sql语句注意的事项
数据表的某些字段具有相同的属性,即具有相同的数据类型、宽度和取值范围。
select emp.empno, emp.ename, emp.deptno, dept.dname,dept.loc
from scott.emp,scott.dept
where scott.emp.deptno!=scott.dept.deptno and scott.emp.deptno=10;
在非等值多表查询中,读者可以使用表 4.1 所示的比较运算符来组合查询条件。
用 SQL 进行嵌套查询
在 select 查询语句里可以嵌入 select 查询语句,称为嵌套查询。有些书上将内嵌的 select
语句称为子查询,子查询形成的结果又成为父查询的条件。
子查询可以嵌套多层,子查询操作的数据表可以是父查询不操作的数据表。子查
询中不能有 order by分组语句。
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal>=(select sal from scott.emp where ename='WARD');
上面的查询过程等价于两步的执行过程。
(1)执行“select sal from scott.emp where ename='WARD'” ,得出 sal=1250;
(2)执行“select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal from scott.emp where
sal>=1250;”
4.4.2 带【in】的嵌套查询
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal in (select sal from scott.emp where ename='WARD');
上述语句完成的是查询薪水和 WARD相等的员工,也可以使用【not in】来进行查询。
4.4.3 带【any】的嵌套查询
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal >any(select sal from scott.emp where job='MANAGER');
带 any的查询过程等价于两步的执行过程。
(1)执行“select sal from scott.emp where job='MANAGER'”,其结果如图 4.22 所示。
(2)查询到 3 个薪水值 2975、2850 和 2450,父查询执行下列语句。
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal >2975 or sal>2850 or sal>2450;
4.4.4 带【some】的嵌套查询
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal =some(select sal from scott.emp where job='MANAGER');
带 some 的嵌套查询与 any的步骤相同。
(1)子查询,执行“select sal from scott.emp where job='MANAGER'”,其结果如图 4.22
所示。
(2)父查询执行下列语句。
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal =2975 or sal=2850 or sal=2450;
带【any】的嵌套查询和【some】的嵌套查询功能是一样的。早期的 SQL 仅仅允
许使用【any】 ,后来的版本为了和英语的【any】相区分,引入了【some】 ,同时还保留了【any】
关键词。
4.4.5 带【all】的嵌套查询
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal >all(select sal from scott.emp where job='MANAGER');
带 all 的嵌套查询与【some】的步骤相同。
(1)子查询,结果如图 4.22 所示。
(2)父查询执行下列语句。
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp
where sal >2975 and sal>2850 and sal>2450;
4.4.6 带【exists】的嵌套查询
select emp.empno,emp.ename,emp.job,emp.sal
from scott.emp,scott.dept
where exists
(select * from scott.emp where scott.emp.deptno=scott.dept.deptno);
4.4.7 并操作的嵌套查询
并操作就是集合中并集的概念。属于集合 A或集合 B 的元素总和就是并集。
(select deptno from scott.emp)
union
(select deptno from scott.dept);
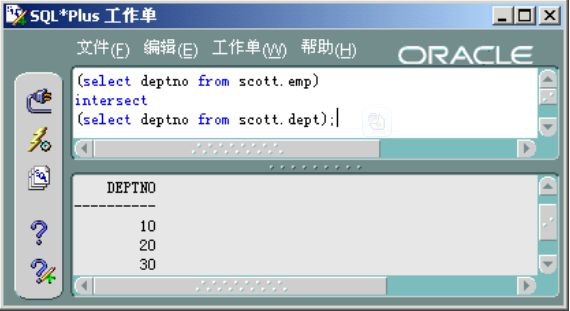
4.4.8 交操作的嵌套查询
交操作就是集合中交集的概念。属于集合 A且属于集合 B 的元素总和就是交集。
(select deptno from scott.emp)
intersect
(select deptno from scott.dept);
单击【执行】按钮,出现如图 4.27 所示的结果。
4.4.9 差操作的嵌套查询
差操作就是集合中差集的概念。属于集合 A且不属于集合 B 的元素总和就是差集。
(select deptno from scott.dept)
minus
(select deptno from scott.emp);
并、交和差操作的嵌套查询要求属性具有相同的定义,包括类型和取值范围
子查询除非能确保内层select只返回一个行的值,否则应在外层where子句中用
一个in限定符,即要返回多个值,要用in或者not in哦,所以当在编译过程中出
现“子查询只返回一个值”的错误时,就要考虑是不是要用in和not in拉~