安卓第九天笔记-Activity
安卓第九天笔记-Activity
1.创建Activity
一个界面对应一个activity
创建一个Activity
1.写一个JAVA类,继承Activity
publicclass CalcActivity extends Activity {
2.为这个Activity写一个布局文件
3.在Activity中重写OnCreate()方法,并设置显示的内容setContentView(R.layout.xxx)xxx表示布局文件的名称
4.在Manifest.xml文件中为Activity注册
<activity android:name="com.itheima.rp.CalcActivity"></activity>
2.人品计算器
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".LogoActivity" > <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/logo"/> </RelativeLayout> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="人品计算器" android:textColor="#66ff0000" android:textSize="32sp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请输入您的姓名" /> <Button android:onClick="calc" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="计算"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_result" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout>
LogoActivity
/** * Logo界面 * @author 刘楠 * * 2016-2-25下午6:47:07 */ public class LogoActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_logo); //打开后显示的LOGO界面 new Thread(){ public void run() { //显示5秒后连接到切换到下一个Activity SystemClock.sleep(5000); startActivity(new Intent(LogoActivity.this, CalcActivity.class)); //关闭掉这个Activity不然后退就又回到Logo界面了 finish(); }; }.start(); } }
CalcActivity
/** * 创建一个Activity * 1.写一个JAVA类,继承Activity * 2.为这个Activity写一个布局文件 * 3.在Activity中重写OnCreate()方法,并设置显示的内容setContentView(R.layout.xxx)xxx表示布局文件的名称 * @author 刘楠 * * 2016-2-25下午6:33:59 */ public class CalcActivity extends Activity { private EditText et_name; private TextView tv_result; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //设置要显示的内容布局文件 setContentView(R.layout.activity_calc); et_name = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_name); tv_result = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_result); } /** * 计算人品 * @param v */ public void calc(View v){ //获取名称 String name = et_name.getText().toString().trim(); if(TextUtils.isEmpty(name)){ Toast.makeText(this, "姓名不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); return; } //不为空就开始计算 byte[] bytes = name.getBytes(); //结果 int sum=0; for (byte b : bytes) { int tmp=b&0xff; sum+=tmp; } //开始计算人品 int rp=sum/100; if (rp>9) { tv_result.setText("人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===人品帅到掉渣,当世的活菩萨"); }else if(rp>6){ tv_result.setText("人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===一般一般世界第三,"); }else{ tv_result.setText("人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===上辈子没有干坏事,好好活着"); } } }
计算和结果都在一个界面完成的,
下面再加一个界面只用于显示结果
并把图片带过去
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="结果显示"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_result" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout>
Activity
更改CalcActivity
//开始计算人品 String str; int rp=sum/100; if (rp>9) { str="人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===人品帅到掉渣,当世的活菩萨"; }else if(rp>6){ str="人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===一般一般世界第三,"; }else{ str="人名:"+name+"--->人品:"+rp+"===上辈子没有干坏事,好好活着"; } // 发送数据到另外一个Activity Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, ResultActivity.class); //添加数据字符串 intent.putExtra("data", str); //把图片的ID放时去 intent.putExtra("rp", R.drawable.logo); startActivity(intent);
结果页面布局
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="结果显示"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_display" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_result" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="结果显示"/> </LinearLayout>
/**
* 创建一个Activity
* 1.写一个JAVA类,继承Activity
* 2.为这个Activity写一个布局文件
* 3.在Activity中重写OnCreate()方法,并设置显示的内容setContentView(R.layout.xxx)xxx表示布局文件的名称
* @author 刘楠
*
* 2016-2-25下午6:33:59
*/
public class ResultActivity extends Activity {
private TextView tv_result;
private ImageView iv_display ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//设置要显示的内容布局文件
setContentView(R.layout.activity_result);
tv_result = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_result);
iv_display = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_display);
//获取Intent
Intent intent = getIntent();
//获取数据
String data = intent.getStringExtra("data");
//设置值
tv_result.setText(data);
//获取图片
int rpMap = intent.getIntExtra("rp", 0);
//设置图片
iv_display.setImageResource(rpMap);
}
}
3.使用Intent传递多种数据
3.1传递简单数据
Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, SecondActivity.class); //传递普通数据 intent.putExtra("name", "张三"); intent.putExtra("age", 18); intent.putExtra("flag", true); startActivity(intent);
3.2传递复杂数据
1.传递一个对象,对象的类要实现Parcelable Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, SecondActivity.class); //传一个对象 //前提 是person实现了Parcelable接口 Person person = new Person("刘楠", 30); intent.putExtra("person", person); startActivity(intent); 获取 Intent intent = getIntent(); //获取数据n String name = intent.getStringExtra("name"); int age = intent.getIntExtra("age", 2); boolean flag = intent.getBooleanExtra("flag", false); Person p=intent.getParcelableExtra("person"); Toast.makeText(this,p.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
实际上只要让javaBean实现Serializable 接口就可以了,不管是传递单个对象,或者是传递一个集合,都没问题。
4. 启动界面的两种方式
4.1显示意图
只要指定上下文,和具体的类就可以跳转
> 能够直接知道跳转的界面
注册: <activity android:name="com.itheima.start.Activity01"></activity> 跳转: Intent intent = new Intent(this , Activity01.class); startActivity(intent);
作用: 一般是启动自己程序的界面,其他程序的界面通过这种方式无法启动
如果使用了显式手法注册,还想被其他应用程序打开, 那么可以在activity标签里面,加上
android:exported="true"
4.2 隐匿意图
不知道要打开的界面是什么样子的,只有运行了才知道
要指定Action与data才可以
/** * 显示意图打开Activity02 * @param v */ public void click1(View v){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, SencondActivity.class); startActivity(intent); } <activity android:name="com.itheima.intentstart.SencondActivity"></activity>
隐匿意图要指定Action,
<!--隐匿意图 --> <activity android:name="com.itheima.intentstart.SencondActivity"> <intent-filter > <!--Action --> <action android:name="com.itheima.intentstart.Second"/> <!--设置为默认的 --> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/> </intent-filter> </activity>
/** * 隐式意图打开Activity02 * * @param v */ public void click2(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.itheima.intentstart.Second"); intent.addCategory("android.intent.category.DEFAULT"); startActivity(intent); }
4.3 参数
作用: 跳转其他的应用程序界面,或者是自己的应用程序界面想被其他的程序打开
详细参数:
- action: 动作
- category 分类
- data: 指定数据, 一般关注两个:scheme 和 mimetype
- android:scheme="itheima" android:path="www.itheima" android:mimeType="text/plain"
4.4隐匿意图打打SMS
<Button
android:onClick="shareSms"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="打开手机短信" />
/** * 隐匿意图 打开手机SMS界面 * 源码 * <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <action android:name="android.intent.action.SENDTO" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:scheme="sms" /> <data android:scheme="smsto" /> </intent-filter> * @param v */ public void shareSms(View v){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("android.intent.action.VIEW"); intent.addCategory("android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"); intent.setData(Uri.parse("sms:")); //设置数据 intent.putExtra("sms_body", "这是要传过去的内容"); startActivity(intent); }
点击按键,显示界面
4.5 打开浏览器
/**打开系统的浏览器 * <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:scheme="http" /> <data android:scheme="https" /> <data android:scheme="about" /> <data android:scheme="javascript" /> </intent-filter> * @param v */ public void onOPenBrower(View v){ Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("android.intent.action.VIEW"); intent.addCategory("android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"); intent.setData(Uri.parse("http://www.baidu.com")); startActivity(intent); }
5.多个Activity之间获取数据与传递
打开下一个界面,然后返回数据
场景
QQ聊天给好友发送图片 (拍照返回、 相册选取)
选择联系人与短信模版把选择到的内容显示在指定的位置
主界面布局
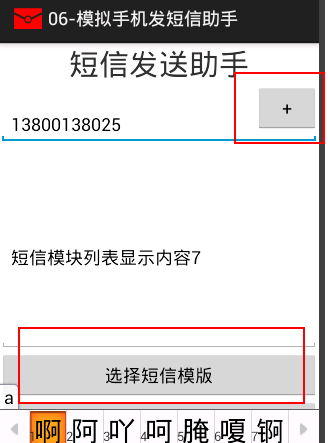
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:text="短信发送助手" android:textSize="30sp" /> <RelativeLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <EditText android:id="@+id/et_contact" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20sp" android:hint="请输入联系人" /> <!-- 选择联系人 --> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:onClick="selectContact" android:text="+" /> </RelativeLayout> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20sp" android:hint="请输入短信内容" android:minLines="8" /> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="selectSms" android:text="选择短信模版" /> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="sendSms" android:text="发送" /> </LinearLayout>
短信列表
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <!--短信列表 --> <ListView android:id="@+id/lv_sms" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > </ListView> </LinearLayout> 联系人列表 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" > <!--联系人列表 --> <ListView android:id="@+id/lv_contact" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > </ListView> </LinearLayout>
主界面 /** * 通过选择联系人,与模版把选择到的内容显示在指定的位置 1.建立布局.设置点击事件 2.跳转到选择页面 3.使用ListView展示数据 * 4.为ListView设置OnItemClickListener监听器与事件把选择到的数据返回给请求 Activity * 5.关闭选择的Activity结束finish() 6 * * @author 刘楠 * * 2016-2-25下午10:01:28 */ public class MainActivity extends Activity { /* * 联系人 */ private EditText et_contact; /* * 内容 */ private EditText et_content; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); et_contact = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_contact); et_content = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_content); } @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { //判断返回的intent是否为空 if(data==null){ return ; } //跟所请求码区别是什么结果 switch (requestCode) { case 100: //设置连联系人 et_contact.setText(data.getStringExtra("contact")); break; case 200: //设置内容 et_content.setText(data.getStringExtra("content")); break; } } /** * 选择联系人 * * @param v */ public void selectContact(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, ContactActivity.class); /* * requestCode:随意写, 如果一个页面内有多个请求结果的要区分 */ startActivityForResult(intent, 100); } /** * 选择SMS模版 * * @param v */ public void selectSms(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClass(this, SmsActivity.class); /* * requestCode:随意写, 如果一个页面内有多个请求结果的要区分 */ startActivityForResult(intent, 200); } /** * 发送SMS * * @param v */ public void sendSms(View v) { String number = et_contact.getText().toString().trim(); String body = et_content.getText().toString().trim(); if(TextUtils.isEmpty(number) || TextUtils.isEmpty(body)){ Toast.makeText(this, "手机号或者内容不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); return ; } /* * 发送短信 */ SmsManager manager = SmsManager.getDefault(); //拆分短信 ArrayList<String> divideMessage = manager.divideMessage(body); for (String str : divideMessage) { manager.sendTextMessage(number, null, str, null, null); } } }
短信列表
/** * 短信模块列表显示 * @author 刘楠 * * 2016-2-25下午9:48:12 */ public class SmsActivity extends Activity { protected static final String TAG = "SmsActivity"; private ListView lv_sms; private String [] objects={ "短信模块列表显示内容1", "短信模块列表显示内容2", "短信模块列表显示内容3", "短信模块列表显示内容4", "短信模块列表显示内容5", "短信模块列表显示内容6", "短信模块列表显示内容7", "短信模块列表显示内容8", "短信模块列表显示内容9", "短信模块列表显示内容10", "短信模块列表显示内容11", "短信模块列表显示内容12", "短信模块列表显示内容45", }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_sms_item); lv_sms = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv_sms); lv_sms = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv_sms); ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, objects); //配置监听器 lv_sms.setAdapter(adapter); //设置监听事件 lv_sms.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() { @Override public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { Log.i(TAG, "position:"+position); Log.i(TAG, "元素:"+objects[position]); //返回返回resultCode 响应码 Intent intent = new Intent(); //保存传递的数据 intent.putExtra("content", objects[position]); //调置结果 setResult(200, intent); //结束 finish(); } }); } }
联系人列表
/** * 联系人列表显示 * @author 刘楠 * * 2016-2-25下午9:48:12 */ public class ContactActivity extends Activity { protected static final String TAG = "ContactActivity"; private ListView lv_contact; private String [] objects ={ "5556", "13800138000", "13800138012", "13800138023", "13800138004", "13800138025", "13800138306", "13800138007", "13800138069", }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_contact_item); lv_contact = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.lv_contact); ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, objects); //配置监听器 lv_contact.setAdapter(adapter); //设置监听事件 lv_contact.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() { @Override public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { Log.i(TAG, "position:"+position); Log.i(TAG, "元素:"+objects[position]); //返回返回resultCode 响应码 Intent intent = new Intent(); //保存传递的数据 intent.putExtra("contact", objects[position]); //调置结果 setResult(200, intent); //结束 finish(); } }); } }
添加权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/>
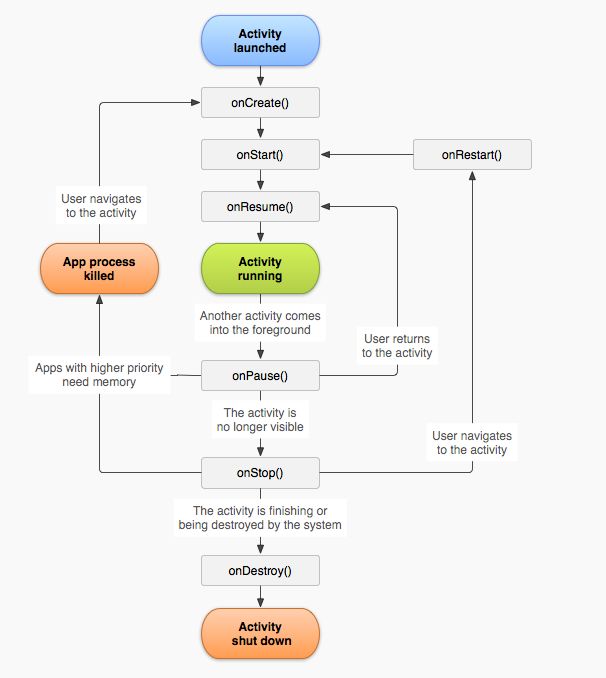
6.生命周期
###Activity生命周期
* 生命周期
> 一类从出生到消亡的过程(时间段)
* 生命周期方法
> 对象从创建到销毁,所调用的方法。
* 创建与销毁
> onCreate 和 onDestroy 数据的保存和回显工作
* 可见与不可见
> onStart 和 onStop 可见的时候播放视频,不可见的时候暂停视频的播放
* 获取焦点和失去焦点
> onResume 和 onPause
###生命周期总结
* entire lifetime
> 完整生命周期 onCreate-- onStart-- onResume -- onPause -- onStop -- onDestroy
* visible lifetime
> 可视生命周期 : onStart() -- onResume -- onPause -- onStop
* foreground lifetime
> 前台生命周期: onResume -- onPause
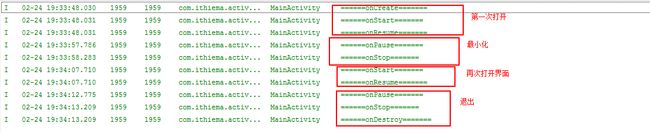
正常的生命周期
一个APP打开到退出
打开最小化,---唤醒-->>退出
/** * Activity生命周期 */ public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; /** * 初始化 * @param savedInstanceState */ @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Log.i(TAG, "======onCreate======="); } /* 界面可见时执行 */ @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); Log.i(TAG, "======onStart======="); } /* 界面最小化后,再打开时执行 */ @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); Log.i(TAG, "======onResume======="); } /* 界面最小化 */ @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); Log.i(TAG, "======onPause======="); } /* 界面不可见 */ @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); Log.i(TAG, "======onStop======="); } /** * 退出Activity里执行 */ @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.i(TAG, "======onDestroy======="); } }
7横竖屏切换:
1. 直接规定了是什么方向显示
android:screenOrientation="landscape" |portrait
2. 不指定方向,横屏就横屏显示,竖屏就竖屏显示
android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize|keyboardHidden"
8任务和栈
* task
> 一个应用程序可以拥有多个界面,一个界面就可以看成是与用户交互的任务 task , 为了方便管理,所以android就使用一个栈来集中管理他们这些任务 , 如果一个应用程序的所有栈都已经清空了,那么这个应用程序也就完全退出了 , 一个应用程序可以拥有多个任务栈
* stack
> 栈 , 是一种数据结构 遵循的是后进先出, 队列 (Queue ) ,先进先出
9.Activity启动模式
* standard
> 这是默认的启动模式,: 启动多少次这个界面,就会有多少个这个界面实例被压入栈中
* singleTop
> 单一顶部模式:如果一个界面的实例已经存在栈顶,那么久不会再继续创建这个界面的实例,而是继续使用这个实例。 只要不是顶部,就与默认的模式一样。
> 场景: 为了避免出现一些奇怪的现象,为了避免让自己启动自己 短信编写界面*
* singleTask
> 单一任务模式:如果一个界面的实例已经存在栈中,那么再次启动就不会继续创建新的实例,而是继续复用它,并且把它与栈顶之间的其他实例全部移除掉。
> 场景: 为了减轻资源的消耗,在栈中值创建一次实例, 比如: 浏览器的界面
* singleInstance
> 全局唯一模式: 无论创建多少次都只有一个实例,并且这个实例放在一个独立的栈中,里面有且只能有它自己一个实例
> 场景: 为了减轻资源的消耗,在栈中值创建一次实例 比如: 通话界面或者紧急通话界面