杭电OJ——1025 Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom(比较有趣的一道题目,思路详解)
Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom
Problem Description
JGShining's kingdom consists of 2n(n is no more than 500,000) small cities which are located in two parallel lines.
Half of these cities are rich in resource (we call them rich cities) while the others are short of resource (we call them poor cities). Each poor city is short of exactly one kind of resource and also each rich city is rich in exactly one kind of resource. You may assume no two poor cities are short of one same kind of resource and no two rich cities are rich in one same kind of resource.
With the development of industry, poor cities wanna import resource from rich ones. The roads existed are so small that they're unable to ensure the heavy trucks, so new roads should be built. The poor cities strongly BS each other, so are the rich ones. Poor cities don't wanna build a road with other poor ones, and rich ones also can't abide sharing an end of road with other rich ones. Because of economic benefit, any rich city will be willing to export resource to any poor one.
Rich citis marked from 1 to n are located in Line I and poor ones marked from 1 to n are located in Line II.
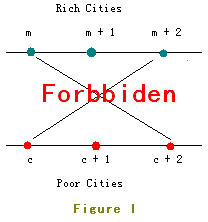
The location of Rich City 1 is on the left of all other cities, Rich City 2 is on the left of all other cities excluding Rich City 1, Rich City 3 is on the right of Rich City 1 and Rich City 2 but on the left of all other cities ... And so as the poor ones.
But as you know, two crossed roads may cause a lot of traffic accident so JGShining has established a law to forbid constructing crossed roads.
For example, the roads in Figure I are forbidden.
In order to build as many roads as possible, the young and handsome king of the kingdom - JGShining needs your help, please help him. ^_^
Half of these cities are rich in resource (we call them rich cities) while the others are short of resource (we call them poor cities). Each poor city is short of exactly one kind of resource and also each rich city is rich in exactly one kind of resource. You may assume no two poor cities are short of one same kind of resource and no two rich cities are rich in one same kind of resource.
With the development of industry, poor cities wanna import resource from rich ones. The roads existed are so small that they're unable to ensure the heavy trucks, so new roads should be built. The poor cities strongly BS each other, so are the rich ones. Poor cities don't wanna build a road with other poor ones, and rich ones also can't abide sharing an end of road with other rich ones. Because of economic benefit, any rich city will be willing to export resource to any poor one.
Rich citis marked from 1 to n are located in Line I and poor ones marked from 1 to n are located in Line II.
The location of Rich City 1 is on the left of all other cities, Rich City 2 is on the left of all other cities excluding Rich City 1, Rich City 3 is on the right of Rich City 1 and Rich City 2 but on the left of all other cities ... And so as the poor ones.
But as you know, two crossed roads may cause a lot of traffic accident so JGShining has established a law to forbid constructing crossed roads.
For example, the roads in Figure I are forbidden.

In order to build as many roads as possible, the young and handsome king of the kingdom - JGShining needs your help, please help him. ^_^
Input
Each test case will begin with a line containing an integer n(1 ≤ n ≤ 500,000). Then n lines follow. Each line contains two integers p and r which represents that Poor City p needs to import resources from Rich City r. Process to the end of file.
Output
For each test case, output the result in the form of sample.
You should tell JGShining what's the maximal number of road(s) can be built.
You should tell JGShining what's the maximal number of road(s) can be built.
Sample Input
2 1 2 2 1 3 1 2 2 3 3 1
Sample Output
Case 1: My king, at most 1 road can be built. Case 2: My king, at most 2 roads can be built.HintHuge input, scanf is recommended.
题目的妙处在于不仅仅是动态规划,还夹杂了二分法查找,所以有一些难度!不过想透了之后就没有多么大的问题了,的确是好题!我写了比较多,比较详细的注释,一来是为了方便大家理解,二来也是方便自己以后再来看!听老师说过这样一句话,特绝!“没有注释的代码就是垃圾!”,说的太对了!代码如下:
/*
//求最长上升子序列的长度,这个算法也可以,不过直接超时!由于数据太多!
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX=500010;
struct ARR
{
int x,y;
}arr[MAX];
bool cmp(const ARR &a,const ARR &b)
{
return a.x<b.x;
}
int dp[MAX],dp1[MAX];
int main()
{
int n,count=0,i;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
int temp;
count++;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>arr[i].x>>arr[i].y;
dp[i]=1;
}
sort(arr,arr+n,cmp);
//现在是最为关键的,求最长上升子序列
//用dp数组记录最长上升子序列的长度,dp[i]表示从arr[i]开始包括arr[i]的最长不降子序列的长度!
//我们从arr[n-1]从后往前搜索,这样的话,如果arr[i].y<=arr[k].y(k>i && k<n),并且dp[k]+1>dp[i],则让dp[i]=dp[k]+1;
//这样一遍搜索完成之后就找到了所有的dp[i];从中选取最大的值即可!
int t=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
for(int k=i+1;k<n;k++)
if(arr[i].y<=arr[k].y && dp[k]+1>temp)
{
temp=dp[i]=dp[k]+1;
break;
}
}
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(dp[i]>max)
max=dp[i];
}
if(max==1) printf("Case %d:\nMy king, at most %d road can be built.\n\n",count,max);
else printf("Case %d:\nMy king, at most %d roads can be built.\n\n",count,max);
}
return 0;
}
*/
//感悟:哥弄点东西出来也不容易!
//这道题目是要求求最长的不降子序列,这东西不难,难点在于数据非常地多,原来的dp就不再那么有效率了!
//因此需要改进算法!这种算法我是想不出来啦,不过我看了比较多的博文,解法大同小异,基本上都是按这种算法干!
//我尽量按照自己的理解解释一下这个算法!
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int size=500050;
struct Co
{
int a,b;
}arr[size];
int dp[size];//dp[i]来表示在长度为i的序列的最长递增子序列的最后一个元素的值
bool cmp(const Co &x,const Co &y)
{
return x.a<y.a;
}
int main()
{
int n,count=0,i;
int len;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
count++;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>arr[i].a>>arr[i].b;
//memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
sort(arr+1,arr+n+1,cmp);//我们先按照arr[i].a从小到大排序,因为测试数据不一定按顺序输入
len=1;//开始时,我们设置len的长度为1,
dp[1]=arr[1].b;//先从arr[1]开始,然后逐步加入新元素
int low,high,mid;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
low=1;high=len;//在1——len的范围内搜索,找到一个合适的位置插入
while(low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(arr[i].b<=dp[mid]) high=mid-1;//dp[i]来表示长度为i的序列的最长递增子序列的最后一个元素的值
else low=mid+1;
}
//low只有两种值可以取,要么low<len,要么low=len+1,可以由程序推断出来
dp[low]=arr[i].b;//一般这里会覆盖掉较大的值,显而易见,dp[i]越小,后面的dp[k](k>i)更大的可能性就会越大
//为什么可以这样做?仔细观察,发现对于一个a[i].b,要判断它是否是某个不降子序列的元素,我们只需要拿它和前面的dp[j](j<len)比较即可,由于dp[j]记录的是到a[j].b为止的序列的最长不降子序列的最后一个元素,如果a[i],b>dp[j]并且a[i].b<dp[j+1],那么我们自然要用a[i].b更新dp[j+1](很明显,最长子序列长度为j+1),而如果a[i].b比dp[j]的值都大,这说明a[i],b可以接在所有的dp[j]后面,自然我们选择最长的dp[len],因此,加入之后,len的长度要自加1
//这里存在一个疑问,会不会出现一个前面一个dp[j]小于a[i].b,我们要插在j+1位,而dp[j+1]<a[i].b呢?这样的话,我们就不能替换dp[j+1]了,事实上,如果dp[j]<a[i].b,dp[j+1]<a[i].b,我们要覆盖dp[j-1]的后方,而不是dp[j+1]
if(len<low)//如果a[i].b最大,此时low会大于len,low=len+1;
len=low;//这里实际表达 len++
}
if(len==1) printf("Case %d:\nMy king, at most %d road can be built.\n\n",count,len);
else printf("Case %d:\nMy king, at most %d roads can be built.\n\n",count,len);
}
return 0;
}