基于linux3.0内核fl2440开发板下的gps数据采集与处理
—————————————————————————————————————————————
主机操作系统:Centos 6.5
交叉编译器环境:arm-linux-gcc-4.5.4
开发板平台: FL2440
Linux内核版本: linux-3.0
开发模块: FIT-GPS-SF2820
作者:hulu<[email protected]>
—————————————————————————————————————————————
开发提醒:在开发gps模块之前需满足fl2440开发版能正常加载linux内核及文件系统,同时fl2440开发板上的dm9000网卡能正常上网(ping通自己的主机)。
==================================================================================================================================================
GPS(Global Positioning System)即全球定位系统,是由美国建立的一个卫星导航定位系统,利用该系统,用户可以在全球范围内实现全天候、连续、实时的三维导航定位和测速;另外,利用该系统,用户还能够进行高精度的时间传递和高精度的精密定位,通过GPS系统可以实现跟踪定位、防盗、里程统计、汽车导航、电子地图等等现实生活不可或缺的功能。本文着眼于在嵌入式linux系统上GPS功能的实现和研究。
==================================================================================================================================================
由于GPS,串口都是设备,难道就不需要再在linux内核中使能驱动吗?是这样的,在一开始内核中就已经对串口驱动进行了使能,而GPS模块中有GPS模块的驱动,这个模块通过自身的串口不断的发送数据开发板需要做的就是读取然后处理就够了。
有了上面的预热是不是感觉对这个模块简单了许多,所以我们接下来要做的就是通过编程配置好串口的状态获取GPS数据,然后提取GPS传回来的数据,并解析出来。
开发步骤:
1.linux下c语言编程配置串口(串口参数的配置主要包括:波特率、数据位、校验位、停止位)
2.获取GPS传回的数据包
3.解析GPS数据包,提取有效数据
一:GPS模块与fl2440开发板硬件连接
==================================================================================================================================================
fl2440开发板有两个串口ttys0和ttys1,其中ttys0用来连接电脑终端,则ttys1连接GPS模块的串口,linux中的串口设备文件放于/de/目录下,串口一,串口二分别为”/dev/ttyS0”,”/dev/ttyS1”.在linux下操作串口与操作文件相同.
==================================================================================================================================================
GPS模块接上电,监听串口了发回的数据包
~> microcom -s 4800 /dev/ttyS1
$GPGGA,024907.000,3029.6642,N,11423.6203,E,1,10,1.0,35.7,M,-13.7,M,,0000*41
$GPGSA,A,3,04,08,32,17,28,30,07,11,20,01,,,1.9,1.0,1.7*3B
$GPRMC,024907.000,A,3029.6642,N,11423.6203,E,0.07,244.07,210914,,,A*67
$GPGGA,024908.000,3029.6643,N,11423.6202,E,1,10,1.0,35.3,M,-13.7,M,,0000*4A
$GPGSA,A,3,04,08,32,17,28,30,07,11,20,01,,,1.9,1.0,1.7*3B
$GPGSV,3,1,11,04,78,178,38,01,74,066,31,30,56,242,44,11,54,043,31*75
$GPGSV,3,2,11,28,47,328,27,07,40,194,40,08,31,177,47,17,29,277,27*74
$GPGSV,3,3,11,20,23,145,36,32,21,098,33,19,15,059,*4C
$GPRMC,024908.000,A,3029.6643,N,11423.6202,E,0.09,238.16,210914,,,A*6D
$GPGGA,024909.000,3029.6643,N,11423.6202,E,1,10,1.0,35.0,M,-13.7,M,,0000*48
$GPGSA,A,3,04,08,32,17,28,30,07,11,20,01,,,1.9,1.0,1.7*3B
$GPRMC,024909.000,A,3029.6643,N,11423.6202,E,0.07,251.95,210914,,,A*66
有了上述结果。说明接收数据是可以实现的,且硬件连接成功,注意:microcom是内核自带的监听串口的命令
本次开发包含以下这几个文件:gps_main.c gps_analysis.c set_com.c gpd.h makefile 主函数在gps_main.c文件中,gps_analysis.c主要是GPS数据解析函数设计,set_com.c主要是设置GPS串口设备函数设计,gpd.h是头文件!
二:串口编程
至于串口编程的详细介绍,如何设置波特率,如何设置停止位等等,以下给出两个linux串口编程的博客链接,讲的很详细,我就在此不多说了:
http://www.cnblogs.com/wblyuyang/archive/2011/11/21/2257544.html
http://blog.csdn.net/mtv0312/article/details/6599162
其中串口设置其实就相当于串口通信的协议,
波特率:是为了两者信号流能同步,
数据位:是指又几位数据封装成一帧
结束位:是指以帧传输数据时,协定好结束位,便于提取有效数据
奇偶校验:检验数据的一种手段
四者的设置又通信双方协定。
串口设置由下面的结构体实现:
struct termios
{
tcflag_t c_iflag; //input flags
tcflag_t c_oflag; //output flags
tcflag_t c_cflag; //control flags
tcflag_t c_lflag; //local flags
cc_t c_cc[NCCS]; //control characters
}; 该结构体中c_cflag最为重要,可设置波特率、数据位、校验位、停止位。在设置波特率时需要在数字前加上'B',如B9600,B15200.使用其需通过“与”“或”操作方式:
串口使用详解
打开串口 :
fd = open(“/dev/ttyS0”,O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY);
参数–
O_NOCTTY:通知linux系统,这个程序不会成为这个端口的控制终端.
O_NDELAY:通知linux系统不关心DCD信号线所处的状态(端口的另一端是否激活或者停止).
然后恢复串口的状态为阻塞状态,用于等待串口数据的读入,用fcntl函数: fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,0); //F_SETFL:设置文件flag为0,即默认,即阻塞状态
读写串口:
串口的读写与普通文件一样,使用read,write函数
read(fd,buff,8);
write(fd,buff,8);
通过详细浏览以上博客链接,就可以编写串口配置的代码:
/********************************************************************************* * Copyright: (C) 2016 SCUEC * All rights reserved. * * Filename: set_ttyS1.c * Description: This file * * Version: 1.0.0(2016年02月25日) * Author: hulu <[email protected]> * ChangeLog: 1, Release initial version on "2016年02月25日 21时40分23秒" * ********************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/************************************************************************************** * Description: 串口参数配置 * Input Args: fd:open打开的文件描述符 nspeed:波特率 nBits:数据位数 nEvent:奇偶校验 nStop:停止位 * Output Argtingzhis: 串口参数设置失败返回-1 * Return Value: *************************************************************************************/
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed,int nBits,char nEvent,int nStop)
{
struct termios newttys1,oldttys1;
if(tcgetattr(fd,&oldttys1)!=0) //保存原先串口配置
{
perror("Setupserial 1");
return -1;
}
bzero(&newttys1,sizeof(newttys1)); //将一段内存区域的内容全清为零
newttys1.c_cflag|=(CLOCAL|CREAD ); //CREAD 开启串行数据接收,CLOCAL并打开本地连接模式
newttys1.c_cflag &=~CSIZE; //设置数据位数
switch(nBits) //选择数据位
{
case 7:
newttys1.c_cflag |=CS7;
break;
case 8:
newttys1.c_cflag |=CS8;
break;
}
switch( nEvent ) //设置校验位
{
case '0': //奇校验
newttys1.c_cflag |= PARENB; //开启奇偶校验
newttys1.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); //INPCK打开输入奇偶校验;ISTRIP去除字符的第八个比特
newttys1.c_cflag |= PARODD; //启用奇校验(默认为偶校验)
break;
case 'E' : //偶校验
newttys1.c_cflag |= PARENB; //开启奇偶校验
newttys1.c_iflag |= ( INPCK | ISTRIP); //打开输入奇偶校验并去除字符第八个比特
newttys1.c_cflag &= ~PARODD; //启用偶校验;
break;
case 'N': //关闭奇偶校验
newttys1.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
switch( nSpeed ) //设置波特率
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newttys1, B2400); //设置输入速度
cfsetospeed(&newttys1, B2400); //设置输出速度
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newttys1, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newttys1, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newttys1, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newttys1, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newttys1, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newttys1, B115200);
break;
default:
cfsetispeed(&newttys1, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newttys1, B9600);
break;
}
if( nStop == 1) //设置停止位;若停止位为1,则清除CSTOPB,若停止位为2,则激活CSTOPB。
{
newttys1.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; //默认为送一位停止位;
}
else if( nStop == 2)
{
newttys1.c_cflag |= CSTOPB; //CSTOPB表示送两位停止位;
}
//设置最少字符和等待时间,对于接收字符和等待时间没有特别的要求时
newttys1.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; //非规范模式读取时的超时时间;
newttys1.c_cc[VMIN] = 0; //非规范模式读取时的最小字符数;
tcflush(fd ,TCIFLUSH); //tcflush清空终端未完成的输入/输出请求及数据;TCIFLUSH表示清空正收到的数据,且不读取出来
// 在完成配置后,需要激活配置使其生效
if((tcsetattr( fd, TCSANOW,&newttys1))!=0) //TCSANOW不等数据传输完毕就立即改变属性
{
perror("com set error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
} /* ----- End of if() ----- */二.GPS数据解析
==================================================================================================================================================
模块协议支持NMEA-0183协议。 NMEA-0183 是美国国家海洋电子协会(National Marine
ElectronicsAssociation)所指定的标准规格,这一标准制订所有航海电子仪器间的通讯标准 ,
其中包含传输资料的格式以及传输资料的通讯协议。
==================================================================================================================================================
GPS返回的数据如何理解呢?这一大串的数据到底代表了什么意思呢?要想编写GPS数据解析程序,肯定要知道这些数据代表什么,还要知道如何转换这些数据。以下给出一个博客链接详细地说明了GPS数据,这里不在做赘述:
http://www.cnblogs.com/csMapx/archive/2011/11/02/2232663.html
GPS 上电后,每隔一定的时间就会返回一定格式的数据,数据格式为:
信息类型,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x,x每行开头的字符都是‘ ’,接着是信息类型,后面是数据,以逗号分隔开。
一行完整的数据如下:
$GPRMC,080655.00,A,4546.40891,N,12639.65641,E,1.045,328.42,170809,,,A*60
信息类型为:
GPGSV:可见卫星信息
GPGLL:地理定位信息
GPRMC:推荐最小定位信息
GPVTG:地面速度信息
GPGGA:GPS定位信息
GPGSA:当前卫星信息
GPRMC(建议使用最小 GPS 定位信息)
$GPRMC,082006.000,A,3852.9276,N,11527.4283,E,0.00,0.0,261009,,*38
$GPRMC,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,<10>,<11>,<12>*hh
1) 标准定位时间(UTC time)格式:时时分分秒秒.秒秒秒(hhmmss.sss) 。(前面的0也将被传输)
2) 定位状态,A= 数据可用,V = 数据不可用。
3) 纬度,格式:度度分分.分分分分(ddmm.mmmm) 。(前面的0也将被传输)
4) 纬度区分,北半球(N)或南半球(S) 。
5) 经度,格式:度度分分.分分分分。(前面的0也将被传输)
6) 经度区分,东(E)半球或西(W)半球。
7) 地面速率(000.0~999.9节,前面的0也将被传输)
8) 地面航向(000.0~359.9度,以真北为参考基准,前面的0也将被传输)
9) 日期,格式:日日月月年年(ddmmyy) 。
10) 磁偏角(000.0~180.0度,前面的0也将被传输)
11) 磁偏角方向,E(东)或W(西)
12) 模式指示(仅NMEA01833.00版本输出,A=自主定位,D=差分,E=估算,N=数据无效)
解析内容:
1.时间,这个是格林威治时间,是世界时间(UTC),我们需要把它转换成北京时间(BTC),BTC和UTC差了8个小时,要在这个时间基础上加8个小时。
2. 定位状态,在接收到有效数据前,这个位是‘V’,后面的数据都为空,接到有效数据后,这个位是‘A’,后面才开始有数据。
3. 纬度,我们需要把它转换成度分秒的格式,计算方法:如接收到的纬度是:4546.40891
4546.40891/100=45.4640891可以直接读出45度, 4546.40891–45*100=46.40891, 可以直接读出46分
46.40891–46 =0.40891*60=24.5346读出24秒, 所以纬度是:45度46分24秒。
4. 南北纬,这个位有两种值‘N’(北纬)和‘S’(南纬)
5. 经度的计算方法和纬度的计算方法一样
6. 东西经,这个位有两种值‘E’(东经)和‘W’(西经)
7.速率,这个速率值是海里/时,单位是节,要把它转换成千米/时,根据:1海里=1.85公里,把得到的速率乘以1.85。
8. 航向,指的是偏离正北的角度
9. 日期,这个日期是准确的,不需要转换
根据以上GPS协议信息,本次开发使用的是GPRMC最小定位信息,解析代码如下:
/*********************************************************************************
* Copyright: (C) 2016 SCUEC
* All rights reserved.
*
* Filename: analyse_gps.c
* Description: This file
*
* Version: 1.0.0(2016年02月25日)
* Author: hulu <[email protected]>
* ChangeLog: 1, Release initial version on "2016年02月25日 22时48分25秒"
*
********************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "gps.h"
/**************************************************************************************
* Description:从GPS数据包中抽取出GPRMC最小定位信息
* Input Args:buff:GPS返回的数据包 gps_date:GPRMC信息存储结构体
* Output Args:
* Return Value:
*************************************************************************************/
int gps_analysis(char *buff,GPRMC *gps_date)
{
char *ptr=NULL;
if(gps_date==NULL)
return -1;
if(strlen(buff)<10)
return -1;
if(NULL==(ptr=strstr(buff,"$GPRMC")))
return -1;
sscanf(ptr,"$GPRMC,%d.000,%c,%f,N,%f,E,%f,%f,%d,,,%c*",&(gps_date->time),&(gps_date->pos_state),&(gps_date->latitude),&(gps_date->longitude),&(gps_date->speed),&(gps_date->direction),&(gps_date->date),&(gps_date->mode));
return 0;
} /* ----- End of if() ----- */
/********************************************************************************************
strstr(str1,str2) 函数用于在字符串str1中搜寻str2,并返回str2在str1中首次出现的地址;否则,返回NULL
sscanf()格式化字符串输入,从一个字符串中读进与指定格式相符的数据并在存入到另一个字符串中
**********************************************************************************************/
/**************************************************************************************
* Description:解析GPRMC最小定位信息,并打印到屏幕上
* Input Args:gps_date:gps_analysis函数抽取的GPRMC信息
* Output Args:
* Return Value:
*************************************************************************************/
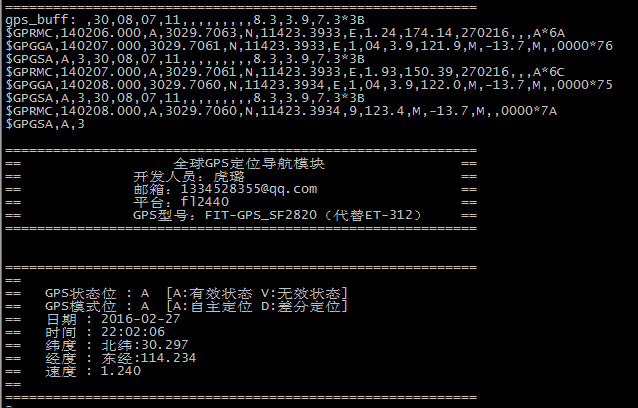
int print_gps(GPRMC *gps_date)
{
printf(" \n");
printf(" \n");
printf("===========================================================\n");
printf("== 全球GPS定位导航模块 ==\n");
printf("== 开发人员:虎璐 ==\n");
printf("== 邮箱:[email protected] ==\n");
printf("== 平台:fl2440 ==\n");
printf("== GPS型号:FIT-GPS_SF2820(代替ET-312) ==\n");
printf("===========================================================\n");
printf(" \n");
printf(" \n");
printf("===========================================================\n");
printf("== \n");
printf("== GPS状态位 : %c [A:有效状态 V:无效状态] \n",gps_date->pos_state);
printf("== GPS模式位 : %c [A:自主定位 D:差分定位] \n", gps_date->mode);
printf("== 日期 : 20%02d-%02d-%02d \n",gps_date->date%100,(gps_date->date%10000)/100,gps_date->date/10000);
printf("== 时间 : %02d:%02d:%02d \n",(gps_date->time/10000+8)%24,(gps_date->time%10000)/100,gps_date->time%100);
printf("== 纬度 : 北纬:%.3f \n",(gps_date->latitude/100));
printf("== 经度 : 东经:%.3f \n",(gps_date->longitude/100));
printf("== 速度 : %.3f \n",gps_date->speed);
printf("== \n");
printf("===========================================================\n");
return 0;
} /* ----- End of print_gps() ----- */三.编写gps_main.c测试程序
1.gps_main.c:
/*********************************************************************************
* Copyright: (C) 2016 SCUEC
* All rights reserved.
*
* Filename: GPS_main.c
* Description: This file
*
* Version: 1.0.0(2016年02月25日)
* Author: hulu <[email protected]>
* ChangeLog: 1, Release initial version on "2016年02月25日 23时53分32秒"
*
********************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "gps.h"
#define GPS_LEN 512
int gps_analysis(char *buff,GPRMC *gps_date);
int print_gps(GPRMC *gps_date);
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop);
/********************************************************************************
* Description: main():程序执行的入口
* Input Args:
* Output Args:
* Return Value:
********************************************************************************/
int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = 0;
int nread = 0;
GPRMC gprmc;
char gps_buff[GPS_LEN];
char *dev_name = "/dev/ttyS1";
fd=open(dev_name,O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY);
if(fd<0)
{
printf("open ttyS1 error!!\n");
return -1;
}
set_opt( fd,4800,8,'N',1);
while(1)
{
sleep(2);
nread = read(fd,gps_buff,sizeof(gps_buff));
if(nread<0)
{
printf("read GPS date error!!\n");
return -2;
}
printf("gps_buff: %s\n", gps_buff);
memset(&gprmc, 0 , sizeof(gprmc));
gps_analysis(gps_buff,&gprmc);
print_gps(&gprmc);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
} /* ----- End of main() ----- */
2.gps.h头文件:
/******************************************************************************** * Copyright: (C) 2016 SCUEC * All rights reserved. * * Filename: gps.h * Description: This head file * * Version: 1.0.0(2016年02月25日) * Author: hulu <[email protected]> * ChangeLog: 1, Release initial version on "2016年02月25日 23时38分14秒" * ********************************************************************************/
#ifndef __GPS_H__
#define __GPS_H__
typedef unsigned int UINT;
typedef int BYTE;
typedef long int WORD;
typedef struct __gprmc__
{
UINT time; //格林威治时间
char pos_state; //定位状态
float latitude; //纬度
float longitude; //经度
float speed; //移动速度
float direction; //方向
UINT date; //日期
float declination; //磁偏角
char dd; //磁偏角方向
char mode;
}GPRMC;
extern int gps_analysis(char *buff,GPRMC *gps_date);
extern int print_gps(GPRMC *gps_date);
extern int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop);
#endif3.mkaefile文件:
CC =/opt/buildroot-2012.08/arm920t/usr/bin/arm-linux-gcc
objs =set_ttyS1.o analyse_gps.o GPS_main.o
srcs =set_ttyS1.c analyse_gps.c GPS_main.c
gps_bin: $(objs)
$(CC) -o gps_bin $(objs)
@make clean
GPS_main.o: $(srcs) gps.h
$(CC) -c $(srcs)
set_ttyS1.o: set_ttyS1.c
$(CC) -c set_ttyS1.c
analyse_gps.o: analyse_gps.c gps.h
$(CC) -c analyse_gps.c
clear:
@rm gps_bin
.PHONY: clean
clean:
@rm *.o 四:编译并烧录到开发板apps目录下执行
注意:将上图gps_bin烧录到开发板后,记得更改可执行权限