KNN(K Nearest Neighbor)算法的MatLab实现
有关K近邻的文章有很多,也是非常简单但是又很实用的一种分类方法。
可以参考维基百科:点击打开链接
或者这篇博客:点击打开链接
代码实现:
function y = knn(X, X_train, y_train, K)
%KNN k-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm.
%
% INPUT: X: testing sample features, P-by-N_test matrix.
% X_train: training sample features, P-by-N matrix.
% y_train: training sample labels, 1-by-N row vector.
% K: the k in k-Nearest Neighbors
%
% OUTPUT: y : predicted labels, 1-by-N_test row vector.
%
% Author: Ren Kan
[~,N_test] = size(X);
predicted_label = zeros(1,N_test);
for i=1:N_test
[dists, neighbors] = top_K_neighbors(X_train,y_train,X(:,i),K);
% calculate the K nearest neighbors and the distances.
predicted_label(i) = recog(y_train(neighbors),max(y_train));
% recognize the label of the test vector.
end
y = predicted_label;
end
查找最近K近邻的部分代码:
function [dists,neighbors] = top_K_neighbors( X_train,y_train,X_test,K ) % Author: Ren Kan % Input: % X_test the test vector with P*1 % X_train and y_train are the train data set % K is the K neighbor parameter [~, N_train] = size(X_train); test_mat = repmat(X_test,1,N_train); dist_mat = (X_train-double(test_mat)) .^2; % The distance is the Euclid Distance. dist_array = sum(dist_mat); [dists, neighbors] = sort(dist_array); % The neighbors are the index of top K nearest points. dists = dists(1:K); neighbors = neighbors(1:K); end
利用概率求解测试集预测标签部分代码:
function result = recog( K_labels,class_num )
%RECOG Summary of this function goes here
% Author: Ren Kan
[~,K] = size(K_labels);
class_count = zeros(1,class_num+1);
for i=1:K
class_index = K_labels(i)+1; % +1 is to avoid the 0 index reference.
class_count(class_index) = class_count(class_index) + 1;
end
[~,result] = max(class_count);
result = result - 1; % Do not forget -1 !!!
end
应用可以有:
手写体识别、数字验证码识别等。
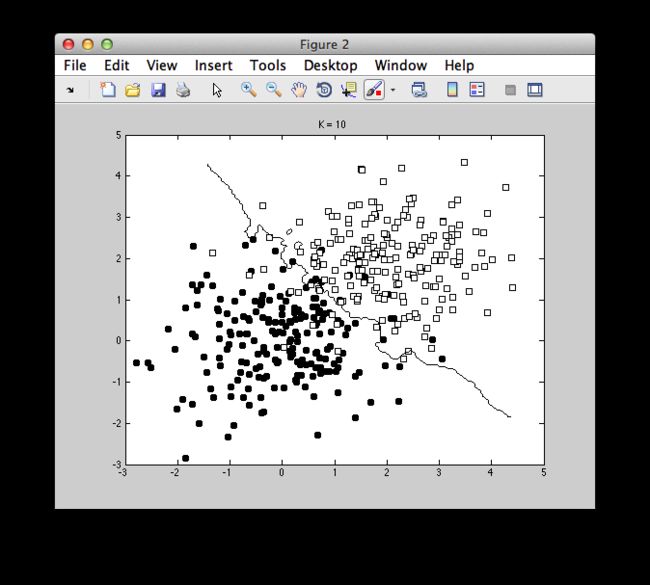
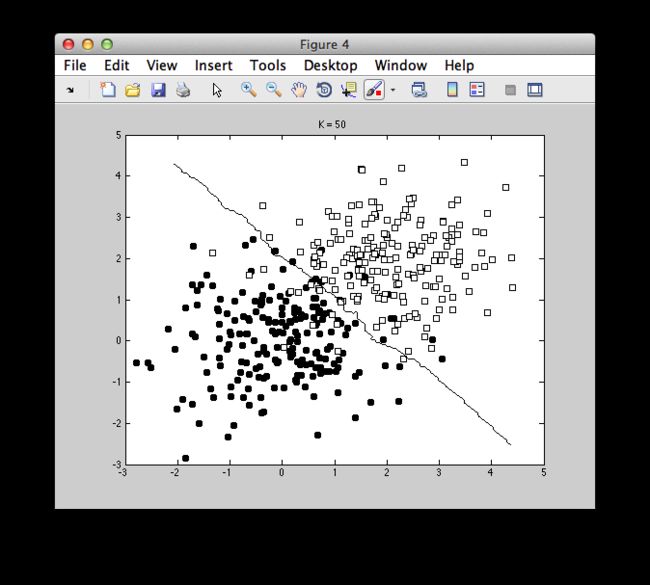
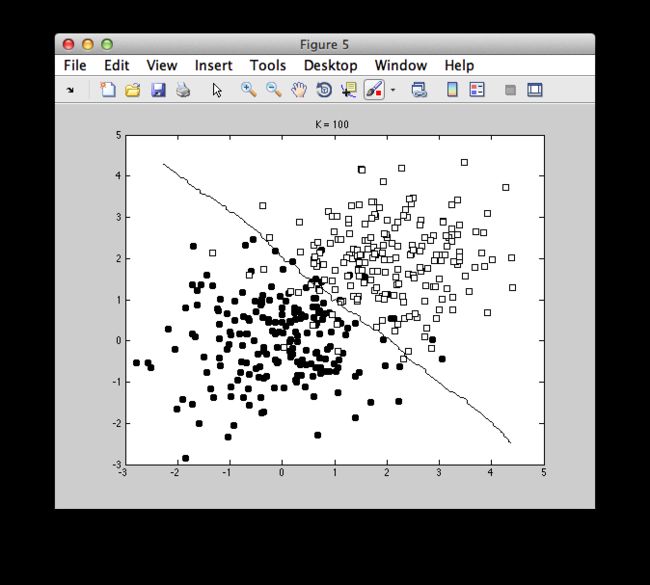
不同的K的取值对于分界面的选取有很大影响,结果如图: