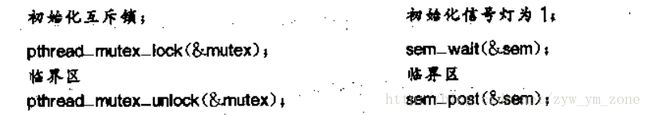linux进程间通信--信号量
概述
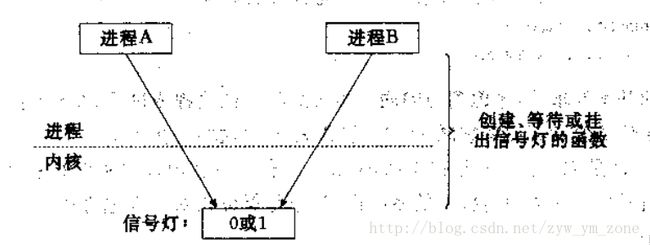
信号量是一种用于提供不同进程间或一个给定进程的不同线程间同步手段的原语。下图表示的是由两个进程使用的一个二值信号量
一个进程可以在信号量执行三种操作:
1. 创建(create)一个信号量,这要求调用者指定初始值,对于二值信号量来说,它通常是1,
2. 等待(wait)一个信号量,该操作会测试这个信号量的值,如果其值小于或等于0,那就等待or阻塞,一旦其值变为大于1就将它减1,过程如以下伪代码
3. 挂出(post)一个信号量,该操作将信号量的值加1
当然,信号量也可以实现互斥的目的,下图就是一个例子
其中信号量与其他同步操作(互斥锁,条件变量,读写锁)的区别有
1.互斥锁必须总是由锁住它的线程解锁,信号量的挂出却不必由执行过它的等待操作的同一线程执行(一个线程可以等待某个给定信号量,而另一个线程可以挂出该信号量)
2. 任何一个线程都可以挂起一个信号,即使当时没有线程在等待该信号值变为正数也没有关系。但是,如果某个新城调用了pthread_cond_signal,不过当时没有任何线程阻塞在pthread_cond_wait调用中,那么发往相应的条件变量的信号将丢失
3. 能够从信号处理程序中安全调用的唯一函数是sem_post
解决一个生产者与一个消费者问题,如下图模型
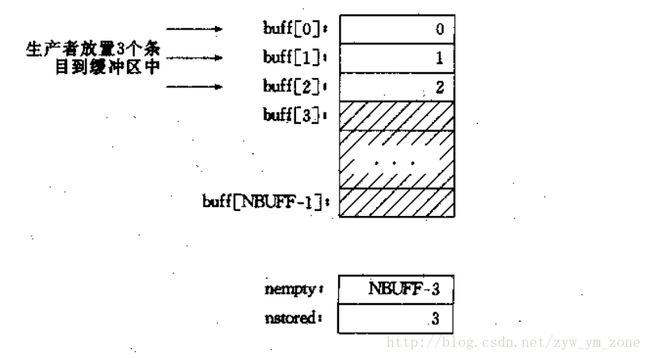
现在把共享缓冲区当作一个环绕缓冲区,生产者填写最后一项后,回过头来填写第一项,消费者也可以这样做。此时,我们必须用代码来为池以下三个条件:
当缓冲区为空时,消费者不能试图从其中去除一个条目
当缓冲区填满时,生产者不能试图往其中放置一个条目
共享变量可能描述缓冲区的当前状态,因此生产者与消费者的所有缓冲区操纵都必须保护起来(互斥操作),以避免竟争状态
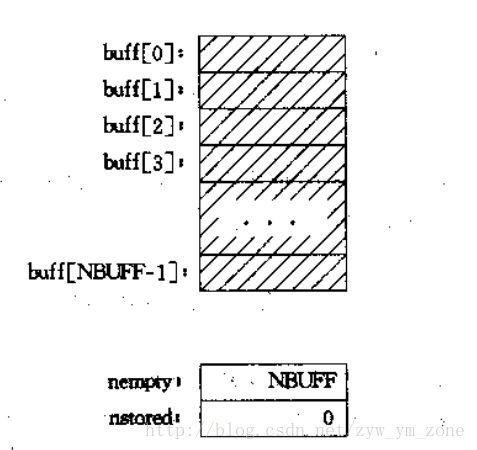
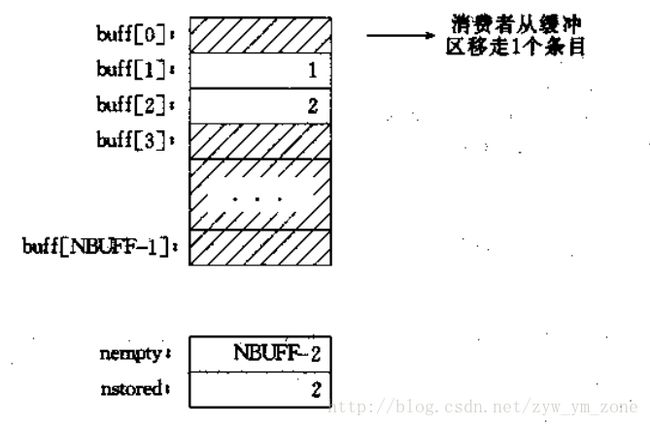
开始时,我们需要初始化一个缓冲区,和两个计数信号量(表示缓冲区满,和空的信号量),具体如下图
初始化后的缓冲区和两个计数信号量
具体代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define NBUFF 10
char SEM_MUTEX[] = "mutex";
char SEM_NEMPTY[] = "nempty";
char SEM_NSTORED[] = "nstored";
#define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH)
int nitems;
struct
{
int buff[NBUFF];
sem_t mutex, nempty, nstored;
}shared;
void *producer(void *);
void *consumer(void *);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid_producer, tid_consumer;
if(argc!=2)
{
printf("useage: procon <#items>");
exit(1);
}
nitems = atoi(argv[1]);
//create three non-name semaphores
sem_init(&shared.mutex, 0, 1);
sem_init(&shared.nempty, 0, NBUFF);
sem_init(&shared.nstored, 0, 0);
//create one producer thread and consumer thread
pthread_create(&tid_producer, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid_consumer, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_setconcurrency(2);
//wait for two threads
pthread_join(tid_producer, NULL);
pthread_join(tid_consumer, NULL);
//destory three semaphores
sem_destroy(&shared.mutex);
sem_destroy(&shared.nempty);
sem_destroy(&shared.nstored);
return 0;
}
void *producer(void *arg)
{
int i=0;
for(i=0; i<nitems; i++)
{
sem_wait(&shared.nempty);
sem_wait(&shared.mutex);
shared.buff[i % NBUFF] = i+1;
sem_post(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(&shared.nstored);
}
return NULL;
}
void *consumer(void *arg)
{
int i=0;
for(i=0; i<nitems; i++)
{
//here, if we exchange first two sem_wait's position, then it will cause dead lock
sem_wait(&shared.nstored);
sem_wait(&shared.mutex);
if(shared.buff[i % NBUFF] == i+1)
printf("buff[%d] = %d\n", i, shared.buff[i % NBUFF]);
sem_post(&shared.mutex);
sem_post(&shared.nempty);
}
return NULL;
}
注意,在消费者函数中,如果交换两个sem_wait的顺序,即先sem_wait(&shared.mutex),再sem_wait(&shared.nstored),则会到这死锁。原因:假设,生产者线程先工作,它使shared.nempty从NBUFF减到1,shared.nstored从0增至NBUFF。接下来消费者线程将shared.nstored从NBUFF减至0,使shared.nempty从0增至NBUFF后,接下来调用sem_wait(&shared.mutex),阻塞,此时生产者线程也调用sem_wait(&shared.mutex),阻塞,这时候导致死锁现象。因为此时生产者在等待mutex信号,但是消费者却持有该信号量并等待shared.nstored信号量。然而生产者只有获取了mutex信号才能挂出nstored信号量。