PHP-关于模板的原理和解析
将PHP代码和静态HTML代码进行分离,使代码的可读性和维护性得到显著提高。
使用模板引擎:
我们所说的模板是Web模板,是主要由HTML标记组成的语言来编写的页面,但也有如何表示包含动态生成内容的方式(解析标签)。模板引擎是一种软件库,允许我们从模板生成HTML代码,并指定要包含的动态内容。
模板引擎的特点:
1.鼓励分离:让更个系统的可读性和维护性得到提高。
2.促进分工:使得程序员和美工去专心处理自己的设计。
3.比PHP更容易解析:编译文件和缓存文件加载更快、占资源更少。
4.增加安全性:可限制模板设计师进行不安全的操作的能力避免误删误访问等。
模板处理的流程图
创建模板:
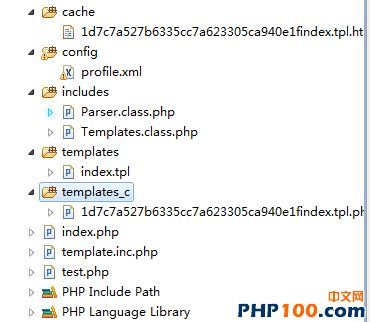
1、创建初始模板所需要的文件夹和文件。
a) index.php主文件,用于编写业务逻辑。
b) template.inc.php模板初始化文件,用于初始模版信息。
c) templates目录存放所有的模板文件。
d) templates_c目录存放所有编译文件。
e) cache目录存放所有缓存文件。
f) includes目录存放所有的类文件。
g) config目录存放模板系统变量配置文件。
以下是源码:
主文件 index.php
php //index.php
//设置编码为UTF-8
header('Content-Type:text/html;Charset=utf-8');
//网站根目录
define('ROOT_PATH', dirname(__FILE__));
//存放模板文件夹
define('TPL_DIR', ROOT_PATH.'/templates/');
//编译文件夹
define('TPL_C_DIR', ROOT_PATH.'/templates_c/');
//缓存文件夹
define('CACHE_DIR', ROOT_PATH.'/cache/');
//定义缓存状态
define('IS_CACHE',true);
//设置缓存状态开关
IS_CACHE ? ob_start() : null;
include ROOT_PATH.'/includes/Templates.class.php';
$_name = '方块李'; $array = array(1,2,3,4,5,6); $_tpl = new Templates(); $_tpl->assign('name', $_name); $_tpl->assign('a', 5>4); $_tpl->assign('array', $array); //显示 $_tpl->display('index.tpl'); ?>
模板文件 HTML
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
{include "test.php"}
{#}这是一条PHP的注释,在HTML页面里是不显示的,只会在生成的编译文件里显示{#}
我将被index.php导入
{$name}这个标签必须经过Parser.class.php这个解析类来解析它1
这里的内容改变了,为什么?
{if $a}
显示一号皮肤
{else}
显示二号皮肤
{/if}
{foreach $array(key,value)}
{/foreach}
|
模板类:
解析类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
|
//Parser.class.php
class
Parser {
//获取模板内容
private
$_tpl
;
//构造方法,初始化模板
public
function
__construct(
$_tplFile
){
//判断文件是否存在
if
(!
$this
->_tpl =
file_get_contents
(
$_tplFile
)){
exit
(
'ERROR:读取模板出错!'
);
}
}
//解析普通变量
private
function
parVar(){
$_pattern
=
'/\{\$([\w]+)\}/'
;
if
(preg_match(
$_pattern
,
$this
->_tpl)) {
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_pattern
,
"_vars['$1'] ?>"
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
}
//解析IF条件语句
private
function
parIf(){
//开头if模式
$_patternIf
=
'/\{if\s+\$([\w]+)\}/'
;
//结尾if模式
$_patternEnd
=
'/\{\/if\}/'
;
//else模式
$_patternElse
=
'/\{else\}/'
;
//判断if是否存在
if
(preg_match(
$_patternIf
,
$this
->_tpl)){
//判断是否有if结尾
if
(preg_match(
$_patternEnd
,
$this
->_tpl)){
//替换开头IF
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternIf
,
"_vars['$1']){ ?>"
,
$this
->_tpl);
//替换结尾IF
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternEnd
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
//判断是否有else
if
(preg_match(
$_patternElse
,
$this
->_tpl)){
//替换else
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternElse
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
}
else
{
exit
(
'ERROR:语句没有关闭!'
);
}
}
}
//解析foreach
private
function
parForeach(){
$_patternForeach
=
'/\{foreach\s+\$(\w+)\((\w+),(\w+)\)\}/'
;
$_patternEndForeach
=
'/\{\/foreach\}/'
;
//foreach里的值
$_patternVar
=
'/\{@(\w+)\}/'
;
//判断是否存在
if
(preg_match(
$_patternForeach
,
$this
->_tpl)){
//判断结束标志
if
(preg_match(
$_patternEndForeach
,
$this
->_tpl)){
//替换开头
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternForeach
,
"_vars['$1'] as \$$2=>\$$3){?>"
,
$this
->_tpl);
//替换结束
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternEndForeach
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
//替换值
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_patternVar
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
else
{
exit
(
'ERROR:Foreach语句没有关闭'
);
}
}
}
//解析include
private
function
parInclude(){
$_pattern
=
'/\{include\s+\"(.*)\"\}/'
;
if
(preg_match(
$_pattern
,
$this
->_tpl,
$_file
)){
//判断头文件是否存在
if
(!
file_exists
(
$_file
[1]) ||
empty
(
$_file
[1])){
exit
(
'ERROR:包含文件不存在!'
);
}
//替换内容
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_pattern
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
}
//解析系统变量
private
function
configVar(){
$_pattern
=
'//'
;
if
(preg_match(
$_pattern
,
$this
->_tpl,
$_file
)){
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_pattern
,
"_config['$1'] ?>"
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
}
//解析单行PHP注释
private
function
parCommon(){
$_pattern
=
'/\{#\}(.*)\{#\}/'
;
if
(preg_match(
$_pattern
,
$this
->_tpl)){
$this
->_tpl = preg_replace(
$_pattern
,
""
,
$this
->_tpl);
}
}
//生成编译文件
public
function
compile(
$_parFile
){
//解析模板变量
$this
->parVar();
//解析IF
$this
->parIf();
//解析注释
$this
->parCommon();
//解析Foreach
$this
->parForeach();
//解析include
$this
->parInclude();
//解析系统变量
$this
->configVar();
//生成编译文件
if
(!
file_put_contents
(
$_parFile
,
$this
->_tpl)){
exit
(
'ERROR:编译文件生成失败!'
);
}
}
}
|
总结:模板引擎的整个过程:
1、当浏览器请求index.php文件时,实例化模板类对像 $_tpl = new Templates();
2、当Templates实例化的时候,生成两个数组,一个用来存放模板变量,另一个存放系统变量,通过构造方法,判断文件夹是否存在,同时通过XML文件将系统变量数组初始化
3、通过模板类Templates的注入方法,assign(),将对应模板index.tpl中变量的index.php的内容注入到模板类的私有变量,完成初始化
4、模板类Templates类显示方法display() 通过实例化解析类Parser,将取到的注入变量通过解析类进行解析(即替换)
5、解析(替换)后,将文件写入PHP、HTML混全文件
6、通过Templates类的显示方法将文件输出:
1、第一次执行显示方法时,将会把PHP、HTML混合文件,生成纯静态的缓存文件
2、调用缓存文件,显示页面
3、当浏览器再次调用显示方法时,首先根据各文件的最后修改时间,判断是否重新生成缓存文件或直接调用已存在的缓存文件
重点:
1、通过正则表达式进行字符串的替换
2、熟悉OOP