Nginx的负载均衡 - 加权轮询 (Weighted Round Robin) 上篇
算法介绍
来看一个简单的Nginx负载均衡配置。![]()
- http {
- upstream cluster {
- server a weight=5;
- server b weight=1;
- server c weight=1;
- }
- server {
- listen 80;
- location / {
- proxy_pass http://cluster;
- }
- }
- }
当在upstream配置块中没有指定使用的负载均衡算法时,默认使用的是加权轮询。
按照上述配置,Nginx每收到7个客户端的请求,会把其中的5个转发给后端a,把其中的1个转发给后端b,
把其中的1个转发给后端c。
这就是所谓的加权轮询,看起来很简单,但是最早使用的加权轮询算法有个问题,就是7个请求对应的
后端序列是这样的:{ c, b, a, a, a, a, a },会有5个连续的请求落在后端a上,分布不太均匀。
目前使用的加权轮询叫做平滑的加权轮询(smooth weighted round-robin balancing),它和前者的区别是:
每7个请求对应的后端序列为 { a, a, b, a, c, a, a },转发给后端a的5个请求现在分散开来,不再是连续的。
摘录此算法的描述:
On each peer selection we increase current_weight of each eligible peer by its weight,
select peer with greatest current_weight and reduce its current_weight by total number
of weight points distributed among peers.
To preserve weight reduction in case of failures the effective_weight variable was introduced,
which usually matches peer's weight, but is reduced temoprarily on peer failures.[1]
每个后端peer都有三个权重变量,先解释下它们的含义。
(1) weight
配置文件中指定的该后端的权重,这个值是固定不变的。
(2) effective_weight
后端的有效权重,初始值为weight。
在释放后端时,如果发现和后端的通信过程中发生了错误,就减小effective_weight。
此后有新的请求过来时,在选取后端的过程中,再逐步增加effective_weight,最终又恢复到weight。
之所以增加这个字段,是为了当后端发生错误时,降低其权重。
(3) current_weight
后端目前的权重,一开始为0,之后会动态调整。那么是怎么个动态调整呢?
每次选取后端时,会遍历集群中所有后端,对于每个后端,让它的current_weight增加它的effective_weight,
同时累加所有后端的effective_weight,保存为total。
如果该后端的current_weight是最大的,就选定这个后端,然后把它的current_weight减去total。
如果该后端没有被选定,那么current_weight不用减小。
弄清了三个weight字段的含义后,加权轮询算法可描述为:
1. 对于每个请求,遍历集群中的所有可用后端,对于每个后端peer执行:
peer->current_weight += peer->effecitve_weight。
同时累加所有peer的effective_weight,保存为total。
2. 从集群中选出current_weight最大的peer,作为本次选定的后端。
3. 对于本次选定的后端,执行:peer->current_weight -= total。
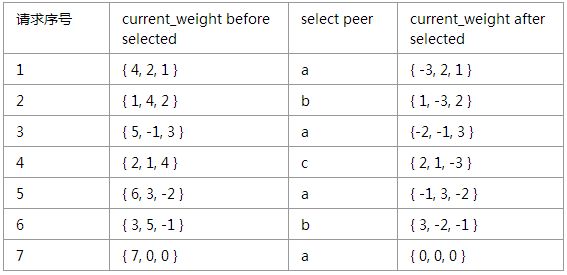
上述描述可能不太直观,来看个例子。
现在使用以下的upstream配置块:
upstream backend {
server a weight=4;
server b weight=2;
server c weight=1;
}
按照这个配置,每7个客户端请求中,a会被选中4次、b会被选中2次、c会被选中1次,且分布平滑。
我们来算算看是不是这样子的。
initial current_weight of a, b, c is { 0, 0, 0 }
通过上述过程,可得以下结论:
1. 7个请求中,a、b、c分别被选取了4、2、1次,符合它们的权重值。
2. 7个请求中,a、b、c被选取的顺序为a, b, a, c, a, b, a,分布均匀,权重大的后端a没有被连续选取。
3. 每经过7个请求后,a、b、c的current_weight又回到初始值{ 0, 0, 0 },因此上述流程是不断循环的。
这个平滑的加权轮询算法背后应该有数学论证,这里就不继续研究了:)
本模块的数据结构
ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t
表示一台后端服务器。peer就是对端,指的是上游服务器端。![]()
- struct ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_s {
- struct sockaddr *sockaddr; /* 后端服务器的地址 */
- socklen_t socklen; /* 地址的长度*/
- ngx_str_t name; /* 后端服务器地址的字符串,server.addrs[i].name */
- ngx_str_t server; /* server的名称,server.name */
- ngx_int_t current_weight; /* 当前的权重,动态调整,初始值为0 */
- ngx_int_t effective_weight; /* 有效的权重,会因为失败而降低 */
- ngx_int_t weight; /* 配置项指定的权重,固定值 */
- ngx_uint_t conns; /* 当前连接数 */
- ngx_uint_t fails; /* "一段时间内",已经失败的次数 */
- time_t accessed; /* 最近一次失败的时间点 */
- time_t checked; /* 用于检查是否超过了"一段时间" */
- ngx_uint_t max_fails; /* "一段时间内",最大的失败次数,固定值 */
- time_t fail_timeout; /* "一段时间"的值,固定值 */
- ngx_uint_t down; /* 服务器永久不可用的标志 */
- ...
- ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t *next; /* 指向下一个后端,用于构成链表 */
- ...
- } ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t;
ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t
表示一组后端服务器,比如一个后端集群。![]()
- struct ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_s {
- ngx_uint_t number; /* 后端服务器的数量 */
- ...
- ngx_uint_t total_weight; /* 所有后端服务器权重的累加值 */
- unsigned single:1; /* 是否只有一台后端服务器 */
- unsigned weighted:1; /* 是否使用权重 */
- ngx_str_t *name; /* upstream配置块的名称 */
- ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t *next; /* backup服务器集群 */
- ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t *peer; /* 后端服务器组成的链表 */
- };
ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_data_t
保存每个请求的负载均衡数据。![]()
- typedef struct {
- ngx_http_upstream_rr_peers_t *peers; /* 后端集群 */
- ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_t *current; /* 当前使用的后端服务器 */
- uintptr_t *tried; /* 指向后端服务器的位图 */
- uintptr_t data; /* 当后端服务器的数量较少时,用于存放其位图 */
- } ngx_http_upstream_rr_peer_data_t;
通用的数据结构
以下是所有负载均衡模块都会使用到的一些数据结构。
ngx_http_upstream_server_t
表示upstream配置块中的一条server指令。
- typedef struct {
- ngx_str_t name; /* 服务器的名称 */
- ngx_addr_t *addrs; /* 服务器地址的数组,因为同一个域名可能解析为多个IP */
- ngx_uint_t naddrs; /* 服务器地址数组的元素个数 */
- ngx_uint_t weight; /* 服务器的权重 */
- ngx_uint_t max_fails; /* 一段时间内,访问失败的次数超过此值,判定服务器不可用 */
- time_t fail_timeout; /* 上述“一段时间”的长度 */
- unsigned down:1; /* 服务器不可用的标志 */
- unsigned backup:1; /* 服务器为备用的标志 */
- } ngx_http_upstream_server_t;
server指令
Syntax: server address [parameters];
Context: upstream
Defines the address and other parameters of a server.
The address can be specified as domain name or IP address, with an optional port, or...
If a port is not specified, the port 80 is used. A domain name that resolves to serveral IP
addresses defines multiple servers at once.
server指令支持如下参数
weight = number
sets the weight of the server, by default 1.
max_fails = number
By default, the number of unsuccessful attempts is set to 1.
The zero value disables the accounting of attempts.
fail_timout = number
By default it is set to 10 seconds.
backup
marks the server as a backup server.
down
marks the server as permanently unavailable.
ngx_peer_connection_t
表示本机和后端的连接,也叫主动连接,用于upstream机制。
- struct ngx_peer_connection_s {
- ngx_connection_t *connection; /* 后端连接 */
- struct sockaddr *sockaddr; /* 后端服务器的地址 */
- socklen_t socklen; /* 后端服务器地址的长度 */
- ngx_str_t *name; /* 后端服务器的名称 */
- ngx_uint_t tries; /* 对于一个请求,允许尝试的后端服务器个数 */
- ngx_event_get_peer_pt get; /* 负载均衡模块实现,用于选取一个后端服务器 */
- ngx_event_free_peer_pt free; /* 负载均衡模块实现,用于释放一个后端服务器 */
- void *data; /* 请求的负载均衡数据,一般指向ngx_http_upstream_<name>_peer_data_t */
- ...
- ngx_addr_t *local; /* 本机地址 */
- int rcvbuf; /* 套接字接收缓冲区的大小 */
- ngx_log_t *log;
- unsigned cached:1;
- unsigned log_error:2;
- };
ngx_peer_connection_t *pc;
pc->get 就是负载均衡模块中,用于选取后端服务器的函数。
当选定一台后端服务器时,把它的地址信息保存在pc->sockaddr、pc->socklen、pc->name。
pc->tries表示对于一个请求,最多能尝试多少个后端。当尝试一个后端失败时,会调用pc->free,
一个主要目的就是更新pc->tries,比如pc->tries--。如果pc->tries降到0,就不再尝试了。
在请求的负载均衡数据初始化函数peer.init中,会给该请求创建一个ngx_http_upstream_<name>_peer_data_t实例,
用于保存该请求的负载均衡数据,pc->data就是该实例的地址。
ngx_http_upstream_peer_t
保存upstream块的数据,是负载均衡中一个很重要的结构体。
- typedef struct {
- /* upstream块的初始化函数,ngx_http_upstream_module创建main配置时调用。
- * 针对每个upstream块。
- */
- ngx_http_upstream_init_pt init_upstream;
- /* request在初始化upstream机制时调用,初始化该请求的负载均衡数据。
- * 针对每个request。
- */
- ngx_http_upstream_init_peer_pt init;
- void *data; /* 保存upstream块的数据 */
- } ngx_http_upstream_peer_t;
upstream块的数据,在解析配置文件时就创建和初始化了。
如果写了一个新的负载均衡模块,则需要在它的指令解析函数中指定init_upstream的值,
用来创建和初始化包含该指令的upstream配置块的数据。
ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t
ngx_http_upstream_module的server块。
- struct ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_s {
- ngx_http_upstream_peer_t peer; /* upstream块的数据 */
- void **srv_conf; /* 所有HTTP模块的server conf */
- ngx_array_t *server; /* upstream块的server数组,元素类型为ngx_http_upstream_server_t */
- ngx_uint_t flags; /* upstream块的server指令支持的参数 */
- ngx_str_t host; /* upstream块的名称 */
- u_char *file_name;
- ngx_uint_t line;
- in_port_t port; /* 使用的端口 */
- in_port_t default_port; /* 默认的端口 */
- ngx_uint_t no_port;
- ...
- };
- #define ngx_http_conf_upstream_srv_conf(uscf, module) uscf->srv_conf[module.ctx_index]
Reference
[1]. https://github.com/phusion/nginx/commit/27e94984486058d73157038f7950a0a36ecc6e35