封装iOS自定义控件的体会
一、概述
1、对于经常使用的控件或类,通常将其分装为一个单独的类来供外界使用,以此达到事半功倍的效果
2、由于分装的类不依赖于其他的类,所以若要使用该类,可直接将该类拖进项目文件即可
3、在进行分装的时候,通常需要用到代理设计模式
二、自定义布局类的封装
1、业务逻辑
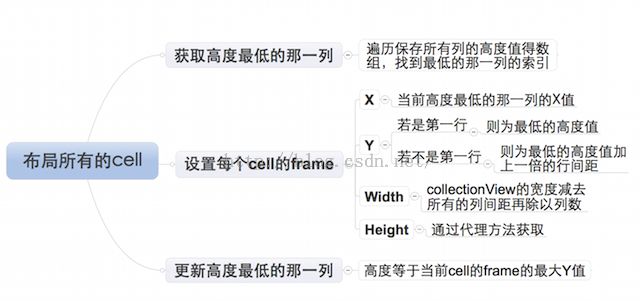
如图
2、布局每个cell的业务逻辑
由于设置每个cell的布局属性的业务逻辑较复杂,特附上如下思维导图3、封装思路封装需要根据客户类业务逻辑需求来提供接口
1)、通过代理协议的可选实现的方法获取的属性值的属性,需要设置默认值
2)、未提供默认值的且必须使用的属性,需要通过必须实现的方法来获得
3)、自定义布局提供的接口可选:
1.列数 2.列之间的间距 3.行之间的间距 4.内边距
4)、自定义布局提供的接口必选
每个元素的高度,宽度可以通过列数和列间距计算得到
三、封装步骤
设置代理协议,提供接口?
//声明LYPWaterFlowLayout为一个类 @classLYPWaterFlowLayout; @protocol LYPWaterFlowLayoutDelegate <NSObject> //必须实现的方法 @required /**获取瀑布流每个元素的高度*/ - (CGFloat)waterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout heightForItemAtIndex:(NSInteger)index itemWith:(CGFloat)itemWith; //可选实现的方法 @optional /**获取瀑布流的列数*/ - (NSInteger)columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流列间距*/ - (CGFloat)columnMarginInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流的行间距*/ - (CGFloat)rowMarginInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; /**获取瀑布流的内边距*/ - (UIEdgeInsets)edgeInsetsInWaterFlowLayout:(LYPWaterFlowLayout *)waterFlowLayout; @end
设置代理属性
@interface LYPWaterFlowLayout : UICollectionViewLayout /**代理*/ @property (nonatomic, weak) id<LYPWaterFlowLayoutDelegate> delegate; @end
设置通过可选代理方法获取属性值的属性的默认值
/**默认的列数*/
staticconst NSInteger LYPDefaultColumnCount = 3;
/**默认每一列之间的间距*/
staticconst CGFloat LYPDefaultColumMargin = 10;
/**默认每一行之间的间距*/
staticconst CGFloat LYPDefaultRowMargin = 10;
/**默认边缘间距*/
staticconst UIEdgeInsets LYPDefaultEdgeInsets = {10, 10, 10, 10};
设置通过可选代理方法获取属性值的属性的访问方式若代理提供属性值,则忽略默认值
- (NSInteger)columnCount
{
//判断代理是否实现了获取列数的可选方法
if([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:)])
{
//实现,返回通过代理设置的列数
return[self.delegate columnCountInWaterFlowLayout:self];
}
else
{
//为实现,返回默认的列数
returnLYPDefaultColumnCount;
}
}
设置布局
1)、设置需要的成员属性
/**所有cell的布局属性*/ @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *attrsArray; /**所有列的当前高度*/ @property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *columnHeights;
2)、通过懒加载的方式初始化成员属性
/**--attrsArray--懒加载*/
- (NSMutableArray *)attrsArray
{
if(_attrsArray == nil)
{
_attrsArray = [NSMutableArray array];
}
return_attrsArray;
}
/**--columnHeights--懒加载*/
- (NSMutableArray *)columnHeights
{
if(_columnHeights == nil)
{
_columnHeights = [NSMutableArray array];
}
return_columnHeights;
}
- (nullable NSArray<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *> *)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect
{
returnself.attrsArray;
}
设置每一个cell的布局属性
- (nullable UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:(nonnull NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
//获取indexPath位置的布局属性
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *attrs = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:indexPath];
/**设置cell布局属性的frame*/
/***确定cell的尺寸***/
//获取collectionView的宽度
CGFloat collectionViewWidth = self.collectionView.frame.size.width;
//cell宽度
CGFloat width = ((collectionViewWidth - self.edgeInsets.left - self.edgeInsets.right - (self.columnCount - 1) * self.columMargin)) / self.columnCount;
//cell高度
CGFloat height = [self.delegate waterFlowLayout:self heightForItemAtIndex:indexPath.item itemWith:width];
/***设置cell的位置***/
NSInteger destColumn = 0;
CGFloat minColumnHeight = [self.columnHeights[0] doubleValue];
for(NSInteger i = 1; i<self.columnCount; i++)
{
CGFloat columnHeight = [self.columnHeights[i] doubleValue];
if(minColumnHeight > columnHeight)
{
minColumnHeight = columnHeight;
destColumn = i;
}
}
//计算cell的位置
CGFloat x = self.edgeInsets.left + destColumn * (width + self.columMargin);
CGFloat y = minColumnHeight;
//判断是不是第一行
if(y != self.edgeInsets.top)
{
//若不是第一行,需要加上行间距
y += self.rowMargin;
}
/**给cell的布局属性的frame赋值*/
attrs.frame = CGRectMake(x, y, width, height);
//更新最短那列的高度
self.columnHeights[destColumn] = @(CGRectGetMaxY(attrs.frame));
/**返回indexPath位置的cell的布局属性*/
returnattrs;
}
5)、设置collectionView内容的尺寸
- (CGSize)collectionViewContentSize
{
//获取最高的那一列的高度
CGFloat maxColumnHeight = [self.columnHeights[0] doubleValue];
for(NSInteger i = 1; i<self.columnCount; i++)
{
CGFloat columnHeight = [self.columnHeights[i] doubleValue];
if(maxColumnHeight < columnHeight)
{
maxColumnHeight = columnHeight;
}
}
//返回collectionView的contentSize,高度为最高的高度加上一个行间距
returnCGSizeMake(0, maxColumnHeight + self.rowMargin);
}
<pre name="code" class="objc">四、封装体会 一个良好的自定义控件,能大大减少控制器里的代码,让代码在它最应该在的地方,显得层次清晰。此外,一个没有耦合的自定义控件,能拿到之后的任何项目中用,提高开发效率。接口友好、使用简单、不存在耦合、代码层次清晰易维护等是一个好控件的必备素质。项目中常见的自定义控件,往往是一些弹窗,方便用户进行查看、输入、选择等操作。 相关封装实例:
时间选择器
1. 使用方法:先调用show方法,再定义回调block。
2. 效果截图:控件内部加入了时间过滤(截图时间12-09 09:55)并记忆了上次的选择,无耦合 。
3. 思路分析:这个便是小伙伴问到我的控件, 这个控件当时是用于这样的 场景:用户约时间咨询专家,通过这个控件选择一个时间点。我的思路如下:
1) 分析界面(view):
这个界面上部分是一个工具条,左右两个按钮分别切换到上一天/下一天,中间的lable显示日期和星期几。再看中间的12个按钮,每个按钮都代表某一个时间点,有可点击状态/不可点击状态/选中状态三种样式,在Demo中我用的是按钮来实现,用collectionView应该能让代码更简洁。
同时需要考虑到,用户每切换到另一天,控件需要刷新一下,要根据新的一天里,专家空闲时间(服务器返回),来刷新中间12个按钮的显示样式[可预约/不可预约/当前选择]。
2) 分析数据(model):
先分析当前展示的一天中需要的数据,我们需要告诉用户该专家哪些时间点可预约,哪些不可预约,用一个字段来表示就可以了,这里一共是12个时间点,也就是说这个控件的每一次展示,需要一个有12个元素的数组,这12个元素分别对应这12个时间点是否可预约。
假设我们允许用户的预约范围是未来一周,那么这个控件就需要一个包含7个子数组的大数组,每个子数组有12个元素,是专家某一天的可否预约的数据。好,所以控制器需要给这个控件一个大数组。
3) 上一天/下一天按钮的点击事件处理:
自定义多行输入框
1. 使用方法:先设置数据,再调用show方法,最后定义回调block。
2. 效果截图:控件内部加入了手机号、邮箱检测方法,无耦合; 非法 提示方式也较合适 。
3. 思路分析:这个控件很简单,用起来也很方便,控件内部会根据传进来的数据决定展示几行输入框出来,内部有做了数据的合法性检查、键盘处理等 ...思路倒没什么好说的...
日期选择器
1. 使用方法:先调用show方法,再定义回调block。
2. 效果截图:控件内部加入了简单的时间判断和非法选择时的提示,只有当时间合法时,才调用回调block,传递合法的时间string出去。
3. 思路分析:好吧,这个控件更简单了...
五、小结
当我拿到设计图时,第一步先分析界面什么地方应该是什么控件,再分析需要控制器传过来什么数据,然后把需要暴露的属性放在h文件里,不需要暴露的属性放在m文件里。我封装的自定义控件,一直努力做到以下两点 :
1. 接口友好,使用尽量简单。显示就是show,隐藏就是hide,不需要控制器来完成显示和隐藏的代码,控制器只需要告诉我什么时候show,什么时候hide就行。
2. 该封装的封装好,减少控制器里的代码。 控制器只需要关心给你什么数据、什么时候让你show、什么时候让你hide和你的点击事件我应该怎么处理。而不去关心你怎么展示数据、怎么处理数据等。
Demo的下载地址: http://download.csdn.net/detail/lxl_815520/9450956