServletRequest request, Object object) {
Enumeration<String> e = request.getParameterNames();
Class clazz = object.getClass();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramterKey = e.nextElement();
try {
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(paramterKey);
field.setAccessible(true);
String param = request.getParameter(paramterKey);
if (field.getType() == String.class) {
field.set(object, param);
System.out.println("setted string");
continue;
}
if (field.getType() == Integer.class) {
field.set(object, Integer.parseInt(param));
continue;
}
// 更多的类型转化在这里补充,这里就写了2个类型的转化。
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e1) {
// 如果类中没有request中的参数,那也正常,直接跳过。不给提示
} catch (Exception e3) {
e3.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private <T> T newInstance(Class<T> clazz) {
try {
return clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
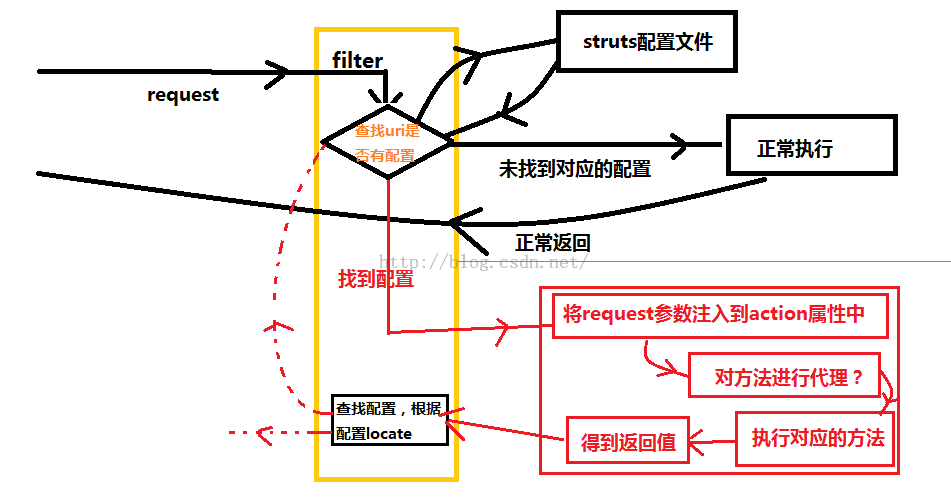
其实就是做了5件事情:
1.查配置,看是否有记录,有记录则调用action,继续第2步,否则直接放行,结束。
2.将request中的参数放到属性中
3.生成个Action对象(这里可以做些手脚)
4.调用方法,得到返回结果
5.拿着返回结果再去找配置文件,看该怎么办。
---------------------
留下个问题:
在action的execute方法上,我的想法是可以再加个Transaction注解,可以选择是否使用事务。
在上面的doAction方法中可以再加几行,对method的注解进行判断,从而选择是否进行事务。
苦于找不到好的方法,又不想用耦合性太高的办法,也不想用transactionManager,恨不得直接把connection注入到方法的局部变量中。。。。
求好的方法。。。