hdoj 5476 Explore Track of Point 【托勒密定理】
Explore Track of PointTime Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 279 Accepted Submission(s): 109
Problem Description
In Geometry, the problem of track is very interesting. Because in some cases, the track of point may be beautiful curve. For example, in polar Coordinate system,
ρ=cos3θ is like rose,
ρ=1−sinθ is a Cardioid, and so on. Today, there is a simple problem about it which you need to solve.
Give you a triangle ΔABC and AB = AC. M is the midpoint of BC. Point P is in ΔABC and makes min{∠MPB+∠APC,∠MPC+∠APB} maximum. The track of P is Γ . Would you mind calculating the length of Γ ? Given the coordinate of A, B, C, please output the length of Γ .
Input
There are T (
1≤T≤104 ) test cases. For each case, one line includes six integers the coordinate of A, B, C in order. It is guaranteed that AB = AC and three points are not collinear. All coordinates do not exceed
104 by absolute value.
Output
For each case, first please output "Case #k: ", k is the number of test case. See sample output for more detail. Then, please output the length of
Γ with exactly 4 digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
Sample Output
|
队友提交WA9次,就因为两个变量写错了 ( ˇˍˇ )
给你一个等腰三角形ABC其中AB = AC,点M为底边中点。
现在让你找一个在三角形ABC内部的点P使 {∠MPB+∠APC,∠MPC+∠APB} 的最小值最大,问你P点的轨迹长度是多少。
渣渣猜答案,大牛用定理证答案。
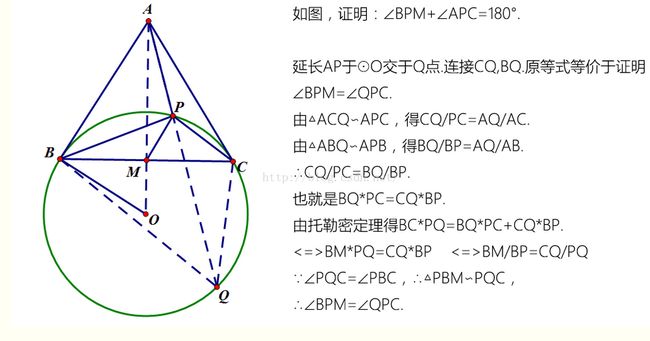
证明:
ans = 三角形中线长度AM + 过三角形内心(原O与AM交点)、B和C三点的圆弧BC。
AC代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
int main()
{
int t, k = 1;
scanf("%d", &t);
double ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &ax, &ay, &bx, &by, &cx, &cy);
double a = sqrt((bx - cx) * (bx - cx) + (by - cy) * (by - cy));
double b = sqrt((ax - cx) * (ax - cx) + (ay - cy) * (ay - cy));
double c = sqrt((ax - bx) * (ax - bx) + (ay - by) * (ay - by));
double h = sqrt(b*b - a*a/4);
double angA = acos((b*b + c*c - a*a) / (2.0*c*b));
double r = tan(angA / 2.0) * c;
printf("Case #%d: %.4lf\n", k++, r*(PI - angA) + h);
}
return 0;
}