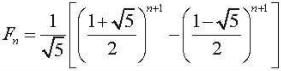斐波那契数列
[1]递归法
int Fib(int index)
{
if(index<1)
{
return-1;
}
if(index==1|| index==2)
{
return1;
}
return Fib1(index-1)+Fib1(index-2);
}
[2]递推法
int Fib(int index)
{
if(index<1)
{
return-1;
}
int a1=1,a2=1,a3=1;
for(int i=0;i<index-2;i++)
{
a3=a1+a2;
a1=a2;
a2=a3;
}
return a3;
}
[3]通项公式法
Fibonacci 数列的递推公式是二次递推式,二次递推式的通用解法是转换为如下形式:
![]()
转换后的一次递推式很容易生成联合方程,求出通项式,以下是a0=0, a1=1时的 Fibonacci 通项式:
int Fib(int n)
{
double gh5=sqrt((double)5);
return (pow((1+gh5),n)-pow((1-gh5),n))/(pow((double)2,n)*gh5);
}
[4]矩阵快幂法
Fibonacci 数列可以转化为一个等价矩阵,其通项为:
利用乘法的高效性提升性能,一般用于较大的Fibonacci数,因为在int范围内,其性能和代码简洁性不如递推法。
乘法的好处是,如F(90),利用递推,需要90次循环。但利用幂乘,将A^90拆分为A^90=A^64 * A^16 * A^8 * A^2,而A^64、A^16、A^8可以依次由A^2计算得出。只用几次乘法即可达到90次循环递推的效果,n越大,加速性越好。
矩阵乘法的实现代码比较简单,不再给出具体代码。只讨论其中的拆分子步骤。
n的拆分有多种, 甚至无需拆分,直接分割递归也可以。代码如下:
//来自 http://www.2cto.com/kf/201208/148361.html
Matrix power1 (LLD p) //矩阵幂 A^k
{
Matrix tp = a2 ;
Matrix tr = tmp ;
while (p)
{
if (p&1)
{
tr = Multi (tr, tp) ;
p -- ;
continue ;
}
tp = Multi (tp, tp) ;
p >>= 1 ;
}
return tr ;
}
Matrix Multi (Matrix a, Matrix b) //两矩阵相乘
{
Matrix c ;
for (int i = 0; i < 2;i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j ++)
{
c.mat[i][j] = 0 ;
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k ++)
c.mat[i][j] += (LLD)a.mat[i][k]*b.mat[k][j] ,c.mat[i][j] %= M ; //矩阵相乘时,需要防止溢出
}
return c ;
}
[5]数的二幂拆分避免递归重复计算
将任意正整数拆分为2的幂的和,如90=2^6+2^4+2^3+2^1.
拆分算法各种各样,下面给出我的二幂拆分法:基于位操作的二幂拆分
这种方法的核心是找到幂指数,下面是找幂指数的代码(核心是分离数的bit位)
typedef struct _x //_x is a tag of type x, generally used in the body for self pointer
{
unsigned bits[8*sizeof(unsigned)]; //sizeof operator returns the number of bytes of type unsigned
} x; //define struct x
x SplitInt(unsigned value)
{
x bitArray; //used to store the bit value of n
//get each bit from right
const unsigned MASK = 1; //MASK = 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
for(unsigned i=8*sizeof(unsigned)-1; i>=0; i--)
{
bitArray.bits[i] = (value & MASK ? 1 : 0 ); //if value&MASK is 0(false), set the bit to 0;else if it is not 0(true), set the bit to 1;
value >>= 1; //shift value left by 1;
}
return bitArray;
}
更一般地,分离数的bit位代码模板如下(核心代码只有一行,即可分离所有位):
void func_SplitInt(unsigned value)
{
for(unsigned i=8*sizeof(unsigned)-1; i>=0; i--,value>>=1)
cout<<(value & 1 ?1:0)<<endl;
}
根据《剑指offer》一书中作者提到的方法,书中介绍了一个数学公式如下:
我进行了如下验算:
因此f(n)就等于等式右边的二阶方阵的(n-1)次方所求得方阵的第一行第一列个数的值。代码实现如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
//求矩阵a的n次幂的函数
long long * Matrix(long long *a,int n)
{
long long *result = (long long *)malloc(sizeof(long long)*4);
long long *finnal = (long long *)malloc(sizeof(long long)*4);
//如果n等于1的话,则直接返回矩阵a,毕竟,一次幂就不必求了。
if(n==1)
return a;
//先求出矩阵的n/2次幂
long long *CurMatrix = Matrix(a,n/2);
//两个矩阵的n/2次幂相乘得到矩阵的n次幂
result[0] = CurMatrix[0]*CurMatrix[0]+CurMatrix[1]*CurMatrix[2];
result[1] = CurMatrix[0]*CurMatrix[1]+CurMatrix[1]*CurMatrix[3];
result[2] = CurMatrix[2]*CurMatrix[0]+CurMatrix[3]*CurMatrix[2];
result[3] = CurMatrix[2]*CurMatrix[1]+CurMatrix[3]*CurMatrix[3];
//如果n为奇数的话,则(n/2)会少一位,补回来。a = a^(n/2)*a^(n/2) * a;
if(n%2==1)
{
finnal[0] = result[0]*a[0]+result[1]*a[2];
finnal[1] = result[0]*a[1]+result[1]*a[3];
finnal[2] = result[2]*a[0]+result[3]*a[2];
finnal[3] = result[2]*a[1]+result[3]*a[3];
}
//如果n为偶数的话,n/2还是n/2
else
finnal = result;
return finnal;
}
int main(void)
{
long long a[4];
int n;
cin>>n;
//矩阵按一位数组设置,t[0]即为febonacci(n)
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 1;
a[2] = 1;
a[3] = 0;
long long *t = Matrix(a,n-1);
cout<<t[0]<<endl;
return 0;
}
该算法的复杂度为O(logn)。