Locality Preserving Projections局部保持投影
本文是对何晓飞老师的论文Locality Preserving Projections及其代码的一些简单j介绍,论文及代码均可以在何老师主页上下载。
一、LPP简介
- 线性投影映射
- 最优化地保存了数据集的邻近结构
- 与PCA可作为二选一的技术
- 在外围空间各处均有定义(不只在训练数据点上有定义,在新的测试数据点上也能够定义)
二、LPP算法实现
设有数据集 ,现在要找到一个转换矩阵
,现在要找到一个转换矩阵 将这m个点映射到新的数据集空间
将这m个点映射到新的数据集空间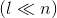 ,因此便可以用
,因此便可以用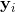 表示,
表示,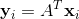 .
.
1、构建邻接图
定义图G有m个节点,如果与“邻近”,则在节点与节点之间连接一条边。两个变量:
(a) neighborhoods
neighborhoods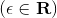
如果满足: ,则节点与节点之间有边连接。
,则节点与节点之间有边连接。
(b) nearest neighbors
如果在的 nearest neighbors内,或者在的 nearest neighbors内,则节点与节点之间有边连接。
注:如果数据确实是在低维流内,则上述邻接图的构建成立。一旦该邻接图构建成功,LPP会试着将其构建为最优。
2、选择权重
定义![]() 为稀疏对称阵,维数为
为稀疏对称阵,维数为![]() ,表示顶点与顶点的边的权重,如果与之间没有边,则
,表示顶点与顶点的边的权重,如果与之间没有边,则![]() 。
。
(a)Heat kernel![]()
如果与连接,则有:
(b)Simple-minded
如果当且仅当顶点与顶点被一条边连接时,有:
3、特征映射
计算以下问题的特征值与特征向量:
(1)
其中,![]() 是对角矩阵,其元素值为的列和(或者行和,因为是对称阵),
是对角矩阵,其元素值为的列和(或者行和,因为是对称阵),
![]() 是Laplacian矩阵。
是Laplacian矩阵。![]() 的第
的第![]() 列记作。
列记作。
设(1)的解为列向量![]() ,按他们的特征值大小排序
,按他们的特征值大小排序![]() ,降维过程化为:
,降维过程化为:
![]() ,
,
其中![]() 是
是![]() 维向量,
维向量,![]() 是
是![]() 维矩阵,即要求的转换矩阵。
维矩阵,即要求的转换矩阵。
三、LPP代码实现
LPP.m
function [eigvector, eigvalue] = LPP(W, options, data)
% LPP: Locality Preserving Projections
%
% [eigvector, eigvalue] = LPP(W, options, data)
%
% Input:
% data - Data matrix. Each row vector of fea is a data point.
% W - Affinity matrix. You can either call "constructW"
% to construct the W, or construct it by yourself.
% options - Struct value in Matlab. The fields in options
% that can be set:
%
% Please see LGE.m for other options.
%
% Output:
% eigvector - Each column is an embedding function, for a new
% data point (row vector) x, y = x * eigvector
% will be the embedding result of x.
% eigvalue - The sorted eigvalue of LPP eigen-problem.
%
%
% Examples:
%
% fea = rand(50,70);
% options = [];
% options.Metric = 'Euclidean';
% options.NeighborMode = 'KNN';
% options.k = 5;
% options.WeightMode = 'HeatKernel';
% options.t = 5;
% W = constructW(fea,options);
% options.PCARatio = 0.99
% [eigvector, eigvalue] = LPP(W, options, fea);
% Y = fea * eigvector;
%
% fea = rand(50,70);
% gnd = [ones(10,1);ones(15,1)*2;ones(10,1)*3;ones(15,1)*4];
% options = [];
% options.Metric = 'Euclidean';
% options.NeighborMode = 'Supervised';
% options.gnd = gnd;
% options.bLDA = 1;
% W = constructW(fea,options);
% options.PCARatio = 1;
% [eigvector, eigvalue] = LPP(W, options, fea);
% Y = fea*eigvector;
%
%
% Note: After applying some simple algebra, the smallest eigenvalue problem:
% data^T*L*data = \lemda data^T*D*data
% is equivalent to the largest eigenvalue problem:
% data^T*W*data = \beta data^T*D*data
% where L=D-W; \lemda= 1 - \beta.
% Thus, the smallest eigenvalue problem can be transformed to a largest
% eigenvalue problem. Such tricks are adopted in this code for the
% consideration of calculation precision of Matlab.
%
%
% See also constructW, LGE
%
%Reference:
% Xiaofei He, and Partha Niyogi, "Locality Preserving Projections"
% Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16 (NIPS 2003),
% Vancouver, Canada, 2003.
%
% Xiaofei He, Shuicheng Yan, Yuxiao Hu, Partha Niyogi, and Hong-Jiang
% Zhang, "Face Recognition Using Laplacianfaces", IEEE PAMI, Vol. 27, No.
% 3, Mar. 2005.
%
% Deng Cai, Xiaofei He and Jiawei Han, "Document Clustering Using
% Locality Preserving Indexing" IEEE TKDE, Dec. 2005.
%
% Deng Cai, Xiaofei He and Jiawei Han, "Using Graph Model for Face Analysis",
% Technical Report, UIUCDCS-R-2005-2636, UIUC, Sept. 2005
%
% Xiaofei He, "Locality Preserving Projections"
% PhD's thesis, Computer Science Department, The University of Chicago,
% 2005.
%
% version 2.1 --June/2007
% version 2.0 --May/2007
% version 1.1 --Feb/2006
% version 1.0 --April/2004
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai2 AT cs.uiuc.edu)
%
if (~exist('options','var'))
options = [];
end
[nSmp,nFea] = size(data);
if size(W,1) ~= nSmp
error('W and data mismatch!');
end
%====================================================
% If data is too large, the following centering codes can be commented
% options.keepMean = 1;
%====================================================
if isfield(options,'keepMean') && options.keepMean
;
else
if issparse(data)
data = full(data);
end
sampleMean = mean(data);
data = (data - repmat(sampleMean,nSmp,1));
end
%====================================================
D = full(sum(W,2));
if ~isfield(options,'Regu') || ~options.Regu
DToPowerHalf = D.^.5;
D_mhalf = DToPowerHalf.^-1;
if nSmp < 5000
tmpD_mhalf = repmat(D_mhalf,1,nSmp);
W = (tmpD_mhalf .* W) .* tmpD_mhalf';
clear tmpD_mhalf;
else
[i_idx,j_idx,v_idx] = find(W);
v1_idx = zeros(size(v_idx));
for i=1:length(v_idx)
v1_idx(i) = v_idx(i) * D_mhalf(i_idx(i)) * D_mhalf(j_idx(i));
end
W = sparse(i_idx,j_idx,v1_idx);
clear i_idx j_idx v_idx v1_idx
end
W = max(W,W');
data = repmat(DToPowerHalf,1,nFea) .* data;
[eigvector, eigvalue] = LGE(W, [], options, data);
else
options.ReguAlpha = options.ReguAlpha*sum(D)/length(D);
D = sparse(1:nSmp,1:nSmp,D,nSmp,nSmp);
[eigvector, eigvalue] = LGE(W, D, options, data);
end
eigIdx = find(eigvalue < 1e-3);
eigvalue (eigIdx) = [];
eigvector(:,eigIdx) = [];
constructW.m
function W = constructW(fea,options)
% Usage:
% W = constructW(fea,options)
%
% fea: Rows of vectors of data points. Each row is x_i
% options: Struct value in Matlab. The fields in options that can be set:
%
% NeighborMode - Indicates how to construct the graph. Choices
% are: [Default 'KNN']
% 'KNN' - k = 0
% Complete graph
% k > 0
% Put an edge between two nodes if and
% only if they are among the k nearst
% neighbors of each other. You are
% required to provide the parameter k in
% the options. Default k=5.
% 'Supervised' - k = 0
% Put an edge between two nodes if and
% only if they belong to same class.
% k > 0
% Put an edge between two nodes if
% they belong to same class and they
% are among the k nearst neighbors of
% each other.
% Default: k=0
% You are required to provide the label
% information gnd in the options.
%
% WeightMode - Indicates how to assign weights for each edge
% in the graph. Choices are:
% 'Binary' - 0-1 weighting. Every edge receiveds weight
% of 1.
% 'HeatKernel' - If nodes i and j are connected, put weight
% W_ij = exp(-norm(x_i - x_j)/2t^2). You are
% required to provide the parameter t. [Default One]
% 'Cosine' - If nodes i and j are connected, put weight
% cosine(x_i,x_j).
%
% k - The parameter needed under 'KNN' NeighborMode.
% Default will be 5.
% gnd - The parameter needed under 'Supervised'
% NeighborMode. Colunm vector of the label
% information for each data point.
% bLDA - 0 or 1. Only effective under 'Supervised'
% NeighborMode. If 1, the graph will be constructed
% to make LPP exactly same as LDA. Default will be
% 0.
% t - The parameter needed under 'HeatKernel'
% WeightMode. Default will be 1
% bNormalized - 0 or 1. Only effective under 'Cosine' WeightMode.
% Indicates whether the fea are already be
% normalized to 1. Default will be 0
% bSelfConnected - 0 or 1. Indicates whether W(i,i) == 1. Default 0
% if 'Supervised' NeighborMode & bLDA == 1,
% bSelfConnected will always be 1. Default 0.
% bTrueKNN - 0 or 1. If 1, will construct a truly kNN graph
% (Not symmetric!). Default will be 0. Only valid
% for 'KNN' NeighborMode
%
%
% Examples:
%
% fea = rand(50,15);
% options = [];
% options.NeighborMode = 'KNN';
% options.k = 5;
% options.WeightMode = 'HeatKernel';
% options.t = 1;
% W = constructW(fea,options);
%
%
% fea = rand(50,15);
% gnd = [ones(10,1);ones(15,1)*2;ones(10,1)*3;ones(15,1)*4];
% options = [];
% options.NeighborMode = 'Supervised';
% options.gnd = gnd;
% options.WeightMode = 'HeatKernel';
% options.t = 1;
% W = constructW(fea,options);
%
%
% fea = rand(50,15);
% gnd = [ones(10,1);ones(15,1)*2;ones(10,1)*3;ones(15,1)*4];
% options = [];
% options.NeighborMode = 'Supervised';
% options.gnd = gnd;
% options.bLDA = 1;
% W = constructW(fea,options);
%
%
% For more details about the different ways to construct the W, please
% refer:
% Deng Cai, Xiaofei He and Jiawei Han, "Document Clustering Using
% Locality Preserving Indexing" IEEE TKDE, Dec. 2005.
%
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai2 AT cs.uiuc.edu), April/2004, Feb/2006,
% May/2007
%
bSpeed = 1;
if (~exist('options','var'))
options = [];
end
if isfield(options,'Metric')
warning('This function has been changed and the Metric is no longer be supported');
end
if ~isfield(options,'bNormalized')
options.bNormalized = 0;
end
%=================================================
if ~isfield(options,'NeighborMode')
options.NeighborMode = 'KNN';
end
switch lower(options.NeighborMode)
case {lower('KNN')} %For simplicity, we include the data point itself in the kNN
if ~isfield(options,'k')
options.k = 5;
end
case {lower('Supervised')}
if ~isfield(options,'bLDA')
options.bLDA = 0;
end
if options.bLDA
options.bSelfConnected = 1;
end
if ~isfield(options,'k')
options.k = 0;
end
if ~isfield(options,'gnd')
error('Label(gnd) should be provided under ''Supervised'' NeighborMode!');
end
if ~isempty(fea) && length(options.gnd) ~= size(fea,1)
error('gnd doesn''t match with fea!');
end
otherwise
error('NeighborMode does not exist!');
end
%=================================================
if ~isfield(options,'WeightMode')
options.WeightMode = 'HeatKernel';
end
bBinary = 0;
bCosine = 0;
switch lower(options.WeightMode)
case {lower('Binary')}
bBinary = 1;
case {lower('HeatKernel')}
if ~isfield(options,'t')
nSmp = size(fea,1);
if nSmp > 3000
D = EuDist2(fea(randsample(nSmp,3000),:));
else
D = EuDist2(fea);
end
options.t = mean(mean(D));
end
case {lower('Cosine')}
bCosine = 1;
otherwise
error('WeightMode does not exist!');
end
%=================================================
if ~isfield(options,'bSelfConnected')
options.bSelfConnected = 0;
end
%=================================================
if isfield(options,'gnd')
nSmp = length(options.gnd);
else
nSmp = size(fea,1);
end
maxM = 62500000; %500M
BlockSize = floor(maxM/(nSmp*3));
if strcmpi(options.NeighborMode,'Supervised')
Label = unique(options.gnd);
nLabel = length(Label);
if options.bLDA
G = zeros(nSmp,nSmp);
for idx=1:nLabel
classIdx = options.gnd==Label(idx);
G(classIdx,classIdx) = 1/sum(classIdx);
end
W = sparse(G);
return;
end
switch lower(options.WeightMode)
case {lower('Binary')}
if options.k > 0
G = zeros(nSmp*(options.k+1),3);
idNow = 0;
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
D = EuDist2(fea(classIdx,:),[],0);
[dump idx] = sort(D,2); % sort each row
clear D dump;
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
nSmpClass = length(classIdx)*(options.k+1);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,1) = repmat(classIdx,[options.k+1,1]);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,2) = classIdx(idx(:));
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,3) = 1;
idNow = idNow+nSmpClass;
clear idx
end
G = sparse(G(:,1),G(:,2),G(:,3),nSmp,nSmp);
G = max(G,G');
else
G = zeros(nSmp,nSmp);
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
G(classIdx,classIdx) = 1;
end
end
if ~options.bSelfConnected
for i=1:size(G,1)
G(i,i) = 0;
end
end
W = sparse(G);
case {lower('HeatKernel')}
if options.k > 0
G = zeros(nSmp*(options.k+1),3);
idNow = 0;
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
D = EuDist2(fea(classIdx,:),[],0);
[dump idx] = sort(D,2); % sort each row
clear D;
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = dump(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = exp(-dump/(2*options.t^2));
nSmpClass = length(classIdx)*(options.k+1);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,1) = repmat(classIdx,[options.k+1,1]);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,2) = classIdx(idx(:));
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,3) = dump(:);
idNow = idNow+nSmpClass;
clear dump idx
end
G = sparse(G(:,1),G(:,2),G(:,3),nSmp,nSmp);
else
G = zeros(nSmp,nSmp);
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
D = EuDist2(fea(classIdx,:),[],0);
D = exp(-D/(2*options.t^2));
G(classIdx,classIdx) = D;
end
end
if ~options.bSelfConnected
for i=1:size(G,1)
G(i,i) = 0;
end
end
W = sparse(max(G,G'));
case {lower('Cosine')}
if ~options.bNormalized
fea = NormalizeFea(fea);
end
if options.k > 0
G = zeros(nSmp*(options.k+1),3);
idNow = 0;
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
D = fea(classIdx,:)*fea(classIdx,:)';
[dump idx] = sort(-D,2); % sort each row
clear D;
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = -dump(:,1:options.k+1);
nSmpClass = length(classIdx)*(options.k+1);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,1) = repmat(classIdx,[options.k+1,1]);
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,2) = classIdx(idx(:));
G(idNow+1:nSmpClass+idNow,3) = dump(:);
idNow = idNow+nSmpClass;
clear dump idx
end
G = sparse(G(:,1),G(:,2),G(:,3),nSmp,nSmp);
else
G = zeros(nSmp,nSmp);
for i=1:nLabel
classIdx = find(options.gnd==Label(i));
G(classIdx,classIdx) = fea(classIdx,:)*fea(classIdx,:)';
end
end
if ~options.bSelfConnected
for i=1:size(G,1)
G(i,i) = 0;
end
end
W = sparse(max(G,G'));
otherwise
error('WeightMode does not exist!');
end
return;
end
if bCosine && ~options.bNormalized
Normfea = NormalizeFea(fea);
end
if strcmpi(options.NeighborMode,'KNN') && (options.k > 0)
if ~(bCosine && options.bNormalized)
G = zeros(nSmp*(options.k+1),3);
for i = 1:ceil(nSmp/BlockSize)
if i == ceil(nSmp/BlockSize)
smpIdx = (i-1)*BlockSize+1:nSmp;
dist = EuDist2(fea(smpIdx,:),fea,0);
if bSpeed
nSmpNow = length(smpIdx);
dump = zeros(nSmpNow,options.k+1);
idx = dump;
for j = 1:options.k+1
[dump(:,j),idx(:,j)] = min(dist,[],2);
temp = (idx(:,j)-1)*nSmpNow+[1:nSmpNow]';
dist(temp) = 1e100;
end
else
[dump idx] = sort(dist,2); % sort each row
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = dump(:,1:options.k+1);
end
if ~bBinary
if bCosine
dist = Normfea(smpIdx,:)*Normfea';
dist = full(dist);
linidx = [1:size(idx,1)]';
dump = dist(sub2ind(size(dist),linidx(:,ones(1,size(idx,2))),idx));
else
dump = exp(-dump/(2*options.t^2));
end
end
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),1) = repmat(smpIdx',[options.k+1,1]);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),2) = idx(:);
if ~bBinary
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),3) = dump(:);
else
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),3) = 1;
end
else
smpIdx = (i-1)*BlockSize+1:i*BlockSize;
dist = EuDist2(fea(smpIdx,:),fea,0);
if bSpeed
nSmpNow = length(smpIdx);
dump = zeros(nSmpNow,options.k+1);
idx = dump;
for j = 1:options.k+1
[dump(:,j),idx(:,j)] = min(dist,[],2);
temp = (idx(:,j)-1)*nSmpNow+[1:nSmpNow]';
dist(temp) = 1e100;
end
else
[dump idx] = sort(dist,2); % sort each row
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = dump(:,1:options.k+1);
end
if ~bBinary
if bCosine
dist = Normfea(smpIdx,:)*Normfea';
dist = full(dist);
linidx = [1:size(idx,1)]';
dump = dist(sub2ind(size(dist),linidx(:,ones(1,size(idx,2))),idx));
else
dump = exp(-dump/(2*options.t^2));
end
end
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),1) = repmat(smpIdx',[options.k+1,1]);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),2) = idx(:);
if ~bBinary
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),3) = dump(:);
else
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),3) = 1;
end
end
end
W = sparse(G(:,1),G(:,2),G(:,3),nSmp,nSmp);
else
G = zeros(nSmp*(options.k+1),3);
for i = 1:ceil(nSmp/BlockSize)
if i == ceil(nSmp/BlockSize)
smpIdx = (i-1)*BlockSize+1:nSmp;
dist = fea(smpIdx,:)*fea';
dist = full(dist);
if bSpeed
nSmpNow = length(smpIdx);
dump = zeros(nSmpNow,options.k+1);
idx = dump;
for j = 1:options.k+1
[dump(:,j),idx(:,j)] = max(dist,[],2);
temp = (idx(:,j)-1)*nSmpNow+[1:nSmpNow]';
dist(temp) = 0;
end
else
[dump idx] = sort(-dist,2); % sort each row
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = -dump(:,1:options.k+1);
end
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),1) = repmat(smpIdx',[options.k+1,1]);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),2) = idx(:);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:nSmp*(options.k+1),3) = dump(:);
else
smpIdx = (i-1)*BlockSize+1:i*BlockSize;
dist = fea(smpIdx,:)*fea';
dist = full(dist);
if bSpeed
nSmpNow = length(smpIdx);
dump = zeros(nSmpNow,options.k+1);
idx = dump;
for j = 1:options.k+1
[dump(:,j),idx(:,j)] = max(dist,[],2);
temp = (idx(:,j)-1)*nSmpNow+[1:nSmpNow]';
dist(temp) = 0;
end
else
[dump idx] = sort(-dist,2); % sort each row
idx = idx(:,1:options.k+1);
dump = -dump(:,1:options.k+1);
end
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),1) = repmat(smpIdx',[options.k+1,1]);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),2) = idx(:);
G((i-1)*BlockSize*(options.k+1)+1:i*BlockSize*(options.k+1),3) = dump(:);
end
end
W = sparse(G(:,1),G(:,2),G(:,3),nSmp,nSmp);
end
if bBinary
W(logical(W)) = 1;
end
if isfield(options,'bSemiSupervised') && options.bSemiSupervised
tmpgnd = options.gnd(options.semiSplit);
Label = unique(tmpgnd);
nLabel = length(Label);
G = zeros(sum(options.semiSplit),sum(options.semiSplit));
for idx=1:nLabel
classIdx = tmpgnd==Label(idx);
G(classIdx,classIdx) = 1;
end
Wsup = sparse(G);
if ~isfield(options,'SameCategoryWeight')
options.SameCategoryWeight = 1;
end
W(options.semiSplit,options.semiSplit) = (Wsup>0)*options.SameCategoryWeight;
end
if ~options.bSelfConnected
W = W - diag(diag(W));
end
if isfield(options,'bTrueKNN') && options.bTrueKNN
else
W = max(W,W');
end
return;
end
% strcmpi(options.NeighborMode,'KNN') & (options.k == 0)
% Complete Graph
switch lower(options.WeightMode)
case {lower('Binary')}
error('Binary weight can not be used for complete graph!');
case {lower('HeatKernel')}
W = EuDist2(fea,[],0);
W = exp(-W/(2*options.t^2));
case {lower('Cosine')}
W = full(Normfea*Normfea');
otherwise
error('WeightMode does not exist!');
end
if ~options.bSelfConnected
for i=1:size(W,1)
W(i,i) = 0;
end
end
W = max(W,W');
LGE.w
function [eigvector, eigvalue] = LGE(W, D, options, data)
% LGE: Linear Graph Embedding
%
% [eigvector, eigvalue] = LGE(W, D, options, data)
%
% Input:
% data - data matrix. Each row vector of data is a
% sample vector.
% W - Affinity graph matrix.
% D - Constraint graph matrix.
% LGE solves the optimization problem of
% a* = argmax (a'data'WXa)/(a'data'DXa)
% Default: D = I
%
% options - Struct value in Matlab. The fields in options
% that can be set:
%
% ReducedDim - The dimensionality of the reduced
% subspace. If 0, all the dimensions
% will be kept. Default is 30.
%
% Regu - 1: regularized solution,
% a* = argmax (a'X'WXa)/(a'X'DXa+ReguAlpha*I)
% 0: solve the sinularity problem by SVD (PCA)
% Default: 0
%
% ReguAlpha - The regularization parameter. Valid
% when Regu==1. Default value is 0.1.
%
% ReguType - 'Ridge': Tikhonov regularization
% 'Custom': User provided
% regularization matrix
% Default: 'Ridge'
% regularizerR - (nFea x nFea) regularization
% matrix which should be provided
% if ReguType is 'Custom'. nFea is
% the feature number of data
% matrix
%
% PCARatio - The percentage of principal
% component kept in the PCA
% step. The percentage is
% calculated based on the
% eigenvalue. Default is 1
% (100%, all the non-zero
% eigenvalues will be kept.
% If PCARatio > 1, the PCA step
% will keep exactly PCARatio principle
% components (does not exceed the
% exact number of non-zero components).
%
% Output:
% eigvector - Each column is an embedding function, for a new
% sample vector (row vector) x, y = x*eigvector
% will be the embedding result of x.
% eigvalue - The sorted eigvalue of the eigen-problem.
% elapse - Time spent on different steps
%
% Examples:
%
% See also LPP, NPE, IsoProjection, LSDA.
%
% Reference:
%
% 1. Deng Cai, Xiaofei He, Jiawei Han, "Spectral Regression for Efficient
% Regularized Subspace Learning", IEEE International Conference on
% Computer Vision (ICCV), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Oct. 2007.
%
% 2. Deng Cai, Xiaofei He, Yuxiao Hu, Jiawei Han, and Thomas Huang,
% "Learning a Spatially Smooth Subspace for Face Recognition", CVPR'2007
%
% 3. Deng Cai, Xiaofei He, Jiawei Han, "Spectral Regression: A Unified
% Subspace Learning Framework for Content-Based Image Retrieval", ACM
% Multimedia 2007, Augsburg, Germany, Sep. 2007.
%
% 4. Deng Cai, "Spectral Regression: A Regression Framework for
% Efficient Regularized Subspace Learning", PhD Thesis, Department of
% Computer Science, UIUC, 2009.
%
% version 3.0 --Dec/2011
% version 2.1 --June/2007
% version 2.0 --May/2007
% version 1.0 --Sep/2006
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai AT gmail.com)
%
MAX_MATRIX_SIZE = 1600; % You can change this number according your machine computational power
EIGVECTOR_RATIO = 0.1; % You can change this number according your machine computational power
if (~exist('options','var'))
options = [];
end
ReducedDim = 30;
if isfield(options,'ReducedDim')
ReducedDim = options.ReducedDim;
end
if ~isfield(options,'Regu') || ~options.Regu
bPCA = 1;
if ~isfield(options,'PCARatio')
options.PCARatio = 1;
end
else
bPCA = 0;
if ~isfield(options,'ReguType')
options.ReguType = 'Ridge';
end
if ~isfield(options,'ReguAlpha')
options.ReguAlpha = 0.1;
end
end
bD = 1;
if ~exist('D','var') || isempty(D)
bD = 0;
end
[nSmp,nFea] = size(data);
if size(W,1) ~= nSmp
error('W and data mismatch!');
end
if bD && (size(D,1) ~= nSmp)
error('D and data mismatch!');
end
bChol = 0;
if bPCA && (nSmp > nFea) && (options.PCARatio >= 1)
if bD
DPrime = data' * D * data;
else
DPrime = data' * data;
end
DPrime = full(DPrime);
DPrime = max(DPrime,DPrime');
[R,p] = chol(DPrime);
if p == 0
bPCA = 0;
bChol = 1;
end
end
%======================================
% SVD
%======================================
if bPCA
[U, S, V] = mySVD(data);
[U, S, V] = CutonRatio(U,S,V,options);
eigvalue_PCA = full(diag(S));
if bD
data = U * S;
eigvector_PCA = V;
DPrime = data' * D * data;
DPrime = max(DPrime,DPrime');
else
data = U;
eigvector_PCA = V*spdiags(eigvalue_PCA.^-1,0,length(eigvalue_PCA),length(eigvalue_PCA));
end
else
if ~bChol
if bD
DPrime = data'*D*data;
else
DPrime = data'*data;
end
switch lower(options.ReguType)
case {lower('Ridge')}
if options.ReguAlpha > 0
for i=1:size(DPrime,1)
DPrime(i,i) = DPrime(i,i) + options.ReguAlpha;
end
end
case {lower('Tensor')}
if options.ReguAlpha > 0
DPrime = DPrime + options.ReguAlpha*options.regularizerR;
end
case {lower('Custom')}
if options.ReguAlpha > 0
DPrime = DPrime + options.ReguAlpha*options.regularizerR;
end
otherwise
error('ReguType does not exist!');
end
DPrime = max(DPrime,DPrime');
end
end
WPrime = data' * W * data;
WPrime = max(WPrime,WPrime');
%======================================
% Generalized Eigen
%======================================
dimMatrix = size(WPrime,2);
if ReducedDim > dimMatrix
ReducedDim = dimMatrix;
end
if isfield(options,'bEigs')
bEigs = options.bEigs;
else
if (dimMatrix > MAX_MATRIX_SIZE) && (ReducedDim < dimMatrix * EIGVECTOR_RATIO)
bEigs = 1;
else
bEigs = 0;
end
end
if bEigs
%disp('use eigs to speed up!');
option = struct('disp',0);
if bPCA && ~bD
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eigs(WPrime,ReducedDim,'la',option);
else
if bChol
option.cholB = 1;
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eigs(WPrime,R,ReducedDim,'la',option);
else
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eigs(WPrime,DPrime,ReducedDim,'la',option);
end
end
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
else
if bPCA && ~bD
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eig(WPrime);
else
[eigvector, eigvalue] = eig(WPrime,DPrime);
end
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
[junk, index] = sort(-eigvalue);
eigvalue = eigvalue(index);
eigvector = eigvector(:,index);
if ReducedDim < size(eigvector,2)
eigvector = eigvector(:, 1:ReducedDim);
eigvalue = eigvalue(1:ReducedDim);
end
end
if bPCA
eigvector = eigvector_PCA*eigvector;
end
for i = 1:size(eigvector,2)
eigvector(:,i) = eigvector(:,i)./norm(eigvector(:,i));
end
function [U, S, V] = CutonRatio(U,S,V,options)
if ~isfield(options, 'PCARatio')
options.PCARatio = 1;
end
eigvalue_PCA = full(diag(S));
if options.PCARatio > 1
idx = options.PCARatio;
if idx < length(eigvalue_PCA)
U = U(:,1:idx);
V = V(:,1:idx);
S = S(1:idx,1:idx);
end
elseif options.PCARatio < 1
sumEig = sum(eigvalue_PCA);
sumEig = sumEig*options.PCARatio;
sumNow = 0;
for idx = 1:length(eigvalue_PCA)
sumNow = sumNow + eigvalue_PCA(idx);
if sumNow >= sumEig
break;
end
end
U = U(:,1:idx);
V = V(:,1:idx);
S = S(1:idx,1:idx);
end
EuDist2.m
function D = EuDist2(fea_a,fea_b,bSqrt)
%EUDIST2 Efficiently Compute the Euclidean Distance Matrix by Exploring the
%Matlab matrix operations.
%
% D = EuDist(fea_a,fea_b)
% fea_a: nSample_a * nFeature
% fea_b: nSample_b * nFeature
% D: nSample_a * nSample_a
% or nSample_a * nSample_b
%
% Examples:
%
% a = rand(500,10);
% b = rand(1000,10);
%
% A = EuDist2(a); % A: 500*500
% D = EuDist2(a,b); % D: 500*1000
%
% version 2.1 --November/2011
% version 2.0 --May/2009
% version 1.0 --November/2005
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai AT gmail.com)
if ~exist('bSqrt','var')
bSqrt = 1;
end
if (~exist('fea_b','var')) || isempty(fea_b)
aa = sum(fea_a.*fea_a,2);
ab = fea_a*fea_a';
if issparse(aa)
aa = full(aa);
end
D = bsxfun(@plus,aa,aa') - 2*ab;
D(D<0) = 0;
if bSqrt
D = sqrt(D);
end
D = max(D,D');
else
aa = sum(fea_a.*fea_a,2);
bb = sum(fea_b.*fea_b,2);
ab = fea_a*fea_b';
if issparse(aa)
aa = full(aa);
bb = full(bb);
end
D = bsxfun(@plus,aa,bb') - 2*ab;
D(D<0) = 0;
if bSqrt
D = sqrt(D);
end
end
mySVD.m
function [U, S, V] = mySVD(X,ReducedDim)
%mySVD Accelerated singular value decomposition.
% [U,S,V] = mySVD(X) produces a diagonal matrix S, of the
% dimension as the rank of X and with nonnegative diagonal elements in
% decreasing order, and unitary matrices U and V so that
% X = U*S*V'.
%
% [U,S,V] = mySVD(X,ReducedDim) produces a diagonal matrix S, of the
% dimension as ReducedDim and with nonnegative diagonal elements in
% decreasing order, and unitary matrices U and V so that
% Xhat = U*S*V' is the best approximation (with respect to F norm) of X
% among all the matrices with rank no larger than ReducedDim.
%
% Based on the size of X, mySVD computes the eigvectors of X*X^T or X^T*X
% first, and then convert them to the eigenvectors of the other.
%
% See also SVD.
%
% version 2.0 --Feb/2009
% version 1.0 --April/2004
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai AT gmail.com)
%
MAX_MATRIX_SIZE = 1600; % You can change this number according your machine computational power
EIGVECTOR_RATIO = 0.1; % You can change this number according your machine computational power
if ~exist('ReducedDim','var')
ReducedDim = 0;
end
[nSmp, mFea] = size(X);
if mFea/nSmp > 1.0713
ddata = X*X';
ddata = max(ddata,ddata');
dimMatrix = size(ddata,1);
if (ReducedDim > 0) && (dimMatrix > MAX_MATRIX_SIZE) && (ReducedDim < dimMatrix*EIGVECTOR_RATIO)
option = struct('disp',0);
[U, eigvalue] = eigs(ddata,ReducedDim,'la',option);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
else
if issparse(ddata)
ddata = full(ddata);
end
[U, eigvalue] = eig(ddata);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
[dump, index] = sort(-eigvalue);
eigvalue = eigvalue(index);
U = U(:, index);
end
clear ddata;
maxEigValue = max(abs(eigvalue));
eigIdx = find(abs(eigvalue)/maxEigValue < 1e-10);
eigvalue(eigIdx) = [];
U(:,eigIdx) = [];
if (ReducedDim > 0) && (ReducedDim < length(eigvalue))
eigvalue = eigvalue(1:ReducedDim);
U = U(:,1:ReducedDim);
end
eigvalue_Half = eigvalue.^.5;
S = spdiags(eigvalue_Half,0,length(eigvalue_Half),length(eigvalue_Half));
if nargout >= 3
eigvalue_MinusHalf = eigvalue_Half.^-1;
V = X'*(U.*repmat(eigvalue_MinusHalf',size(U,1),1));
end
else
ddata = X'*X;
ddata = max(ddata,ddata');
dimMatrix = size(ddata,1);
if (ReducedDim > 0) && (dimMatrix > MAX_MATRIX_SIZE) && (ReducedDim < dimMatrix*EIGVECTOR_RATIO)
option = struct('disp',0);
[V, eigvalue] = eigs(ddata,ReducedDim,'la',option);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
else
if issparse(ddata)
ddata = full(ddata);
end
[V, eigvalue] = eig(ddata);
eigvalue = diag(eigvalue);
[dump, index] = sort(-eigvalue);
eigvalue = eigvalue(index);
V = V(:, index);
end
clear ddata;
maxEigValue = max(abs(eigvalue));
eigIdx = find(abs(eigvalue)/maxEigValue < 1e-10);
eigvalue(eigIdx) = [];
V(:,eigIdx) = [];
if (ReducedDim > 0) && (ReducedDim < length(eigvalue))
eigvalue = eigvalue(1:ReducedDim);
V = V(:,1:ReducedDim);
end
eigvalue_Half = eigvalue.^.5;
S = spdiags(eigvalue_Half,0,length(eigvalue_Half),length(eigvalue_Half));
eigvalue_MinusHalf = eigvalue_Half.^-1;
U = X*(V.*repmat(eigvalue_MinusHalf',size(V,1),1));
end
NormalizeFea.m
function fea = NormalizeFea(fea,row)
% if row == 1, normalize each row of fea to have unit norm;
% if row == 0, normalize each column of fea to have unit norm;
%
% version 3.0 --Jan/2012
% version 2.0 --Jan/2012
% version 1.0 --Oct/2003
%
% Written by Deng Cai (dengcai AT gmail.com)
%
if ~exist('row','var')
row = 1;
end
if row
nSmp = size(fea,1);
feaNorm = max(1e-14,full(sum(fea.^2,2)));
fea = spdiags(feaNorm.^-.5,0,nSmp,nSmp)*fea;
else
nSmp = size(fea,2);
feaNorm = max(1e-14,full(sum(fea.^2,1))');
fea = fea*spdiags(feaNorm.^-.5,0,nSmp,nSmp);
end
return;
if row
[nSmp, mFea] = size(fea);
if issparse(fea)
fea2 = fea';
feaNorm = mynorm(fea2,1);
for i = 1:nSmp
fea2(:,i) = fea2(:,i) ./ max(1e-10,feaNorm(i));
end
fea = fea2';
else
feaNorm = sum(fea.^2,2).^.5;
fea = fea./feaNorm(:,ones(1,mFea));
end
else
[mFea, nSmp] = size(fea);
if issparse(fea)
feaNorm = mynorm(fea,1);
for i = 1:nSmp
fea(:,i) = fea(:,i) ./ max(1e-10,feaNorm(i));
end
else
feaNorm = sum(fea.^2,1).^.5;
fea = fea./feaNorm(ones(1,mFea),:);
end
end
Reference:
LPP(Locality Preserving Projection),局部保留投影