OpenCV学习(九)之Mat的基本操作_1
实验环境:VS2010 + OpenCV2.4.9.0
参考手册:The OpenCV Tutorials, Release 2.4.9.0
Mat:OpenCV中图像的基本容器,自OpenCV2.0之后的新功能,正在逐渐代替IplImage和CvMat。相比于IplImage和CvMat,Mat型侧重于计算,数学性较高,OpenCV对Mat类型的计算也进行了优化。而CvMat和IplImage类型更侧重于“图像”,OpenCV对其中的图像操作(缩放、单通道提取、图像阈值操作等)进行了优化。在OpenCV2.0之前,OpenCV是完全用C实现的,但是,IplImage类型与CvMat类型的关系类似于面向对象中的继承关系。实际上,CvMat之上还有一个更抽象的基类----CvArr,这在源代码中会常见。根据参考手册看来,Mat类表示一个 n 维的密集数值单通道或多通道数组。它可以用于存储实数或复数值的向量和矩阵、灰度或彩色图像、体素、向量场、点云、张量、直方图 (尽管较高维的直方图存储在SparseMat可能更好)。大概介绍至此,下面学习一些最基本用法:都以main函数的形式列出,头文件略。
1、Mat矩阵的建立
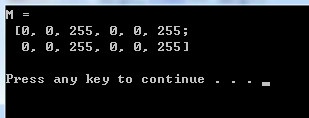
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
Mat M(2,2,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0,0,255));
//Mat M;
//M.create(4,4,CV_8UC2);
cout << "M = " << endl <<" " << M << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、几类基本矩阵的创建
//Define some matrices
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
Mat E = Mat::eye(4,4,CV_64F);
cout << "E = " << endl <<" " << E<< endl << endl;
Mat ON = Mat::ones(4,4,CV_32F);
cout << "ON = " << endl <<" " << ON << endl << endl;
Mat Z = Mat::zeros(3,3,CV_8UC1);
cout << "Z = " << endl << " " << Z << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3、小矩阵的创建和矩阵的复制/克隆
//For small matrices,may use comma separated initializers
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
Mat C = (Mat_<double>(3,3)<<0,-1,0,-1,5,-1,0,-1,0);
cout << "C = " << endl <<" " << C<< endl << endl;
//Create a new header for an existing Mat object and clone() or copyTo() it
Mat rowClone = C.row(1).clone();
cout << "rowClone = " << endl <<" " << rowClone << endl << endl;
Mat rowCopy;
C.row(1).copyTo(rowCopy);
cout << "rowCopy = " << endl <<" " << rowCopy << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//random function
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
Mat R = Mat(3,2,CV_8UC3);
randu(R,Scalar::all(0),Scalar::all(255));
cout << "R = " << endl <<" " << R << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5、C++容器和Mat
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
//2D Point
Point2f P(5,1);
cout << "Point (2D) = " << P << endl << endl;
//3D Point
Point3f P3f(2,6,7);
cout << "Point (3D) = " << P3f << endl << endl;
//std::vector via cv::Mat
vector<float> v;
v.push_back((float)CV_PI);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3.01f);
cout << "Vector of float via Mat = " << Mat(v) << endl << endl;
//std::vector of points
vector<Point2f> vPoints(20);
for(size_t i = 0;i < vPoints.size();i++)
vPoints[i] = Point2f((float)(i*5),(float)(i % 7));
cout << "A vector of 2D Points = " << vPoints << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}