[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)
引言
机器学习栏目记录我在学习Machine Learning过程的一些心得笔记,涵盖线性回归、逻辑回归、Softmax回归、神经网络和SVM等等,主要学习资料来自Standford Ag老师的教程,同时也查阅并参考了大量网上的相关资料(在后面列出)。
本文主要记录我在学习ICA(独立成分分析)过程中的心得笔记,对于ICA模型的理解和疑问,也纠正网络上一些Tutorial、资料和博文中的错误,欢迎大家一起讨论。
全文共分为两个部分:
ICA: Representation:ICA的模型描述;
ICA: Code:ICA的代码实现。
前言
本文主要介绍ICA的训练过程、代码以及实验结果(对应UFLDL的课后练习),源自于我在学习ICA过程中的笔记资料,包括了我个人对ICA模型的理解和代码实现,引用部分我都会标注出来,文章小节安排如下:
1)实验基础
2)实验结果
3)实验代码
4)参考资料
5)结语
关于ICA模型的基础知识可以参考:
[机器学习] 笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Representation)
实验基础
实验主要是基于UFLDL Tutorial中ICA部分的练习:Exercise:Independent Component Analysis,大家可以先参考该练习自己尝试完成实验。
实验数据:STL-10 dataset
通过使用近似值“平滑” L1 范数,将ICA模型如下,
标准正交ICA的目标函数:
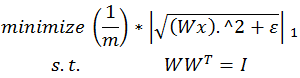
标准正交ICA的目标函数对W的梯度:
注意事项:
(1)基底线性独立
因为要学习到一组标准正交基,所以基向量的个数必须小于输入数据的维度。
(2)正交化
注意一点,正交化通过来完成,其实现为:
![]()
而不是
(3)白化
对于标准正交ICA,样本数据必须经过无正则 ZCA 白化,即 ε 设为 0。
(4)均值化
代价值和梯度必须除以样本数。
实验结果
(1)优化过程中采用Batch gradient descent,即梯度下降中利用全样本计算代价值及梯度
>>参数设置:
alpha = 0.5,iteration = 50000,miniBatchSize = all
>>迭代输出:
Iteration Cost time(s)
1000 0.599483 62.35046
2000 0.579602 158.1045
3000 0.567833 222.5326
4000 0.560265 287.4616
5000 0.554130 349.7853
……………………………………………………
16000 0.513359 1051.224
17000 0.511163 1115.36
18000 0.509213 1178.468
19000 0.507456 1242.144
20000 0.505815 1305.169
……………………………………………………
36000 0.493431 2337.619
37000 0.493253 2401.839
38000 0.493097 2466.276
39000 0.492961 2531.151
40000 0.492841 2594.416
……………………………………………………
46000 0.492322 2980.948
47000 0.492257 3044.261
48000 0.492197 3107.959
49000 0.492144 3172.782
50000 0.492096 3237.636
迭代次数=50000
(2)优化过程中采用Mini-Batch Gradient Descent,即梯度下降中利用随机小批量样本计算代价值及梯度
>>参数设置:
alpha = 0.5,iteration = 50000,miniBatchSize = 256
>>迭代输出:
Iteration Cost time(s)
1000 0.609892 4.643359
2000 0.587216 9.270881
3000 0.576038 13.96519
4000 0.550711 18.70056
5000 0.559629 23.6164
……………………………………………………
16000 0.454444 79.16564
17000 0.492942 84.36821
18000 0.491434 89.44777
19000 0.467292 94.3471
20000 0.496667 99.20195
……………………………………………………
26000 0.481736 138.9745
27000 0.508776 144.397
28000 0.462674 149.7803
29000 0.524727 155.0663
30000 0.480356 160.018
……………………………………………………
36000 0.500814 190.5871
37000 0.470674 195.8069
38000 0.481720 200.8657
39000 0.501621 205.682
40000 0.536511 210.5624
……………………………………………………
46000 0.478799 240.977
47000 0.487278 246.0048
48000 0.465347 250.7841
49000 0.493228 255.54
50000 0.495050 260.2548
>>可视化:
迭代次数=50000
>>分析
采用 Mini-Batch Gradient Descent 可以在保证训练效果的同时,显著加快训练速度。
采用Batch Gradient Descent和Mini-Batch Gradient Descent的最终效果对比如下:
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/584ee1f6ae654761be9ac218d3a728de.jpg)
(3)优化过程中采用Mini-Batch Gradient Descent,并设置 alpha = 16.0
>>参数设置:
alpha = 16,iteration = 10000,miniBatchSize = 256
>>迭代输出:
Iteration Cost time(s)
1000 0.512445 4.92836
2000 0.519963 9.913733
3000 0.508143 14.9235
4000 0.499603 19.89993
5000 0.488427 24.81049
6000 0.520706 29.91749
7000 0.489411 34.86197
8000 0.503602 39.87117
9000 0.507514 44.86402
10000 0.494073 49.80321
>>分析
可以发现,随着 alpha 的增大,收敛速度越快,当alpha=16.0,基本上迭代10000次就可以达到不错的效果。但另一方面,cost下降的就没有那么稳定了。
实验代码
在UFLDL - Exercise:Independent Component Analysis 基础上,我分别实现了Batch Gradient Descent和Mini-Batch Gradient Descent,并对参数 alpha 进行调整以实验不同参数下的训练情况。
需要重点说明的是,
第一,我在ICA优化过程中去除了线性搜索部分(代码中的while 1循环),因为我觉得这段线性搜索代码有些问题,因此非常容易陷入死循环。如果有朋友能理解这部分代码实现,务必请留言交流。
第二,在orthonormalICACost函数中添加了一个miniBatchSize参数,用于实现Mini-Batch Gradient Descent。
关于参数设置,
迭代次数 iteration 和 学习率 alpha 的设置对训练速度和效果有直接的影响,对于本文中实现的ICA算法,实验了下面几种设置,
1)alpha = 0.5,iteration = 10000, 20000, 50000
2)alpha = 1.0,iteration = 10000, 20000, 50000
3)alpha = 2.0,iteration = 10000, 20000, 50000
4)alpha = 4.0,iteration = 10000, 20000, 50000
5)alpha = 16.0,iteration = 10000, 20000, 50000
可以发现随着 alpha 的增大,收敛速度越快,基本上 (alpha = 16.0,iteration = 10000) 就可以达到 (alpha = 0.5,iteration = 50000) 的效果。
以下给出代码关键部分的实现:
ICAExercise.m
%% CS294A/CS294W Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Exercise
%% STEP 0: Initialization
numPatches = 20000;
numFeatures = 121;
imageChannels = 3;
patchDim = 8;
visibleSize = patchDim * patchDim * imageChannels;
miniBatchSize = 256;
% 说明:
% 如果采用Batch Gradient Descent,则另 miniBatchSize = numPatches
% 如果采用Mini-Batch Gradient Descent,则另 miniBatchSize = 随机采样值,例如 256。
%% STEP 1: Sample patches
%% STEP 2: ZCA whiten patches
%% STEP 3: ICA cost functions
% 说明:
% 这部分是 ICA cost function测试,测试通过后注释掉。
%% STEP 4: Optimization for orthonormal ICA
% 随机初始化W
weightMatrix = rand(numFeatures, visibleSize);
fprintf('%11s%16s%10s%12s\n','Iteration','Cost','t','time');
startTime = tic();
% Initialize some parameters for the backtracking line search
% 初始化参数设置
alpha = 0.5; % 0.5, 16.0
t = 0.02;
lastCost = 1e40;
% 梯度下降
[cost, grad] = orthonormalICACost(weightMatrix(:), visibleSize, numFeatures, patches, epsilon, miniBatchSize);
% Do 10000 iterations of gradient descent
for iteration = 1:50000
grad = reshape(grad, size(weightMatrix));
newCost = Inf;
linearDelta = sum(sum(grad .* grad));
% ===> 直接计算,去除线性搜索
% 梯度下降
considerWeightMatrix = weightMatrix - alpha * grad;
% 正交化
considerWeightMatrix = (considerWeightMatrix * considerWeightMatrix') ^ (-0.5) * considerWeightMatrix;
[newCost, newGrad] = orthonormalICACost(considerWeightMatrix(:), visibleSize, numFeatures, patches, epsilon, miniBatchSize);
% 更新参数矩阵(基底)
weightMatrix = considerWeightMatrix;
% ===> 线性搜索,确定最优的alpha。这段代码似乎有点问题,这里注释掉了。
%{
% Perform the backtracking line search
while 1
considerWeightMatrix = weightMatrix - alpha * grad;
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
% Instructions:
% Write code to project considerWeightMatrix back into the space
% of matrices satisfying WW^T = I.
%
% Once that is done, verify that your projection is correct by
% using the checking code below. After you have verified your
% code, comment out the checking code before running the
% optimization.
% Project considerWeightMatrix such that it satisfies WW^T = I
%error('Fill in the code for the projection here');
% 正交化
considerWeightMatrix = (considerWeightMatrix * considerWeightMatrix') ^ (-0.5) * considerWeightMatrix;
%{
% 正交化计算结果验证,完成后注释掉
% Verify that the projection is correct
temp = considerWeightMatrix * considerWeightMatrix';
temp = temp - eye(numFeatures);
assert(sum(temp(:).^2) < 1e-23, 'considerWeightMatrix does not satisfy WW^T = I. Check your projection again');
%error('Projection seems okay. Comment out verification code before running optimization.');
%}
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
[newCost, newGrad] = orthonormalICACost(considerWeightMatrix(:), visibleSize, numFeatures, patches, epsilon, miniBatchSize);
if newCost > lastCost - alpha * t * linearDelta
t = 0.9 * t;
else
break;
end
end
lastCost = newCost;
weightMatrix = considerWeightMatrix;
t = 1.1 * t;
%}
cost = newCost;
grad = newGrad;
% Visualize the learned bases as we go along
if mod(iteration, 1000) == 0
duration = toc(startTime);
fprintf(' %9d %14.6f %8.7g %10.7g\n', iteration, newCost, t, duration);
% Visualize the learned bases over time in different figures so
% we can get a feel for the slow rate of convergence
figure(floor(iteration / 1000));
displayColorNetwork(weightMatrix');
end
end
% 可视化
% Visualize the learned bases
displayColorNetwork(weightMatrix');
orthonormalICACost.m
function [cost, grad] = orthonormalICACost(theta, visibleSize, numFeatures, patches, epsilon, miniBatchSize)
%orthonormalICACost - compute the cost and gradients for orthonormal ICA
% (i.e. compute the cost ||Wx||_1 and its gradient)
weightMatrix = reshape(theta, numFeatures, visibleSize);
cost = 0;
grad = zeros(numFeatures, visibleSize);
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
% Instructions:
% Write code to compute the cost and gradient with respect to the
% weights given in weightMatrix.
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
% Random sampling
patches_rndIdx = randperm(size(patches, 2));
patches = patches(:, patches_rndIdx(1:miniBatchSize));
numExamples = miniBatchSize;
% Compute cost value
L1Matrix = sqrt((weightMatrix * patches).^2 + epsilon);
cost = sum(sum(L1Matrix)) / numExamples;
% Compute gradient
grad = weightMatrix * patches ./ L1Matrix * patches';
grad = grad(:) ./ numExamples;
end
参考资料
UFLDL Tutorial (new version)
http://ufldl.stanford.edu/tutorial/
UFLDL Tutorial (old version)
http://ufldl.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/UFLDL_Tutorial
Exercise:Independent Component Analysis
http://ufldl.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Exercise:Independent_Component_Analysis
Deep learning:三十九(ICA模型练习)
http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/05/07/3065953.html
结语
以上就是ICA模型的训练过程,包括实验代码以及实验结果,至此完成对ICA算法的初步学习,也将笔记资料写在这里与大家交流,谢谢!
本文的文字、公式和图形都是笔者根据所学所看的资料经过思考后认真整理和撰写编制的,如有朋友转载,希望可以注明出处:
[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)
http://blog.csdn.net/walilk/article/details/50471658
·
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/c8f934ae145a4f988b5fefad996c7585.png)
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/4e06917a10c640c9b11d55a19f58ef1f.png)
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/64bd69a16ad8446a9bdecaf116e450cb.png)
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/b14bd35c374b44e1ba61c8c56bfe7ee0.png)
![[机器学习] UFLDL笔记 - ICA(Independent Component Analysis)(Code)_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info5/c8f15fc1c89a4e9b80853e6eaff421a1.png)