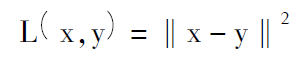Autoencoder
自动编码器 AutoEncoder)是一种单隐层无监督学习神经网络,网络结构如下图
多层AE堆叠可以得到深度自动编码器(DAE) 。DAE 的产生和应用免去了人工提取数据特征的巨大工作量,提高了特征提取的效率,降低了原始输入的维数,得到数据的逆向映射特征,展现了从少数类标样本和大量无类标数据中学习输入数据本质特征的强大能力,并将学习到的特征分层表示,为构建深度结构奠定了基础,成为神经网络研究的一个里程碑。
AE原理
输入d维向量x,在输入和隐层之间网络把x映射到d'维向量y
![]() (1)
(1)
s是编码器激活函数,例如sigmoid函数。
然后从隐层到输出层,网络把y映射回到d维空间,要求z与x尽可能的相似,从而完成重建
![]()
s是解码器激活函数,例如sigmoid函数。如果限定W'是W的转置,这叫tied weights,当然这是可选的。
如果没有选用tied weights,网络就需要训练W,W',b,b'四个参数,使得重建的误差最小。
重构误差可用平方误差函数或交叉熵损失函数,二者分别表示为:
其中,平方误差用于线性解码函数s,交叉熵损失函数用于 sigmoid。
参数的训练用梯度下降法。
"""
This tutorial introduces denoising auto-encoders (dA) using Theano.
Denoising autoencoders are the building blocks for SdA.
They are based on auto-encoders as the ones used in Bengio et al. 2007.
An autoencoder takes an input x and first maps it to a hidden representation
y = f_{\theta}(x) = s(Wx+b), parameterized by \theta={W,b}. The resulting
latent representation y is then mapped back to a "reconstructed" vector
z \in [0,1]^d in input space z = g_{\theta'}(y) = s(W'y + b'). The weight
matrix W' can optionally be constrained such that W' = W^T, in which case
the autoencoder is said to have tied weights. The network is trained such
that to minimize the reconstruction error (the error between x and z).
For the denosing autoencoder, during training, first x is corrupted into
\tilde{x}, where \tilde{x} is a partially destroyed version of x by means
of a stochastic mapping. Afterwards y is computed as before (using
\tilde{x}), y = s(W\tilde{x} + b) and z as s(W'y + b'). The reconstruction
error is now measured between z and the uncorrupted input x, which is
computed as the cross-entropy :
- \sum_{k=1}^d[ x_k \log z_k + (1-x_k) \log( 1-z_k)]
References :
- P. Vincent, H. Larochelle, Y. Bengio, P.A. Manzagol: Extracting and
Composing Robust Features with Denoising Autoencoders, ICML'08, 1096-1103,
2008
- Y. Bengio, P. Lamblin, D. Popovici, H. Larochelle: Greedy Layer-Wise
Training of Deep Networks, Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems 19, 2007
"""
import os
import sys
import time
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.shared_randomstreams import RandomStreams
from logistic_sgd import load_data
from utils import tile_raster_images
try:
import PIL.Image as Image
except ImportError:
import Image
class dA(object):
"""Denoising Auto-Encoder class (dA)
A denoising autoencoders tries to reconstruct the input from a corrupted
version of it by projecting it first in a latent space and reprojecting
it afterwards back in the input space. Please refer to Vincent et al.,2008
for more details. If x is the input then equation (1) computes a partially
destroyed version of x by means of a stochastic mapping q_D. Equation (2)
computes the projection of the input into the latent space. Equation (3)
computes the reconstruction of the input, while equation (4) computes the
reconstruction error.
.. math::
\tilde{x} ~ q_D(\tilde{x}|x) (1)
y = s(W \tilde{x} + b) (2)
x = s(W' y + b') (3)
L(x,z) = -sum_{k=1}^d [x_k \log z_k + (1-x_k) \log( 1-z_k)] (4)
"""
def __init__(
self,
numpy_rng,
theano_rng=None,
input=None,
n_visible=784,
n_hidden=500,
W=None,
bhid=None,
bvis=None
):
"""
Initialize the dA class by specifying the number of visible units (the
dimension d of the input ), the number of hidden units ( the dimension
d' of the latent or hidden space ) and the corruption level. The
constructor also receives symbolic variables for the input, weights and
bias. Such a symbolic variables are useful when, for example the input
is the result of some computations, or when weights are shared between
the dA and an MLP layer. When dealing with SdAs this always happens,
the dA on layer 2 gets as input the output of the dA on layer 1,
and the weights of the dA are used in the second stage of training
to construct an MLP.
:type numpy_rng: numpy.random.RandomState
:param numpy_rng: number random generator used to generate weights
:type theano_rng: theano.tensor.shared_randomstreams.RandomStreams
:param theano_rng: Theano random generator; if None is given one is
generated based on a seed drawn from `rng`
:type input: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param input: a symbolic description of the input or None for
standalone dA
:type n_visible: int
:param n_visible: number of visible units
:type n_hidden: int
:param n_hidden: number of hidden units
:type W: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param W: Theano variable pointing to a set of weights that should be
shared belong the dA and another architecture; if dA should
be standalone set this to None
:type bhid: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param bhid: Theano variable pointing to a set of biases values (for
hidden units) that should be shared belong dA and another
architecture; if dA should be standalone set this to None
:type bvis: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param bvis: Theano variable pointing to a set of biases values (for
visible units) that should be shared belong dA and another
architecture; if dA should be standalone set this to None
"""
self.n_visible = n_visible
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
# create a Theano random generator that gives symbolic random values
if not theano_rng:
theano_rng = RandomStreams(numpy_rng.randint(2 ** 30))
# note : W' was written as `W_prime` and b' as `b_prime`
if not W:
# W is initialized with `initial_W` which is uniformely sampled
# from -4*sqrt(6./(n_visible+n_hidden)) and
# 4*sqrt(6./(n_hidden+n_visible))the output of uniform if
# converted using asarray to dtype
# theano.config.floatX so that the code is runable on GPU
initial_W = numpy.asarray(
numpy_rng.uniform(
low=-4 * numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_hidden + n_visible)),
high=4 * numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_hidden + n_visible)),
size=(n_visible, n_hidden)
),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
)
W = theano.shared(value=initial_W, name='W', borrow=True)
if not bvis:
bvis = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
n_visible,
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
borrow=True
)
if not bhid:
bhid = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
n_hidden,
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='b',
borrow=True
)
self.W = W
# b corresponds to the bias of the hidden
self.b = bhid
# b_prime corresponds to the bias of the visible
self.b_prime = bvis
# tied weights, therefore W_prime is W transpose
self.W_prime = self.W.T
self.theano_rng = theano_rng
# if no input is given, generate a variable representing the input
if input is None:
# we use a matrix because we expect a minibatch of several
# examples, each example being a row
self.x = T.dmatrix(name='input')
else:
self.x = input
self.params = [self.W, self.b, self.b_prime]
def get_corrupted_input(self, input, corruption_level):
"""This function keeps ``1-corruption_level`` entries of the inputs the
same and zero-out randomly selected subset of size ``coruption_level``
Note : first argument of theano.rng.binomial is the shape(size) of
random numbers that it should produce
second argument is the number of trials
third argument is the probability of success of any trial
this will produce an array of 0s and 1s where 1 has a
probability of 1 - ``corruption_level`` and 0 with
``corruption_level``
The binomial function return int64 data type by
default. int64 multiplicated by the input
type(floatX) always return float64. To keep all data
in floatX when floatX is float32, we set the dtype of
the binomial to floatX. As in our case the value of
the binomial is always 0 or 1, this don't change the
result. This is needed to allow the gpu to work
correctly as it only support float32 for now.
"""
return self.theano_rng.binomial(size=input.shape, n=1,
p=1 - corruption_level,
dtype=theano.config.floatX) * input
def get_hidden_values(self, input):
""" Computes the values of the hidden layer """
return T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)
def get_reconstructed_input(self, hidden):
"""Computes the reconstructed input given the values of the
hidden layer
"""
return T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(hidden, self.W_prime) + self.b_prime)
def get_cost_updates(self, corruption_level, learning_rate):
""" This function computes the cost and the updates for one trainng
step of the dA """
tilde_x = self.get_corrupted_input(self.x, corruption_level)
y = self.get_hidden_values(tilde_x)
z = self.get_reconstructed_input(y)
# note : we sum over the size of a datapoint; if we are using
# minibatches, L will be a vector, with one entry per
# example in minibatch
L = - T.sum(self.x * T.log(z) + (1 - self.x) * T.log(1 - z), axis=1)
# note : L is now a vector, where each element is the
# cross-entropy cost of the reconstruction of the
# corresponding example of the minibatch. We need to
# compute the average of all these to get the cost of
# the minibatch
cost = T.mean(L)
# compute the gradients of the cost of the `dA` with respect
# to its parameters
gparams = T.grad(cost, self.params)
# generate the list of updates
updates = [
(param, param - learning_rate * gparam)
for param, gparam in zip(self.params, gparams)
]
return (cost, updates)
def test_dA(learning_rate=0.1, training_epochs=15,
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz',
batch_size=20, output_folder='dA_plots'):
"""
This demo is tested on MNIST
:type learning_rate: float
:param learning_rate: learning rate used for training the DeNosing
AutoEncoder
:type training_epochs: int
:param training_epochs: number of epochs used for training
:type dataset: string
:param dataset: path to the picked dataset
"""
datasets = load_data(dataset)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
# compute number of minibatches for training, validation and testing
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
# start-snippet-2
# allocate symbolic variables for the data
index = T.lscalar() # index to a [mini]batch
x = T.matrix('x') # the data is presented as rasterized images
# end-snippet-2
if not os.path.isdir(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
os.chdir(output_folder)
####################################
# BUILDING THE MODEL NO CORRUPTION #
####################################
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(123)
theano_rng = RandomStreams(rng.randint(2 ** 30))
da = dA(
numpy_rng=rng,
theano_rng=theano_rng,
input=x,
n_visible=28 * 28,
n_hidden=500
)
cost, updates = da.get_cost_updates(
corruption_level=0.,
learning_rate=learning_rate
)
train_da = theano.function(
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
start_time = time.clock()
############
# TRAINING #
############
# go through training epochs
for epoch in xrange(training_epochs):
# go through trainng set
c = []
for batch_index in xrange(n_train_batches):
c.append(train_da(batch_index))
print 'Training epoch %d, cost ' % epoch, numpy.mean(c)
end_time = time.clock()
training_time = (end_time - start_time)
print >> sys.stderr, ('The no corruption code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % ((training_time) / 60.))
image = Image.fromarray(
tile_raster_images(X=da.W.get_value(borrow=True).T,
img_shape=(28, 28), tile_shape=(10, 10),
tile_spacing=(1, 1)))
image.save('filters_corruption_0.png')
# start-snippet-3
#####################################
# BUILDING THE MODEL CORRUPTION 30% #
#####################################
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(123)
theano_rng = RandomStreams(rng.randint(2 ** 30))
da = dA(
numpy_rng=rng,
theano_rng=theano_rng,
input=x,
n_visible=28 * 28,
n_hidden=500
)
cost, updates = da.get_cost_updates(
corruption_level=0.3,
learning_rate=learning_rate
)
train_da = theano.function(
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
start_time = time.clock()
############
# TRAINING #
############
# go through training epochs
for epoch in xrange(training_epochs):
# go through trainng set
c = []
for batch_index in xrange(n_train_batches):
c.append(train_da(batch_index))
print 'Training epoch %d, cost ' % epoch, numpy.mean(c)
end_time = time.clock()
training_time = (end_time - start_time)
print >> sys.stderr, ('The 30% corruption code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % (training_time / 60.))
# end-snippet-3
# start-snippet-4
image = Image.fromarray(tile_raster_images(
X=da.W.get_value(borrow=True).T,
img_shape=(28, 28), tile_shape=(10, 10),
tile_spacing=(1, 1)))
image.save('filters_corruption_30.png')
# end-snippet-4
os.chdir('../')
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_dA()
稀疏自动编码器
对学习的参数加入稀疏性限制
降噪自动编码器
输入数据中添加腐坏向量,防止出现过拟合现象
收缩自动编码器
卷积自动编码器
用于构建卷积神经网络
DAE 的构建
DAE的核心是先用无监督逐层贪心训练算法完成对隐含层的预训练,然后用BP算法对整个神经网络进行系统性参数优化调整,显著降低了神经网络的性能指数,有效改善了BP算法易陷入局部最小的不良状况。
简单来说,逐层贪婪算法的主要思路是每次只训练网络中的一层,即首先训练一个只含一个隐藏层的网络,仅当这层网络训练结束之后才开始训练一个有两个隐藏层的网络,以此类推。在每一步中,把已经训练好的前k -1 层
固定,然后增加第k 层(也就是将已经训练好的前k -1 的输出作为输入)。
DAE 的预训练
预训练的目的是将所有权值链接和偏置限定在一定的参数空间内,防止随机初始化的发生进而降低每个隐含层的品质因数,便于对整个神经网络进行系统性参数优化,该算法的核心是用无监督的方法将DAE 的输入层和隐含层全部初始化,然后再用逐层贪心训练算法将每个隐含层训练为自动关联器,实现输入数据的重构,其基本步骤可总结如下:1)以无监督的方式训练神经网络的第一层,将其输出(注意,是公式(1)里的y)作为原始输入的最小化重构误差;
2)每个隐含单元的输出作为下一层神经网络的输入,用无类标数据样本对下一层进行训练,将误差控制在一定范围内;
3)重复步骤2),直到完成规定数量隐含层的训练为止;
4)将最后一个隐含层的输出作为有监督层的输入,并且初始化有监督层的参数
DAE 的精雕
精雕又叫微调,是构建DAE 的必要步骤,通常采用BP 算法来完成这一任务(牛顿法、共轭梯度法、MOBP 和SDBP 等,BP 算法的变形也可用于精雕)。精雕的核心思想是将自动编码器的输入层、输
出层和所有隐含层视为一个整体,用有监督学习算法进一步调整经过预训练的神经网络,经过多次迭代后,所有权值及偏置均能被优化。由于最后一个隐含层只能输出原始数据的重构,因而不具有分类识别功能。为了让DAE 具有分类识别的功能,需要在完成精雕的神经网络的输出层之后加入softmax分类器,将整个神经网络训练成能完成分层特征提取和数据分类任务的多重感知器。其基本步骤可总结如下:
1)对权值、偏置和阈值赋值,对网络进行初始化;
2)随机选取类标数据样本用BP 算法对神经网络进行训练,计算各层的输出;
3)求出各层的重构误差,并根据误差修正权值和偏置;
4)根据性能指数判定误差是否满足要求,如果未能满足要求则重复步骤2)和3),直到整个网络输出满足期望 要求。