STL源码剖析—list
相较于vector的连续线性空间,list就显得复杂许多,它的好处是每次插入或删除一个元素,就配置或释放一个元素空间。因此,list对于空间的运用有绝对的精准,一点也不浪费。而且,对于任何位置的元素插入或元素移除,list永远是常数时间。
list不仅是一个双向链表,而且还是一个环状双向链表。另外,还有一个重要性质,插入操作和接合操作都不会造成原有的list迭代器失效,这在vector是不成立的。因为vector的插入操作可能造成记忆体重新配置,导致原有的迭代器全部失效。甚至list的元素删除操作(erase),也只有“指向被删除元素”的那个迭代器失效,其他迭代器不受任何影响。
以下是list的节点的结构:
template <class T>
struct __list_node
{
typedef void* void_pointer;
void_pointer next;
void_pointer prev;
T data;
}; 已下是迭代器数据结构设计以及list的源码剖析
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; // STL标准强制要求
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
link_type node; //迭代器内部当然要有一个普通指针,指向list的节点
__list_iterator(link_type x) : node(x) {}
__list_iterator() {}
__list_iterator(const iterator& x) : node(x.node) {}
// 在STL算法中需要迭代器提供支持
bool operator==(const self& x) const { return node == x.node; }
bool operator!=(const self& x) const { return node != x.node; }
// 以下对迭代器取值(dereference),取的是节点的数据值
reference operator*() const { return (*node).data; }
// 以下是迭代器的成员存取运算子的标准做法
pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
// 前缀自加,对迭代器累加1,就是前进一个节点
self& operator++()
{
node = (link_type)((*node).next);
return *this;
}
// 后缀自加, 需要先产生自身的一个副本, 然会再对自身操作, 最后返回副本
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
// 前缀自减
self& operator--()
{
node = (link_type)((*node).prev);
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
--*this;
return tmp;
}
}; list的数据结构
// 默认allocator为alloc, 其具体使用版本请参照<stl_alloc.h>
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list
{
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __list_node<T> list_node;
// 专属之空间配置器,每次配置一个节点大小
typedef simple_alloc<list_node, Alloc> list_node_allocator;
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef list_node* link_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
protected:
link_type node ; // 只要一个指针,便可表示整个环状双向链表
// 分配一个新结点, 注意这里并不进行构造,
// 构造交给全局的construct, 见<stl_stl_uninitialized.h>
link_type get_node() { return list_node_allocator::allocate(); }
// 释放指定结点, 不进行析构, 析构交给全局的destroy
void put_node(link_type p) { list_node_allocator::deallocate(p); }
// 产生(配置并构造)一个节点, 首先分配内存, 然后进行构造
// 注: commit or rollback
link_type create_node(const T& x)
{
link_type p = get_node();
construct(&p->data, x);
return p;
}
// 析构结点元素, 并释放内存
void destroy_node(link_type p)
{
destroy(&p->data);
put_node(p);
}
protected:
// 用于空链表的建立
void empty_initialize()
{
node = get_node(); // 配置一个节点空间,令node指向它
node->next = node; // 令node头尾都指向自己,不设元素值
node->prev = node;
}
// 创建值为value共n个结点的链表
// 注: commit or rollback
void fill_initialize(size_type n, const T& value)
{
empty_initialize();
__STL_TRY
{
// 此处插入操作时间复杂度O(1)
insert(begin(), n, value);
}
__STL_UNWIND(clear(); put_node(node));
}
public:
list() { empty_initialize(); }
iterator begin() { return (link_type)((*node).next); }
// 链表成环, 当指所以头节点也就是end
iterator end() { return node; }
// 头结点指向自身说明链表中无元素
bool empty() const { return node->next == node; }
// 使用全局函数distance()进行计算, 时间复杂度O(n)
size_type size() const
{
size_type result = 0;
distance(begin(), end(), result);
return result;
}
size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); }
reference front() { return *begin(); }
reference back() { return *(--end()); } iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x)
{
link_type tmp = create_node(x); // 产生一个节点
// 调整双向指针,使tmp插入进去
tmp->next = position.node;
tmp->prev = position.node->prev;
(link_type(position.node->prev))->next = tmp;
position.node->prev = tmp;
return tmp;
} // 指定位置插入n个值为x的元素, 详细解析见实现部分
void insert(iterator pos, size_type n, const T& x);
void insert(iterator pos, int n, const T& x)
{
insert(pos, (size_type)n, x);
}
void insert(iterator pos, long n, const T& x)
{
insert(pos, (size_type)n, x);
} // 在链表前端插入结点
void push_front(const T& x) { insert(begin(), x); }
// 在链表最后插入结点
void push_back(const T& x) { insert(end(), x); } // 移除迭代器position所指节点
iterator erase(iterator position)
{
link_type next_node = link_type(position.node->next);
link_type prev_node = link_type(position.node->prev);
prev_node->next = next_node;
next_node->prev = prev_node;
destroy_node(position.node);
return iterator(next_node);
} / 擦除一个区间的结点, 详细解析见实现部分
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);
void resize(size_type new_size, const T& x);
void resize(size_type new_size) { resize(new_size, T()); }
void clear(); // 删除链表第一个结点
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 删除链表最后一个结点
void pop_back()
{
iterator tmp = end();
erase(--tmp);
}
list(size_type n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
list(int n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
list(long n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
~list()
{
// 释放所有结点 // 使用全局函数distance()进行计算, 时间复杂度O(n)
size_type size() const
{
size_type result = 0;
distance(begin(), end(), result);
return result;
}
clear();
// 释放头结点
put_node(node);
}
list<T, Alloc>& operator=(const list<T, Alloc>& x);
protected:
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
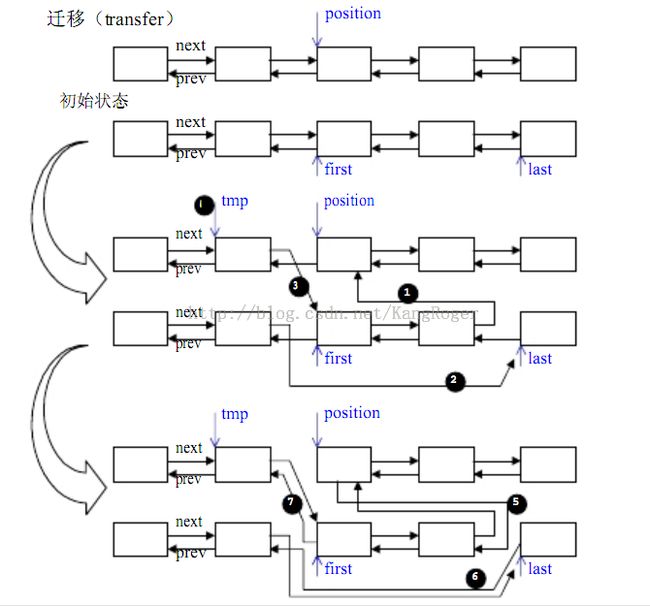
// 将[first, last)内的所有元素移动到position之前
// 如果last == position, 则相当于链表不变化, 不进行操作
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 初始状态
// first last
// ↓ ↓
// -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
// | next |-->| next |-->| next | | next |-->| next |-->| next |
// ... -------- -------- -------- ... -------- -------- -------- ...
// | prev |<--| prev |<--| prev | | prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |
// -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
//
// position
// ↓
// -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
// | next |-->| next |-->| next |-->| next |-->| next |-->| next |
// ... -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- ...
// | prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |
// -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
//
// 操作完成后状态
// first
// |
// --------------|--------------------------------------
// | ------------|------------------------------------ | last
// | | ↓ | | ↓
// -------- | | -------- -------- -------- | | -------- --------
// | next |-- | ----->| next |-->| next | | next |----- | -->| next |-->| next |
// ... -------- | | -------- -------- ... -------- | | -------- -------- ...
// | prev |<--- | ---| prev |<--| prev | | prev |<-- | -----| prev |<--| prev |
// -------- | | -------- -------- -------- | | -------- --------
// | | | |
// | ------ | |
// ------- | ------------------------------ |
// | | | |
// | | | -----------------------------
// | | | |
// | | | | position
// | | | | ↓
// -------- -------- | | | | -------- -------- -------- --------
// | next |-->| next |-- | | -->| next |-->| next |-->| next |-->| next |
// ... -------- -------- | | -------- -------- -------- -------- ...
// | prev |<--| prev |<--- ------| prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |<--| prev |
// -------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 将[first,last)内的所有元素移动到position之前 void transfer(iterator position, iterator first, iterator last)
{
if (position != last) // 如果last == position, 则相当于链表不变化, 不进行操作
{
(*(link_type((*last.node).prev))).next = position.node; //1
(*(link_type((*first.node).prev))).next = last.node; //2
(*(link_type((*position.node).prev))).next = first.node; //3
link_type tmp = link_type((*position.node).prev); //4
(*position.node).prev = (*last.node).prev; //5
(*last.node).prev = (*first.node).prev; //6
(*first.node).prev = tmp; //7
}
}
公共接口 list<T>::splice的许多版本
public
// 将链表x移动到position所指位置之前
void splice(iterator position, list& x)
{
if (!x.empty())
transfer(position, x.begin(), x.end());
}
// 将链表中i指向的内容移动到position之前
void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator i)
{
iterator j = i;
++j;
if (position == i || position == j) return;
transfer(position, i, j);
}
// 将[first, last}元素移动到position之前
void splice(iterator position, list&, iterator first, iterator last)
{
if (first != last)
transfer(position, first, last);
}
void remove(const T& value);
void unique();
void merge(list& x);
void reverse();
void sort();
};
// 销毁所有结点, 将链表置空
template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::clear()
{
link_type cur = (link_type) node->next;
while (cur != node)
{
link_type tmp = cur;
cur = (link_type) cur->next;
destroy_node(tmp);
}
// 恢复node原始状态
node->next = node;
node->prev = node;
}
// 链表赋值操作
// 如果当前容器元素少于x容器, 则析构多余元素,
// 否则将调用insert插入x中剩余的元素
template <class T, class Alloc>
list<T, Alloc>& list<T, Alloc>::operator=(const list<T, Alloc>& x)
{
if (this != &x)
{
iterator first1 = begin();
iterator last1 = end();
const_iterator first2 = x.begin();
const_iterator last2 = x.end();
while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2) *first1++ = *first2++;
if (first2 == last2)
erase(first1, last1);
else
insert(last1, first2, last2);
}
return *this;
}
// 移除容器内所有的相邻的重复结点
// 时间复杂度O(n)
// 用户自定义数据类型需要提供operator ==()重载
template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::unique()
{
iterator first = begin();
iterator last = end();
if (first == last) return;
iterator next = first;
while (++next != last)
{
if (*first == *next)
erase(next);
else
first = next;
next = first;
}
}
// 假设当前容器和x都已序, 保证两容器合并后仍然有序
template <class T, class Alloc>
void list<T, Alloc>::merge(list<T, Alloc>& x)
{
iterator first1 = begin();
iterator last1 = end();
iterator first2 = x.begin();
iterator last2 = x.end();
// 注意:前提是,两个lists都已经递增排序
while (first1 != last1 && first2 != last2)
if (*first2 < *first1)
{
iterator next = first2;
transfer(first1, first2, ++next);
first2 = next;
}
else
++first1;
if (first2 != last2)
transfer(last1, first2, last2);