HDOJ 1054 —— 最小点覆盖
Strategic Game
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 4073 Accepted Submission(s): 1801
Problem Description
Bob enjoys playing computer games, especially strategic games, but sometimes he cannot find the solution fast enough and then he is very sad. Now he has the following problem. He must defend a medieval city, the roads of which form a tree. He has to put the minimum number of soldiers on the nodes so that they can observe all the edges. Can you help him?
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
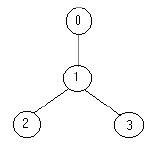
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:

the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Sample Input
4 0:(1) 1 1:(2) 2 3 2:(0) 3:(0) 5 3:(3) 1 4 2 1:(1) 0 2:(0) 0:(0) 4:(0)
Sample Output
1 2
Source
Southeastern Europe 2000
Recommend
JGShining | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1068 1150 1151 1281 1142
题意是让你用最小的点覆盖所有边。
最小点覆盖的模版题,转化为求二分图最大匹配。
/*
ID: xinming2
PROG: stall4
LANG: C++
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <cctype>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <utility>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
///#define Online_Judge
#define outstars cout << "***********************" << endl;
#define clr(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define lson l , mid , rt << 1
#define rson mid + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
#define mk make_pair
#define FOR(i , x , n) for(int i = (x) ; i < (n) ; i++)
#define FORR(i , x , n) for(int i = (x) ; i <= (n) ; i++)
#define REP(i , x , n) for(int i = (x) ; i > (n) ; i--)
#define REPP(i ,x , n) for(int i = (x) ; i >= (n) ; i--)
const int MAXN = 1500 + 5;
const int sigma_size = 26;
const long long LLMAX = 0x7fffffffffffffffLL;
const long long LLMIN = 0x8000000000000000LL;
const int INF = 0x7f7f7f7f;
const int IMIN = 0x80000000;
#define eps 1e-8
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
typedef long long LL;
const LL MOD = 1000000007LL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
typedef pair<int , int> pi;
#define Bug(s) cout << "s = " << s << endl;
///#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
int V;
vector<int>G[MAXN];
int match[MAXN];
bool used[MAXN];
void add_edge(int u , int v)
{
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
bool dfs(int v)
{
used[v] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < G[v].size() ; i++)
{
int u = G[v][i] , w = match[u];
if(w < 0 || !used[w] && dfs(w))
{
match[u] = v;
match[v] = u;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int bipartite_matching()
{
int res = 0;
memset(match , -1 , sizeof(match));
for(int v = 0 ; v < V ; v++)
{
if(match[v] < 0)
{
memset(used , 0 , sizeof(used));
if(dfs(v))res++;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n , k;
while(~scanf("%d" , &n))
{
for(int i = 0 ; i <= MAXN ; i++)G[i].clear();
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
int u , k ,v;
scanf("%d:(%d)" , &u , &k);
// outstars
while(k--)
{
scanf("%d" , &v);
add_edge(u , v);
}
}
// outstars
V = n;
printf("%d\n" , bipartite_matching());
}
return 0;
}