Po一道有意思的题
今天朋友做一家公司发过来的Codility上面的题,有一道小题虽然简单但还蛮好玩的,网上很少碰到类似的题目,记录下来。
A non-empty zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers is given. The array consists only of integers in the range [0..N−1]. Each element of the array can be treated as a pointer to another element of the array: if A[K] = M then element A[K] points to A[M].
The array defines a sequence of jumps of a pawn as follows:
- initially, the pawn is located at position 0;
- on each jump the pawn moves from its current position K to A[K];
- the pawn jumps forever.
Since the number of possible positions of the pawn is finite, eventually, after some initial sequence of jumps, the pawn enters a cycle. Compute the length of this cycle.
For example, for the following array A:
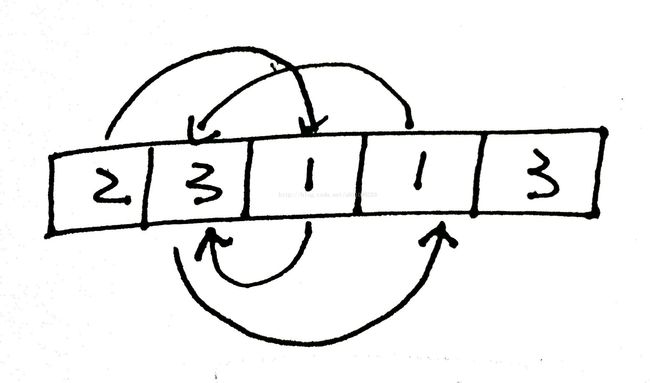
A[0] = 2 A[1] = 3 A[2] = 1 A[3] = 1 A[4] = 3
consecutive positions of the pawn are: 0, 2, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, ..., and the length of the cycle is 2.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [1..200,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..N−1].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N);
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(1), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
Elements of input arrays can be modified.
画个图理解一下这道题什么意思:
假设数组的长度为N,数组里数字的范围为[0,N-1],(不会跳出数组),从第0位开始,里面存的是2,那下一次跳到第2位,里面存的是1,跳到第一位.... 以此类推,因为数组里存的数字有范围并且是有限的,若干步骤之后,会出现一定规律的循环,比如上面这个例子,0, 2, 1, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, ..., 最终以1,3开始循环,循环长度为2. 求给定任意数组后的循环长度。
要求:
Time Complexity O(n)
Space Complexity O(1)
这道题初看非常简单,不过有O(1) Space的要求,我们先简化一下,假设没有Space的限制。
如果没这个要求我们怎么做呢?我们可以建一个HashMap存访问到数组里index的次序,然后发现相同后,用现在的Count值减去当初的次序就可以。
public class JumpAcrossArray {
public int findloop (int[] arr){
java.util.HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new java.util.HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
int num = 1;
int k = 0;
while (true){
if (!map.containsKey(k)){
map.put(k, num++);
k = arr[k];
}
else break;
}
return num - map.get(k);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
JumpAcrossArray jump = new JumpAcrossArray();
int[] arr = new int[]{2,3,1,1,3};
int length = jump.findloop(arr);
System.out.println("The Loop Length of {2,3,1,1,3} is --->" + length);
arr = new int[]{1,2,0};
length = jump.findloop(arr);
System.out.println("The Loop Length of {1,2,0} is --->" + length);
}
}
那好,现在的要求不能用额外的Array, ArrayList, HashMap那么我们怎么做呢。我当时想了一会儿,发现数组的范围是[0,N-1],而且题目中最后一行有一个重大的提示,Elements of input arrays can be modified. 于是乎想出了下面的方法。
先不看下面的提示,你自己想想试试看
分割线--------------------------------------------------------------
那么好,我们能用HashMap做出来的最重要的原因就是我们存进了数组访问的index,和访问到的顺序。
如果不用HashMap,我们能不能改变数组的值来表示这个元素访问过了,并且我知道这个元素是第几次访问到的。
那么就很直观了,我们将第一次访问到的元素置为-1, 第二次访问到的元素置为-2。。。 以此类推,当我们发现下一个要访问的元素小于0的时候,那么说明我们访问过这个元素了,并且这个元素恰恰也是Loop的起始点,并且这个位置存的值是我们之前访问到它的次序,我们只要用现在的次序减去之前的次序即可得到Loop的长度。
public class JumpAcrossArray {
public int findloopConSpace(int[] arr){
int cur = 0;
int num = -1;
while(true){
if (arr[cur]<0) break;
int next = arr[cur];
arr[cur] = num--;
cur = next;
}
return Math.abs(num) - Math.abs(arr[cur]);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
JumpAcrossArray jump = new JumpAcrossArray();
int[] arr = new int[]{2,3,1,1,3};
int length = jump.findloopConSpace(arr);
System.out.println("The Loop Length of {2,3,1,1,3} is --->" + length);
arr = new int[]{1,2,0};
length = jump.findloopConSpace(arr);
System.out.println("The Loop Length of {1,2,0} is --->" + length);
}
}