Android之Fragment的基本使用(一)
一、前言
一个新的东西肯定会问是什么,为什么?
何为Fragment?Android是在Android 3.0 (API level 11)开始引入Fragment的。其实可以把Fragment想成Activity中的模块,这个模块有自己的布局,有自己的生命周期,单独处理自己的输入,在Activity运行的时候可以加载或者移除Fragment模块。
为什么要设计Fragment?个人理解主要是为了解决应用程序对于手机、平板这样不同屏幕大小所造成的适配问题,以前对于这个问题的做法在很多情况下,都是先针对手机开发一套App,然后拷贝一份,修改布局以适应平板之类的大屏;同时因为Fragment有着自己的布局和生命周期,所以可以很好的利用这一点实现灵活的布局,改善用户体验。
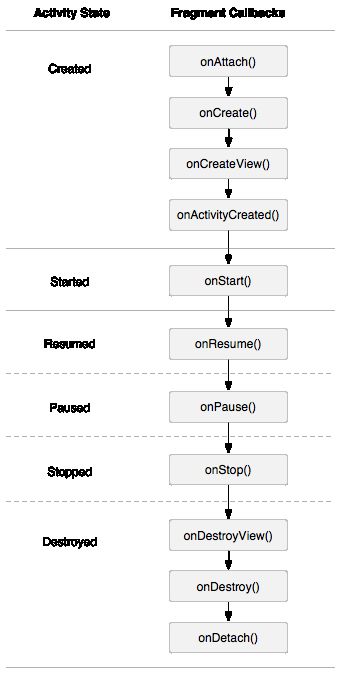
二、Fragment生命周期
一张图搞定,和Activity类似
可以看到Fragment比Activity多了几个额外的生命周期回调方法:
onAttach(Activity)
当Fragment与Activity发生关联时调用。
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup,Bundle)
创建该Fragment的视图
onActivityCreated(Bundle)
当Activity的onCreate方法返回时调用
onDestoryView()
与onCreateView想对应,当该Fragment的视图被移除时调用
onDetach()
与onAttach相对应,当Fragment与Activity关联被取消时调用
注意:除了onCreateView,其他的所有方法如果你重写了,必须调用父类对于该方法的实现。
三、Fragment的基本使用
这里有两种使用方式:静态使用和动态使用
1.静态的使用Fragment(通过Activity的布局文件将Fragment加入Activity,根据就是把它当作一个控件来直接使用。)
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/id_fragment_content"
android:name="com.hiwhitley.fragment.ShowFragment"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</RelativeLayout>frament_content.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="静态使用Fragment"
android:textSize="25sp"
/>
</LinearLayout>ShowFragment.class
重写onCreateView()
package com.hiwhitley.fragment;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class ShowFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_content, container, false);
}
}
MainActivity.class
package com.hiwhitley.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
2.动态的使用Fragment
使用FragmentManager对Fragment进行了动态的加载。
注意:如果使用Android3.0以下的版本,需要引入v4的包,然后Activity继承FragmentActivity,然后通过getSupportFragmentManager获得FragmentManager。不过还是建议版Menifest文件的uses-sdk的minSdkVersion和targetSdkVersion都改为11以上,这样就不必引入v4包了。
只有MainActivity.class和activity_main.xml和上面不一样
package com.hiwhitley.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.beginTransaction();
ShowFragment showFragment = new ShowFragment();
transaction.add(R.id.id_content, showFragment);
transaction.commit();
}
}
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
</FrameLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
四、Fragment中常用的API
1、获取FragmentManage的方式:
getFragmentManager() // v4中,getSupportFragmentManager,前面有讲过
2、主要的操作都是FragmentTransaction的方法
FragmentTransaction transaction = fm.benginTransatcion();//开启一个事务
transaction.add()
往Activity中添加一个Fragment
transaction.remove()
从Activity中移除一个Fragment,如果被移除的Fragment没有添加到回退栈,这个Fragment实例将会被销毁。
transaction.replace()
使用另一个Fragment替换当前的,实际上就是remove()然后add()的合体~
transaction.hide()
隐藏当前的Fragment,仅仅是设为不可见,并不会销毁
transaction.show()
显示之前隐藏的Fragment
detach()
会将view从UI中移除,和remove()不同,此时fragment的状态依然由FragmentManager维护。
attach()
重建view视图,附加到UI上并显示。
transatcion.commit()//提交一个事务
五、源码